Android Launcher全面剖析
Android Launcher全面剖析
首先来说说我为什么写这篇文章,最近公司要我负责搞Launcher,网上一查这方面的资料比较少,并且不全,研究起来相当困难,所以就写了这篇文章,希望对大家有帮助。这篇文章是相当长的,希望读者能耐心读下去,实际上也花了我很长时间来写。好了闲话少说,我们切入正题。
这篇文章我会讲以下Launcher内容:
Launcher UI总体架构
Launcher Res下的Layout
Launcher Res下的Xml文件
Launcher Manifest文件
Launcher 常用类介绍
Launcher 启动过程
Launcher widget添加过程
Launcher celllayout的介绍
一 Launcher UI总体架构
Home screen可以说是一个手机的最重要应用,就像一个门户网站的首页,直接决定了用户的第一印象。下面对home screen做一简要分析。
home screen的代码位于packages/apps/Launcher目录。从文件launcher.xml,workspace_screen.xml可获知home screen的UI结构如下图所示:
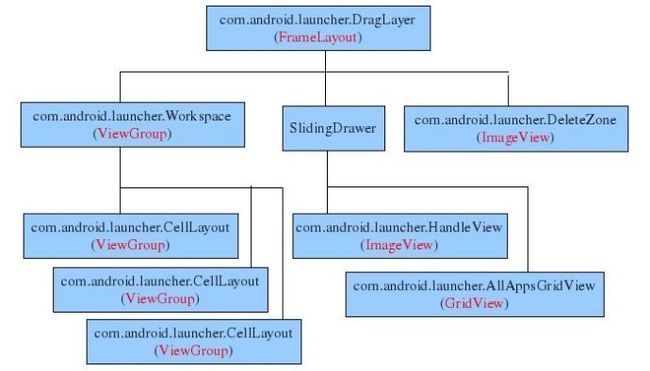
整个homescreen是一个包含三个child view的FrameLayout(com.android.launcher.DragLayer)。
第一个child就是桌面com.android.launcher.Workspace。这个桌面又包含三个child。每个child就对应一个桌面。这就是你在Android上看到的三个桌面。每个桌面上可以放置下列对象:应用快捷方式,appwidget和folder。
第二个child是一个SlidingDrawer控件,这个控件由两个子控件组成。一个是com.android.launcher.HandleView,就是Android桌面下方的把手,当点击这个把手时,另一个子控件,com.android.launcher.AllAppsGridView就会弹出,这个子控件列出系统中当前安装的所有类型为category.launcher的Activity。
第三个child是com.android.launcher.DeleteZone。当用户在桌面上长按一个widget时,把手位置就会出现一个垃圾桶形状的控件,就是这个控件。
在虚拟桌面上可以摆放四种类型的对象:
1. ITEM_SHORTCUT,应用快捷方式
2. ITEM_APPWIDGET,app widget
3. ITEM_LIVE_FOLDER,文件夹
4. ITEM_WALLPAPER,墙纸。
类AddAdapter(AddAdapter.java)列出了这四个类型对象。当用户在桌面空白处长按时,下列函数序列被执行:
Launcher::onLongClick -->
Launcher::showAddDialog -->
Launcher::showDialog(DIALOG_CREATE_SHORTCUT); -->
Launcher::onCreateDialog -->
Launcher::CreateShortcut::createDialog:这个函数创建一个弹出式对话框,询问用户是要添加什么(快捷方式,appwidget, 文件夹和墙纸)其内容就来自AddAdapter。
类Favorites(LauncherSettings.java)和类LauncherProvider定义了一个content provider,用来存储桌面上可以放置的几个对象,包括shortcut, search和clock等。
类DesktopItemsLoader负责将桌面上所有的对象从content provider中提取。
线程private ApplicationsLoader mApplicationsLoader负责从包管理器中获取系统中安装的应用列表。(之后显示在AllAppsGridView上)。ApplicationsLoader::run实现:
1)通过包管理器列出系统中所有类型为Launcher,action为MAIN的activity;
2)对每一个Activity,
a) 将Activity相关元数据信息,如title, icon, intent等缓存到appInfoCache;
b) 填充到ApplicationsAdapter 中。填充过程中用到了一些小技巧,每填充4(UI_NOTIFICATION_RATE)个activity更新一下相应view。
在Launcher::onCreate中,函数startLoaders被调用。而该函数接着调用loadApplications和loadUserItems,分别获取系统的应用列表,以及显示在桌面上的对象列表(快捷方式,appwidget,folder等)。
