HDOJ 2073 无限的路 (DFS)
无限的路
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 7637 Accepted Submission(s): 3936
Problem Description
甜甜从小就喜欢画图画,最近他买了一支智能画笔,由于刚刚接触,所以甜甜只会用它来画直线,于是他就在平面直角坐标系中画出如下的图形:
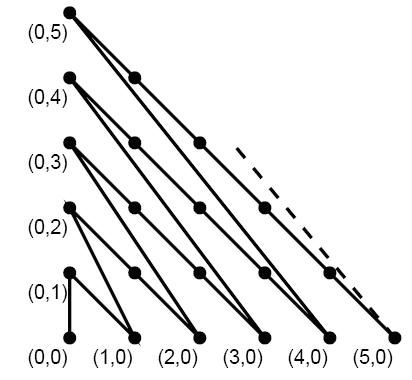
甜甜的好朋友蜜蜜发现上面的图还是有点规则的,于是他问甜甜:在你画的图中,我给你两个点,请你算一算连接两点的折线长度(即沿折线走的路线长度)吧。

甜甜的好朋友蜜蜜发现上面的图还是有点规则的,于是他问甜甜:在你画的图中,我给你两个点,请你算一算连接两点的折线长度(即沿折线走的路线长度)吧。
Input
第一个数是正整数N(≤100)。代表数据的组数。
每组数据由四个非负整数组成x1,y1,x2,y2;所有的数都不会大于100。
每组数据由四个非负整数组成x1,y1,x2,y2;所有的数都不会大于100。
Output
对于每组数据,输出两点(x1,y1),(x2,y2)之间的折线距离。注意输出结果精确到小数点后3位。
Sample Input
5 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 2 3 3 1 99 99 9 9 5 5 5 5
Sample Output
1.000 2.414 10.646 54985.047 0.000
思路:直接DFS搜两个点到原点的距离,然后相减就好了
ac代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stack>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#define MAXN 10100000
#define LL long long
#define ll __int64
#define INF 0xfffffff
#define mem(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define PI acos(-1)
using namespace std;
LL gcd(LL a,LL b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
LL lcm(LL a,LL b){return a/gcd(a,b)*b;}
LL powmod(LL a,LL b,LL MOD){LL ans=1;while(b){if(b%2)ans=ans*a%MOD;a=a*a%MOD;b/=2;}return ans;}
//head
double ans1,ans2;
int x1,x2,y11,y2;
int bz;
double dis(int xx,int yy,int xxx,int yyy)
{
return sqrt(1.0*(xx-xxx)*(xx-xxx)+1.0*(yy-yyy)*(yy-yyy));
}
void dfs1(int x,int y,double D)
{
if(x==x1&&y==y11)
{
bz=1;
ans1=D;
return;
}
if(y==0)
dfs1(0,x+1,D+dis(x,y,0,x+1));
else
dfs1(x+1,y-1,D+dis(x,y,x+1,y-1));
}
void dfs2(int x,int y,double D)
{
if(x==x2&&y==y2)
{
bz=1;
ans2=D;
return;
}
if(y==0)
dfs2(0,x+1,D+dis(x,y,0,x+1));
else
dfs2(x+1,y-1,D+dis(x,y,x+1,y-1));
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x1,&y11,&x2,&y2);
bz=0;
dfs1(0,0,0.0);
bz=0;
dfs2(0,0,0.0);
double ans=fabs(ans1-ans2);
printf("%.3lf\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}