浅谈Android的TabHost
这篇文章主要针对 TabHost 进行分析。相信大家和我一样,在学习TabHost的时候遇到了很多问题,这里我就把我所学到的和大家分享一二。
本人才疏学浅,若有错误,欢迎指正。
首先 TabHost 的用法相信大家都知道,就是用来放置标签页。话不多说,来看代码。
用法如下:
TabHost mTabHost = (TabHost) findViewById(android.R.id.tabhost); mTabHost.setup(); mTabHost.addTab(TabSpec spec);
根据用法,分析代码:
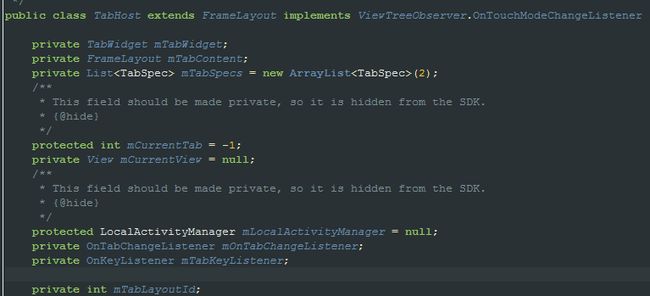
1.首先看 TabHost 的成员变量:
mTabWidget 就是我们 Tab 的 Indicator。
mTabContent 就是我们 Tab 真正要显示的内容。
mCurrentView 就是我们当前展示的内容。
mTabSpecs 就是我们 Tab 的信息,使用的是策略模式。可以理解为TabSpecs是一个实体。
接下来看构造函数,由于构造函数没有什么难点,只有一个函数,发上来大家看看:
private void initTabHost() {
setFocusableInTouchMode(true);
setDescendantFocusability(FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS);
mCurrentTab = -1;
mCurrentView = null;
}
只是对变量进行了初始化已经焦点设置。
2.setup()函数,这个是重点之一:
代码如下:
public void setup() {
//这也就是为何xml中的ID 必须为系统Id的原因
mTabWidget = (TabWidget) findViewById(com.android.internal.R.id.tabs);
if (mTabWidget == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Your TabHost must have a TabWidget whose id attribute is 'android.R.id.tabs'");
}
// KeyListener to attach to all tabs. Detects non-navigation keys
// and relays them to the tab content.
mTabKeyListener = new OnKeyListener() {
public boolean onKey(View v, int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
switch (keyCode) {
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_CENTER:
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_LEFT:
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_RIGHT:
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_UP:
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_DOWN:
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_ENTER:
return false;
}
mTabContent.requestFocus(View.FOCUS_FORWARD);
return mTabContent.dispatchKeyEvent(event);
}
};
mTabWidget.setTabSelectionListener(new TabWidget.OnTabSelectionChanged() {
public void onTabSelectionChanged(int tabIndex, boolean clicked) {
setCurrentTab(tabIndex);
if (clicked) {
mTabContent.requestFocus(View.FOCUS_FORWARD);
}
}
});
//这也就是为何xml中的ID 必须为系统Id的原因
mTabContent = (FrameLayout) findViewById(com.android.internal.R.id.tabcontent);
if (mTabContent == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Your TabHost must have a FrameLayout whose id attribute is "
+ "'android.R.id.tabcontent'");
}
}
setup的函数意图在于,给自己为初始化的变量赋值,以及对焦点,按键进行处理。
3.addTab()。
这个函数写的非常有意思,代码如下:
public void addTab(TabSpec tabSpec) {
if (tabSpec.mIndicatorStrategy == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("you must specify a way to create the tab indicator.");
}
if (tabSpec.mContentStrategy == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("you must specify a way to create the tab content");
}
//通过策略模式,得到当前Tab Indicator的视图
View tabIndicator = tabSpec.mIndicatorStrategy.createIndicatorView();
tabIndicator.setOnKeyListener(mTabKeyListener);
// If this is a custom view, then do not draw the bottom strips for
// the tab indicators.
if (tabSpec.mIndicatorStrategy instanceof ViewIndicatorStrategy) {
//如果是自定义的绘图,不绘制分隔线
mTabWidget.setStripEnabled(false);
}
//在TabWidget(线性布局)中,加入tabIndicator。TabWidget会对childView进行特殊处理,具体看源码。
mTabWidget.addView(tabIndicator);
//在记载Tab信息的List中,加入这条信息
mTabSpecs.add(tabSpec);
if (mCurrentTab == -1) {
//设置当前Tab,比较复杂,继续上源码
setCurrentTab(0);
}
}
public void setCurrentTab(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= mTabSpecs.size()) {
return;
}
if (index == mCurrentTab) {
return;
}
//关闭上一个Tab的Content,通过当前策略去调用tabClosed,一般的策略都是设置当前View为不可见
// notify old tab content
if (mCurrentTab != -1) {
mTabSpecs.get(mCurrentTab).mContentStrategy.tabClosed();
}
mCurrentTab = index;
final TabHost.TabSpec spec = mTabSpecs.get(index);
// Call the tab widget's focusCurrentTab(), instead of just
// selecting the tab.
mTabWidget.focusCurrentTab(mCurrentTab);
//getContentView()这个函数的意图为,设置当前这个View为可见的,并返回这个可见的View。
// tab content
mCurrentView = spec.mContentStrategy.getContentView();
//如果当前的这个可见的View并没有在View的树结构之上,就把它添加上去,如果已经存在,就不需要这样做了。
if (mCurrentView.getParent() == null) {
mTabContent
.addView(
mCurrentView,
new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT));
}
if (!mTabWidget.hasFocus()) {
// if the tab widget didn't take focus (likely because we're in touch mode)
// give the current tab content view a shot
mCurrentView.requestFocus();
}
//mTabContent.requestFocus(View.FOCUS_FORWARD);
invokeOnTabChangeListener();
}
通过以上三步,就大概了解了TabHost是如何运行的。而TabHost中,Tabwidget和TabContent是如何添加到TabHost之中的呢?之前我一直在代码中寻找却苦苦得不到答案,后来突然意识到,其实在布局文件中,已经把TabWidget和TabContent添加到了TabHost中,所以对于TabWidget和TabContent的布局,我们都可以进行单独的定制。在3.0以后,在Fragment 出现的同时,也同时出现了FragmentTabHost,FragmentTabHost 作为TabHost 的子类,修改的十分简单却十分好用。
下篇博客继续分析FragmentTabHost的源码。
第一次写博客,写的非常烂,大家凑合看吧,不好意思。
QQ:157688302 欢迎联系,探讨Android相关知识