Launcher上排列的所有应用图标由AllAppsGridView对象呈现。这个对象是一个GridView。其对应的Adapter是ApplicationsAdapter,对应的model则是ApplicationInfo数组。数组内容是由ApplicationsLoader装载的。
private class ApplicationsLoader implements Runnable。
由Launcher中的AndroidManifest.xml可以看出整个Launcher的代码结构。
首先,是一些权限的声明。例如:
|
这部分可以略过;
其次,Application的构成,如上图:
(1)Launcher:HomeScreen的Activity。
- <intent-filter>
- <actionandroid:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"/>
- <categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.HOME"/>
- <categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
- <categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.MONKEY"/></intent-filter>
- <intent-filter>
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.HOME"/>
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.MONKEY" /> </intent-filter>
上面这段代码就标志着它是开机启动后Home的Activity。通过Launcher.java中onCreat()的分析我们可以大致把握屏幕的主要活动:
|
|
方法onActivityResult():完成在workspace上增加shortcut,appwidge和Livefolder;
方法onSaveInstantceState()和onRestoreInstanceState():为了防止Sensor、Land和Port布局自动切换时数据被置空,通过onSaveInstanceState方法可以保存当前窗口的状态,在即将布局切换前将当前的Activity压入历史堆栈。如果我们的Activity在后台没有因为运行内存吃紧被清理,则切换时回触发onRestoreIntanceState()。
(2)WallpaperChooser:设置墙纸。
同理我们从onCreat()作为入口来分析这个活动的主要功能。
|
|
(3)default_searchable
对于home中任意的Acitivty,使能系统缺省Search模式,这样就可以使用android系统默认的searchUI。
(4)InstallShortcutReceiver:
继承自BroadcastReceiver,重写onReceier()方法,对于发送来的Broadcast(这里指Intent)进行过滤(IntentFilt)并且响应(这里是InstallShortcut())。这里分析下onReceive():
|
|
其中IntallShortcut()方法:首先,对传入的坐标进行判断(findEmptyCell()),如果是空白位置,则可以放置快捷方式;其次,缺省情况下,我们允许创建重复的快捷方式,具体创建过程(addShortcut())就是把快捷方式的信息传入数据库(addItemToDatabase())。
(5)UninstallShortcutReceiver:
同理,UninstallShortcutReceiver()继承自BroadcastReceiver(),实现onReceiver()方法。定义一个ContentResolver对象完成对数据库的访问和操作(通过URI定位),进而删除快捷方式 。
(6)LauncherProvider:
继承自ContentProvider(),主要是建立一个数据库来存放HomeScreen中的数据信息,并通过内容提供者来实现其他应用对launcher中数据的访问和操作。
重写了ContentProvider()中的方法:
getType():返回数据类型。如果有自定义的全新类型,通过此方法完成数据的访问。
query():查询数据。传入URI,返回一个Cursor对象,通过Cursor完成对数据库数据的遍历访问。
Insert():插入一条数据。
bulkInsert():大容量数据的插入。
delete():删除一条数据。
update():更改一条数据。
sendNotify():发送通知。
类DatabaseHelper继承自一个封装类SQLiteOpenHelper(),方便了数据库的管理和维护。
重写的方法:
