游程长度编码
游程长度编码(run-length code)
游程长度编码是栅格数据压缩的重要编码方法,它的基本思路是:对于一幅栅格图像,常常有行(或列)方向上相邻的若干点具有相同的属性代码,因而可采取某种方法压缩那些重复的记录内容。其编码方案是,只在各行(或列)数据的代码发生变化时依次记录该代码以及相同代码重复的个数,从而实现数据的压缩。
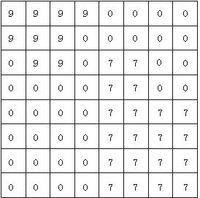
例如对图1所示的栅格数据,可沿行方向进行如下游程长度编码:
(9,4),(0,4),(9,3),(0,5),(0,1)(9,2),(0,1),(7,2),(0,2),(0,4),(7,2),(0,2),(0,4),(7,4),(0,4),(7,4) ,(0,4),(7,4) ,(0,4),(7,4)
游程长度编码对图3-6(a)只用了40个整数就可以表示,而如果用前述的直接编码却需要64个整数表示,可见游程长度编码压缩数据是十分有效又简便的。事实上,压缩比的大小是与图的复杂程度成反比的,在变化多的部分,游程数就多,变化少的部分游程数就少,图件越简单,压缩效率就越高。
游程长度编码在栅格加密时,数据量没有明显增加,压缩效率较高,且易于检索,叠加合并等操作,运算简单,适用于机器存贮容量小,数据需大量压缩,而又要避免复杂的编码解码运算增加处理和操作时间的情况。
[font id="zoom" class="zoom"]游程长度RL (Run—Length),简称游程或游长,指的是由字符(或信号取样值)构成的数据流中各个字符重复出现而形成的字符的长度.如果给出了形成申的字符,申的长度及申的位置,就能恢复出原来的数据流,游程长度编码(RLC)就是用二进制码字给出这些信息的一类方法。游程长度编码的主要思想是将一个相同值的连续申用其值和申长(重复的个数)的数对二元组来替代.例如,在图像编码中,可以定义沿特定方向上具有相同灰度值的相邻像素为一轮,其延续的长度称之为延续的行程,即游程.游程终点位置由前一游程终点的相对距离确定,这样就可以由灰度游程串来表示图像数据.例如,若沿水平方向有一申M 个像素具有相同的灰度N,则按游程长度编码后,只传递两个值(N,M )就可以代替这M个像素的M个灰度值N。简单来说,游程长度编码的主要任务是统计连续相同字符的个数,解码时要根据字符及连续相同字符的个数,恢复原来的数据.在多媒体信息量激增、网络特性和速度都飞速提高的今天,游程长度编码是一种十分简单的压缩方法,编码/解码的速度也非常快,可广泛应用于多媒体信息的存储,传输。
例如对图1所示的栅格数据,可沿行方向进行如下游程长度编码:
(9,4),(0,4),(9,3),(0,5),(0,1)(9,2),(0,1),(7,2),(0,2),(0,4),(7,2),(0,2),(0,4),(7,4),(0,4),(7,4) ,(0,4),(7,4) ,(0,4),(7,4)
游程长度编码对图3-6(a)只用了40个整数就可以表示,而如果用前述的直接编码却需要64个整数表示,可见游程长度编码压缩数据是十分有效又简便的。事实上,压缩比的大小是与图的复杂程度成反比的,在变化多的部分,游程数就多,变化少的部分游程数就少,图件越简单,压缩效率就越高。
游程长度编码在栅格加密时,数据量没有明显增加,压缩效率较高,且易于检索,叠加合并等操作,运算简单,适用于机器存贮容量小,数据需大量压缩,而又要避免复杂的编码解码运算增加处理和操作时间的情况。
[font id="zoom" class="zoom"]游程长度RL (Run—Length),简称游程或游长,指的是由字符(或信号取样值)构成的数据流中各个字符重复出现而形成的字符的长度.如果给出了形成申的字符,申的长度及申的位置,就能恢复出原来的数据流,游程长度编码(RLC)就是用二进制码字给出这些信息的一类方法。游程长度编码的主要思想是将一个相同值的连续申用其值和申长(重复的个数)的数对二元组来替代.例如,在图像编码中,可以定义沿特定方向上具有相同灰度值的相邻像素为一轮,其延续的长度称之为延续的行程,即游程.游程终点位置由前一游程终点的相对距离确定,这样就可以由灰度游程串来表示图像数据.例如,若沿水平方向有一申M 个像素具有相同的灰度N,则按游程长度编码后,只传递两个值(N,M )就可以代替这M个像素的M个灰度值N。简单来说,游程长度编码的主要任务是统计连续相同字符的个数,解码时要根据字符及连续相同字符的个数,恢复原来的数据.在多媒体信息量激增、网络特性和速度都飞速提高的今天,游程长度编码是一种十分简单的压缩方法,编码/解码的速度也非常快,可广泛应用于多媒体信息的存储,传输。
/***********************************************************************************************************
RLE.c
RLE.c
本演示程序提供了游程长度编码法的压缩和解压缩函数,并实现了对图象
文件的压缩和解压缩
**********************************************************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
文件的压缩和解压缩
**********************************************************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_LEN (0x7f) /* maximum length for runs or sequences */
#define MAX_RUN_HEADER (0xff) /* bit 7 == 1 : run follows */
/* bit 6 - 0 : length of run */
#define MAX_SEQ_HEADER (0x7f) /* bit 7 == 0 : unencode sequence follows */
/* bit 6 - 0 : length of sequence */
#define RUN (0x80) /* bit 7 == 1 : run follows */
#define SEQ (0x00) /* bit 7 == 0 : unencoded sequence follows */
#define MAX_RUN_HEADER (0xff) /* bit 7 == 1 : run follows */
/* bit 6 - 0 : length of run */
#define MAX_SEQ_HEADER (0x7f) /* bit 7 == 0 : unencode sequence follows */
/* bit 6 - 0 : length of sequence */
#define RUN (0x80) /* bit 7 == 1 : run follows */
#define SEQ (0x00) /* bit 7 == 0 : unencoded sequence follows */
/* 函数原型 */
int RLE_Compression(char * infile_name, char * outfile_name);
int RLE_Decompression(char * infile_name, char * outfile_name);
int RLE_Compression(char * infile_name, char * outfile_name);
int RLE_Decompression(char * infile_name, char * outfile_name);
/* 主程序 */
void main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
printf("RLE compression and decompression utility/n");
void main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
