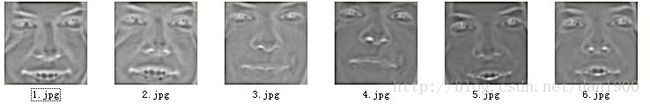
光照归一化算法——DoG滤波,自商图
DoG code:
function pic=DoG(I)
if size(I,3)==3
I=rgb2gray(I);
end
I=double(I);
h1=fspecial('gaussian',15,1);
h2=fspecial('gaussian',15,2);
m=filter2(h2,I)-filter2(h1,I);
R=m;
mi=min(min(R));
ma=max(max(R));
newR=(R-mi)*255/(ma-mi);
pic=uint8(newR);
处理效果:
理论:
Given a m-channels, n-dimensional image
The difference of Gaussians (DoG) of the image is the function
obtained by subtracting the image convolved with the Gaussian of variance from the imageconvolved with a Gaussian of narrower variance , with. In one dimension, is defined as:
and for the centered two-dimensional case :
which is formally equivalent to:
which represents an image convoluted to the difference of two Gaussians, which approximates aMexican Hat function.
自商图code:
function [pic,ipic]=selfQuotient(I)
if size(I,3)==3
G=rgb2gray(I);
else
G=I;
end
G=double(G);
G=(G-min(min(G)))/(max(max(G))-min(min(G)))*255;%对比度拉升
% thr=mean(G);
% w=zeros(rows,cols);
% for i=1:rows
% for j=1:cols
% if(I(i,j)>thr)
% w(i,j)=0;
% else
% w(i,j)=1;
% end
% end
% end
h1=fspecial('gaussian',7,1);
% h1=h1.*w;
f1=filter2(h1,G);
R=G./f1;
mi=min(min(R));
ma=max(max(R));
newR=(R-mi)*255/(ma-mi);
pic=uint8(newR);
ipic=uint8(f1);处理效果图:
ps:
自商图求滤波器h1的时候,赋了权值,不过实验中发现不设置权值效果似乎更佳,所以注释掉了权值部分。权值的设置应该是一个值得探讨的部分。