onCreate():创建一个表。其中db.execSQL()方法执行一条SQL语句,通过一条字符串执行相关的操作。当然,对SQL基本语句应该了解。
onUpgrade():升级数据库。
对HomeScreen数据库操作的一些方法:
addClockWidget(),addSearchWidget,addShortcut,addAppShortcut,
loadFavorites(),launcherAppWidgetBinder(),convertWidget(),updateContactsShortcuts(),
copyFromCursor()
补充:
类AddAdapter(AddAdapter.java)列出了这四个类型对象。当用户在桌面空白处长按时,下列函数序列被执行:
Launcher::onLongClick-->
Launcher::showAddDialog-->
Launcher::showDialog(DIALOG_CREATE_SHORTCUT);-->
Launcher::onCreateDialog-->
Launcher::CreateShortcut::createDialog:这个函数创建一个弹出式对话框,询问用户是要添加什么(快捷方式,appwidget,文件夹和墙纸)其内容就来自AddAdapter。
类DesktopItemsLoader负责将桌面上所有的对象从contentprovider中提取。
线程privateApplicationsLoadermApplicationsLoader负责从包管理器中获取系统中安装的应用列表。(之后显示在AllAppsGridView上)。ApplicationsLoader::run实现:
1)通过包管理器列出系统中所有类型为Launcher,action为MAIN的activity;
2)对每一个Activity,
a)将Activity相关元数据信息,如title,icon,intent等缓存到appInfoCache;
b)填充到ApplicationsAdapter中。填充过程中用到了一些小技巧,每填充4(UI_NOTIFICATION_RATE)个activity更新一下相应view。
在Launcher::onCreate中,函数startLoaders被调用。而该函数接着调用loadApplications和loadUserItems,分别获取系统的应用列表,以及显示在桌面上的对象列表(快捷方式,appwidget,folder等)。
Launcher上排列的所有应用图标由AllAppsGridView对象呈现。这个对象是一个GridView。其对应的Adapter是ApplicationsAdapter,对应的model则是ApplicationInfo数组。数组内容是由ApplicationsLoader装载的。
二 Launcher Res下的Layout
现在我们来看res目录里的布局文件,布局文件都放在layout*目录里。
本以为launcher的layout都放在layout目录里,由于屏幕放置方式的不同会对桌面造成一定的影响,所以google的Android项目组就决定因地制宜。比如当你横着放置屏幕的时候就会使用layout-land目录里的文件来对系统launcher进行布局,竖着屏幕的时候会使用layout-port内的布局文件来对launcher来布局。
横竖屏幕切换之际,会重新进行布局。那我们就以layout-land目录为例来看吧。
layout-land/launcuer.xml
- <?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="utf-8"?>
- <!--
- /*
- **
- **Copyright2008,TheAndroidOpenSourceProject
- **
- **LicensedundertheApacheLicense,Version2.0(the"License");
- **youmaynotusethisfileexceptincompliancewiththeLicense.
- **YoumayobtainacopyoftheLicenseat
- **
- **http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
- **
- **Unlessrequiredbyapplicablelaworagreedtoinwriting,software
- **distributedundertheLicenseisdistributedonan"ASIS"BASIS,
- **WITHOUTWARRANTIESORCONDITIONSOFANYKIND,eitherexpressorimplied.
- **SeetheLicenseforthespecificlanguagegoverningpermissionsand
- **limitationsundertheLicense.