printf("RLE compression and decompression utility/n");
if (4 != argc)
{
printf("/nUsage : rle -c|d sourcefilename targetfilename/n");
exit(0);
}
{
printf("/nUsage : rle -c|d sourcefilename targetfilename/n");
exit(0);
}
if (! strcmp(argv[1], "-c"))
{
printf("/nCompress...");
RLE_Compression(argv[2], argv[3]);
}
else if (! strcmp(argv[1], "-d"))
{
printf("/nDecompress...");
RLE_Decompression(argv[2], argv[3]);
}
else
printf("/nUnknow command./n");
}
{
printf("/nCompress...");
RLE_Compression(argv[2], argv[3]);
}
else if (! strcmp(argv[1], "-d"))
{
printf("/nDecompress...");
RLE_Decompression(argv[2], argv[3]);
}
else
printf("/nUnknow command./n");
}
/**************************************************************************
RLE_Compression ()
RLE_Compression ()
本函数用RLE算法对文件进行压缩
**************************************************************************/
int RLE_Compression(char * infile_name, char * outfile_name)
{
register int cur_char; /* a character */
register unsigned int i; /* generic index variable */
register unsigned short run_len = 0; /* length of character run so far */
int run_char; /* which char run is of */
unsigned int j; /* another index variable */
unsigned short seq_len=0; /* length of non-run sequence */
**************************************************************************/
int RLE_Compression(char * infile_name, char * outfile_name)
{
register int cur_char; /* a character */
register unsigned int i; /* generic index variable */
register unsigned short run_len = 0; /* length of character run so far */
int run_char; /* which char run is of */
unsigned int j; /* another index variable */
unsigned short seq_len=0; /* length of non-run sequence */
char scratch_space[256]; /* string scratch space */
char seq[MAX_LEN]; /* buffer for uncompressible data */
char seq[MAX_LEN]; /* buffer for uncompressible data */
FILE *infile; /* file ptr to input file (uncompressed) */
FILE *outfile; /* file ptr to output file (compressed) */
FILE *outfile; /* file ptr to output file (compressed) */
if ((infile=fopen(infile_name, "rb")) == NULL)
{
strcpy(scratch_space, "Uable to open ");
strcat(scratch_space, infile_name);
puts(scratch_space);
return 1;
}
if ((outfile=fopen(outfile_name, "wb")) == NULL)
{
strcpy(scratch_space, "Uable to open ");
strcat(scratch_space, outfile_name);
puts(scratch_space);
return 1;
}
{
strcpy(scratch_space, "Uable to open ");
strcat(scratch_space, outfile_name);
puts(scratch_space);
return 1;
}
while (!feof(infile))
{
cur_char = fgetc(infile);
{
cur_char = fgetc(infile);
if (feof(infile))
continue;
continue;
if (seq_len ==0) /* haven't got a sequence yet */
{
if (run_len == 0) /* start a new run */
{
run_char = cur_char;
++run_len;
continue;
}
{
if (run_len == 0) /* start a new run */
{
run_char = cur_char;
++run_len;
continue;
}
if (run_char == cur_char) /* got another char in the run */
if (++run_len == MAX_LEN)
{
fputc((int)MAX_RUN_HEADER, outfile);
fputc((int) run_char, outfile);
run_len = 0;
continue;
}
if (++run_len == MAX_LEN)
{
fputc((int)MAX_RUN_HEADER, outfile);
fputc((int) run_char, outfile);
run_len = 0;
continue;
}
/* got a different character */
/* than the run we were building */
if (run_len > 2) /* so write out the run and */
/* start a new one of the new */
/* character. */
{
fputc((int)(RUN | run_len), outfile);
fputc((int)run_char, outfile);
run_len = 1;
run_char = cur_char;
continue;
}
/* than the run we were building */
if (run_len > 2) /* so write out the run and */
/* start a new one of the new */
/* character. */
{
fputc((int)(RUN | run_len), outfile);