- */
- -->
- <manifest
- xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- package="com.android.zkx_launcher"
- android:sharedUserId="@string/sharedUserId"
- >
- <!--应用程序的包名-->
- <!--<original-packageandroid:name="com.android.zkx_launcher2"/>-->
- <!--对系统资源的访问权限-->
- <permission
- android:name="com.android.zkx_launcher.permission.INSTALL_SHORTCUT"
- android:permissionGroup="android.permission-group.SYSTEM_TOOLS"
- android:protectionLevel="normal"
- android:label="@string/permlab_install_shortcut"
- android:description="@string/permdesc_install_shortcut"/>
- <permission
- android:name="com.android.zkx_launcher.permission.UNINSTALL_SHORTCUT"
- android:permissionGroup="android.permission-group.SYSTEM_TOOLS"
- android:protectionLevel="normal"
- android:label="@string/permlab_uninstall_shortcut"
- android:description="@string/permdesc_uninstall_shortcut"/>
- <permission
- android:name="com.android.zkx_launcher.permission.READ_SETTINGS"
- android:permissionGroup="android.permission-group.SYSTEM_TOOLS"
- android:protectionLevel="normal"
- android:label="@string/permlab_read_settings"
- android:description="@string/permdesc_read_settings"/>
- <permission
- android:name="com.android.zkx_launcher.permission.WRITE_SETTINGS"
- android:permissionGroup="android.permission-group.SYSTEM_TOOLS"
- android:protectionLevel="normal"
- android:label="@string/permlab_write_settings"
- android:description="@string/permdesc_write_settings"/>
- <uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.CALL_PHONE"/>
- <uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.EXPAND_STATUS_BAR"/>
- <uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.GET_TASKS"/>
- <uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.READ_CONTACTS"/>
- <uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.SET_WALLPAPER"/>
- <uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.SET_WALLPAPER_HINTS"/>
- <uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.VIBRATE"/>
- <uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.WRITE_SETTINGS"/>
- <uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.BIND_APPWIDGET"/>
- <uses-permissionandroid:name="com.android.launcher.permission.READ_SETTINGS"/>
- <uses-permissionandroid:name="com.android.launcher.permission.WRITE_SETTINGS"/>
- <!--对应用程序的配置-->
- <application
- android:name="LauncherApplication"
- android:process="@string/process"
- android:label="@string/application_name"
- android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher_home">
- <!--配置应用程序额的名字,进程,标签,和图标
- label的值为values/strings.xml中application_name键值对的值
- icon为drawable目录下名为的ic_launcher_home的图片
- 实际上该图片的位置位于drawable-hdpi(高分辨率)目录下,是个小房子这个主要是为了支持多分辨率的.
- hdpi里面主要放高分辨率的图片,
- 如WVGA(480x800),FWVGA(480x854)mdpi里面主要放中等分辨率的图片,
- 如HVGA(320x480)ldpi里面主要放低分辨率的图片,
- 如QVGA(240x320)系统会根据机器的分辨率来分别到这几个文件夹里面去找对应的图片
- 所以在开发程序时为了兼容不同平台不同屏幕,建议各自文件夹根据需求均存放不同版本图片.
- 只需要在res目录下创建不同的layout文件夹,
- 比如layout-640x360,layout-800x480,
- 所有的layout文件在编译之后都会写入R.java里,
- 而系统会根据屏幕的大小自己选择合适的layout进行使用-->
- <!--设置intent-filter可以先启动该Activity-->
- <activity
- android:name="Launcher"
- android:launchMode="singleTask"
- android:clearTaskOnLaunch="true"
- android:stateNotNeeded="true"
- android:theme="@style/Theme"
- android:screenOrientation="nosensor"
- android:windowSoftInputMode="stateUnspecified|adjustPan">
- <intent-filter>
- <actionandroid:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"/>
- <categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.HOME"/>
- <categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
- <categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.MONKEY"/>
- </intent-filter>
- </activity>
- <!--设置Wallpapaer的Activity-->
- <activity
- android:name="WallpaperChooser"
- android:label="@string/pick_wallpaper"
- android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher_wallpaper"
- android:screenOrientation="nosensor"
- android:finishOnCloseSystemDialogs="true">
- <intent-filter>
- <actionandroid:name="android.intent.action.SET_WALLPAPER"/>
- <categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
- </intent-filter>
- </activity>
- <!--安装快捷方式的Intent-->
- <!--Intentreceivedusedtoinstallshortcutsfromotherapplications-->
- <receiver
- android:name="InstallShortcutReceiver"
- android:permission="com.android.zkx_launcher.permission.INSTALL_SHORTCUT">
- <intent-filter>
- <actionandroid:name="com.android.zkx_launcher.action.INSTALL_SHORTCUT"/>
- </intent-filter>
- </receiver>
- <!--卸载快捷方式的Intent-->
- <!--Intentreceivedusedtouninstallshortcutsfromotherapplications-->
- <receiver
- android:name="UninstallShortcutReceiver"
- android:permission="com.android.zkx_launcher.permission.UNINSTALL_SHORTCUT">
- <intent-filter>
- <actionandroid:name="com.android.zkx_launcher.action.UNINSTALL_SHORTCUT"/>
- </intent-filter>
- </receiver>
- <!--供应商信息-->
- <!--ThesettingsprovidercontainsHome'sdata,liketheworkspacefavorites-->
- <provider
- android:name="LauncherProvider"
- android:authorities="com.android.zkx_launcher.settings"
- android:writePermission="com.android.zkx_launcher.permission.WRITE_SETTINGS"
- android:readPermission="com.android.zkx_launcher.permission.READ_SETTINGS"/>
- </application>
- </manifest>
三 Launcher Res下的Xml文件
Res/xml下有两个xml文件,default_workspace.xml&&default_wallpaper.xml
Andorid这个默认壁纸不在launcher里,在源码中frameworks/base/core/res/res /drawable/default_wallpaper.jpg.