fputc((int)run_char, outfile);
run_len = 1;
run_char = cur_char;
continue;
}
/* run was only one or two chars, make a seq out of it instead */
for (j = 0; j < run_len; j++); /* copy 1 or 2 char run to seq[] */
{
seq[seq_len] = run_char;
++seq_len;
if (seq_len == MAX_LEN) /* if seq[] is full, write to disk */
{
fputc((int)MAX_SEQ_HEADER, outfile);
for (i = 0; i < seq_len; i++)
fputc((int)seq[i], outfile);
seq_len = 0;
}
}
{
seq[seq_len] = run_char;
++seq_len;
if (seq_len == MAX_LEN) /* if seq[] is full, write to disk */
{
fputc((int)MAX_SEQ_HEADER, outfile);
for (i = 0; i < seq_len; i++)
fputc((int)seq[i], outfile);
seq_len = 0;
}
}
run_len = 0;
seq[seq_len++] = cur_char;
if (seq_len == MAX_LEN) /* if seq[] is full, write to disk */
{
fputc((int)MAX_SEQ_HEADER, outfile);
for (i = 0; i < seq_len; i++)
fputc((int)seq[i], outfile);
seq_len = 0;
}
}
else /* a sequence exists */
{
if (run_len != 0) /* if a run exists */
{
if (cur_char == run_char ) /* add to run! Yay. */
{
++run_len;
if (run_len == MAX_LEN) /* if run is full */
{
/* write sequence that precedes run */
seq[seq_len++] = cur_char;
if (seq_len == MAX_LEN) /* if seq[] is full, write to disk */
{
fputc((int)MAX_SEQ_HEADER, outfile);
for (i = 0; i < seq_len; i++)
fputc((int)seq[i], outfile);
seq_len = 0;
}
}
else /* a sequence exists */
{
if (run_len != 0) /* if a run exists */
{
if (cur_char == run_char ) /* add to run! Yay. */
{
++run_len;
if (run_len == MAX_LEN) /* if run is full */
{
/* write sequence that precedes run */
fputc((int)(SEQ | seq_len), outfile);
for (i = 0; i < seq_len; i++)
fputc((int)seq[i], outfile);
fputc((int)seq[i], outfile);
/* write run */
fputc((int)(RUN | run_len), outfile);
fputc((int)run_char, outfile);
fputc((int)run_char, outfile);
/* and start out fresh */
seq_len = run_len = 0;
} /* end write full run with existing sequence */
seq_len = run_len = 0;
} /* end write full run with existing sequence */
continue;
} /* end add to run for sequence exists */
} /* end add to run for sequence exists */
/* we couldn't add to the run, and a preceding sequence */
/* exists, so write the sequence and the run, and */
/* try starting a new run with the current character. */
/* write sequence that precedes run */
/* exists, so write the sequence and the run, and */
/* try starting a new run with the current character. */
/* write sequence that precedes run */
fputc((int)(SEQ | seq_len), outfile);
for (i = 0; i < seq_len; i++)
fputc((int)seq[i], outfile);
fputc((int)seq[i], outfile);
/* write run */
fputc((int)(RUN | run_len), outfile);
fputc((int)run_char, outfile);
fputc((int)run_char, outfile);
/* and start a new run w/ cur_char */
seq_len = 0;
run_len = 1;
run_char = cur_char;
continue;
run_len = 1;
run_char = cur_char;
continue;
} /* end can't add to existing run, and preceding seq exists */
/* no run exists, but a sequences does. Try to create a run */
/* by looking at cur_char and the last char of the sequence. */
/* if that fails, add the char to the sequence. */
/* if the sequence is full, write it to disk. (Slightly non */
/* optimal; we could wait one more char. A small thing to fix */
/* if someone gets the urge... */
/* by looking at cur_char and the last char of the sequence. */
/* if that fails, add the char to the sequence. */
/* if the sequence is full, write it to disk. (Slightly non */
/* optimal; we could wait one more char. A small thing to fix */
/* if someone gets the urge... */
if (seq[seq_len - 1] == cur_char) /* if we can make a run */
{
run_char = cur_char;
run_len = 2;
--seq_len;
continue;
}
{
run_char = cur_char;
run_len = 2;
--seq_len;
continue;
}
/* couldn't make a run, add char to seq. Maybe next time */
/* around... */
/* around... */
seq[seq_len++] = cur_char;
if (seq_len == MAX_LEN) /* if the sequence is full, write out */
{
fputc((int)MAX_SEQ_HEADER, outfile);
{
fputc((int)MAX_SEQ_HEADER, outfile);
for (i = 0; i < MAX_LEN; i++)
fputc((int)seq[i], outfile);
seq_len = 0;
}
} /* end branch on sequence exists */
} /* done with whole file */
fputc((int)seq[i], outfile);
seq_len = 0;
}
} /* end branch on sequence exists */
} /* done with whole file */
/* there may be stuff left that hasn't been written yet; if so, write it */
if (seq_len != 0) /* write sequence that precedes run */
{
fputc((int)(SEQ | seq_len), outfile);
{
fputc((int)(SEQ | seq_len), outfile);
for (i = 0; i < seq_len; i++)
fputc((int)seq[i], outfile);
}
fputc((int)seq[i], outfile);
}
if (run_len != 0) /* write run */
{
fputc((int)(RUN | run_len), outfile);
fputc((int)run_char, outfile);
}
{
fputc((int)(RUN | run_len), outfile);
fputc((int)run_char, outfile);
}
fclose(infile);
fclose (outfile);
fclose (outfile);
return 0;
} /* end RLE_Compression() */
/**************************************************************************
RLE_Decompression ()
本函数用RLE算法对文件进行解压缩
**************************************************************************/
int RLE_Decompression(char * infile_name, char * outfile_name)
{
register int byte;
register unsigned short i;
register unsigned short length;
int packet_hdr;
char scratch_space[134];
**************************************************************************/
int RLE_Decompression(char * infile_name, char * outfile_name)
{
register int byte;
register unsigned short i;
register unsigned short length;
int packet_hdr;
char scratch_space[134];
FILE *infile, *outfile;
if ((infile=fopen(infile_name, "rb")) == NULL)
{
strcpy(scratch_space, "Unable to open ");
strcat(scratch_space, infile_name);
puts(scratch_space);
return 1;
}
if ((outfile=fopen(outfile_name, "wb")) == NULL)
{
strcpy(scratch_space, "Unable to open ");
strcat(scratch_space, outfile_name);
puts(scratch_space);
return 1;
}
strcpy(scratch_space, "Unable to open ");
strcat(scratch_space, outfile_name);
puts(scratch_space);
return 1;
}
while (!feof(infile))
{
packet_hdr = fgetc(infile);
{
packet_hdr = fgetc(infile);
if (feof(infile))
continue;
continue;
length = MAX_LEN & packet_hdr;
if (packet_hdr & RUN) /* if it's a run... */
{
byte = fgetc(infile);
{
byte = fgetc(infile);
for (i = 0; i < length; i++)
if (fputc(byte, outfile)== EOF)
{
strcpy(scratch_space, "Error writing to ");
strcat(scratch_space, outfile_name);
puts(scratch_space);
fclose(infile);
fclose(outfile);
return 1;
}
}
else /* it's a sequence */
for (i = 0; i < length; i++)
if (fputc(fgetc(infile), outfile)==EOF)
{
strcpy(scratch_space, "Error writing to ");
strcat(scratch_space, outfile_name);
puts(scratch_space);
fclose(infile);
fclose(outfile);
return 1;
}
}
if (fputc(byte, outfile)== EOF)
{
strcpy(scratch_space, "Error writing to ");
strcat(scratch_space, outfile_name);
puts(scratch_space);
fclose(infile);
fclose(outfile);
return 1;
}
}
else /* it's a sequence */
for (i = 0; i < length; i++)
if (fputc(fgetc(infile), outfile)==EOF)
{
strcpy(scratch_space, "Error writing to ");
strcat(scratch_space, outfile_name);
puts(scratch_space);
fclose(infile);
fclose(outfile);
return 1;
}
}
fclose(infile);
fclose(outfile);
return 0;
} /* end RLE_Uncompression() */
fclose(outfile);
return 0;
} /* end RLE_Uncompression() */