另frameworks/base/core/res/res路径下包含很多default资源。如果需要修改默认设置可以尝试到这里来找一找
<favorites xmlns:launcher="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.unique.launcher">
<!-- Far-left screen [0] -->
<!-- Left screen [1] -->
<appwidget
launcher:packageName="com.google.android.apps.genie.geniewidget"
launcher:className="com.google.android.apps.genie.geniewidget.miniwidget.MiniWidgetProvider"
launcher:screen="1"
launcher:x="0"
launcher:y="0"
launcher:spanX="4"
launcher:spanY="1" />
#天气新闻时钟插件
#packageName:widget的packageName
#className :实现 widget的 receiver 类的名称.
#launcher:container 放置的位 置(只能为desktop)
#screen : 在哪一个screen添加
#x,y: 在screen中的位置
#launcher:spanX:在x方向上所占格数
#launcher:spanY:在y方向上所占格数
<!-- Middle screen [2] -->
<search
launcher:screen="2"
launcher:x="0"
launcher:y="0" />
<appwidget
launcher:packageName="com.android.protips"
launcher:className="com.android.protips.ProtipWidget"
launcher:screen="2"
launcher:x="0"
launcher:y="1"
launcher:spanX="4"
launcher:spanY="1 " />
<!-- Right screen [3] -->
<appwidget
launcher:packageName="com.android.music"
launcher:className="com.android.music.MediaAppWidgetProvider"
launcher:screen="3"
launcher:x="0"
launcher:y="0"
launcher:spanX="4"
launcher:spanY="1" />
<appwidget
launcher:packageName="com.android.vending"
launcher:className="com.android.vending.MarketWidgetProvider"
launcher:screen="3"
launcher:x="1"
launcher:y="1"
launcher:spanX="2"
launcher:spanY="2" />
#电子市场Android Market
<!-- Far-right screen [4] -->
</favorites>
代码如下:
<manifestxmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="net.sunniwell.launcher"
android:versionCode="1"android:versionName="1.0.1">
关于自定义权限,这是很好的例子,其他apk程序要想使用Launcher的功能必须添加这些权限,而这些权限都是在这里声明的。
这个是安装快捷方式的权限定义:
<permission
android:name="com.android.launcher.permission.INSTALL_SHORTCUT"
android:permissionGroup="android.permission-group.SYSTEM_TOOLS"
android:protectionLevel="normal"
android:label="@string/permlab_install_shortcut"
android:description="@string/permdesc_install_shortcut"/>
这个是卸载快捷方式的权限定义:
<permission
android:name="com.android.launcher.permission.UNINSTALL_SHORTCUT"
android:permissionGroup="android.permission-group.SYSTEM_TOOLS"
android:protectionLevel="normal"
android:label="@string/permlab_uninstall_shortcut"
android:description="@string/permdesc_uninstall_shortcut"/>
这个是读取launcher.db内容的权限定义:
<permission
android:name="net.sunniwell.launcher.permission.READ_SETTINGS"
android:permissionGroup="android.permission-group.SYSTEM_TOOLS"
android:protectionLevel="normal"
android:label="@string/permlab_read_settings"
android:description="@string/permdesc_read_settings"/>
这个是修改和删除launcher.db内容的权限定义:
<permission
android:name="net.sunniwell.launcher.permission.WRITE_SETTINGS"
android:permissionGroup="android.permission-group.SYSTEM_TOOLS"
android:protectionLevel="normal"
android:label="@string/permlab_write_settings"
android:description="@string/permdesc_write_settings"/>
这些是Launcher的权限声明,通过这些就能看出launcher的大概功能了:
打电话权限:
<uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.CALL_PHONE"/>
使用状态栏权限:
<uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.EXPAND_STATUS_BAR"/>
获取当前或最近运行的任务的信息的权限:
<uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.GET_TASKS"/>
读取通信录权限:
<uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.READ_CONTACTS"/>
设置壁纸权限:
<uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.SET_WALLPAPER"/>
允许程序设置壁纸hits的权限:
<uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.SET_WALLPAPER_HINTS"/>
使用震动功能权限:
<uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.VIBRATE"/>
修改删除launcher.db内容权限:
<uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.WRITE_SETTINGS"/>
绑定widget权限:
<uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.BIND_APPWIDGET"/>
读取launcher.db内容权限:
<uses-permissionandroid:name="net.sunniwell.launcher.permission.READ_SETTINGS"/>
修改删除launcher.db内容权限:
<uses-permissionandroid:name="net.sunniwell.launcher.permission.WRITE_SETTINGS"/>
读写外部存储设备权限:
<uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"></uses-permission>
<application
android:name="LauncherApplication"
activity应该运行的进程的名字:
android:process="android.process.acore"
android:label="@string/application_name"
android:icon="@drawable/swicon">
<activity
android:name="Launcher"
是否
android:launchMode="singleTask"
android:clearTaskOnLaunch="true"
这个activity是否在被杀死或者重启后能恢复原来的状态:
android:stateNotNeeded="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme"
android:screenOrientation="landscape"
android:windowSoftInputMode="stateUnspecified|adjustPan">
<intent-filter>
<actionandroid:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"/>
<categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"/>
桌面应用的标记:
<categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.HOME"/>
<categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
自动化测试工具Monkey的标记,待研究…
<categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.MONKEY"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
选择壁纸的activity:
<activity
android:name="WallpaperChooser"
android:label="@string/pick_wallpaper"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher_gallery">
设置壁纸的intent-filter:
<intent-filter>
<actionandroid:name="android.intent.action.SET_WALLPAPER"/>
<categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
</intent-filter>
搜索的activity:
</activity>
<!-- Enable system-default search mode for any activity in Home -->
<meta-data
android:name="android.app.default_searchable"
android:value="*"/>
安装快捷方式的广播接收器:
<!-- Intent received used to install shortcuts from other applications -->
<receiver
android:name=".InstallShortcutReceiver"
android:permission="com.android.launcher.permission.INSTALL_SHORTCUT">
<intent-filter>
<actionandroid:name="com.android.launcher.action.INSTALL_SHORTCUT"/>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<!-- Intent received used to uninstall shortcuts from other applications -->
卸载快捷方式的广播接收器:
<receiver
android:name=".UninstallShortcutReceiver"
android:permission="com.android.launcher.permission.UNINSTALL_SHORTCUT">
<intent-filter>
<actionandroid:name="com.android.launcher.action.UNINSTALL_SHORTCUT"/>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
声明ContentProvider,用于对launcher.db操作:
<!-- The settings provider contains Home's data, like the workspace favorites -->
<provider
android:name="SWLauncherProvider"
android:authorities="net.sunniwell.launcher.settings"
android:writePermission="net.sunniwell.launcher.permission.WRITE_SETTINGS"
android:readPermission="net.sunniwell.launcher.permission.READ_SETTINGS"/>
</application>
<uses-sdkandroid:minSdkVersion="4"/>
</manifest>
说明:
1.
<manifest 标签头部还应声明:
android:sharedUserId="android.uid.shared" ,作用是获得系统权限,但是这样的程序属性只能在build整个系统时放进去(就是系统软件)才起作用,手动安装是没有权限的。
AddAdapter:维护了live fold, widget , shortcut , wallpaper 4个ListItem,长按桌面会显示该列表
AllAppsGridView:显示APP的网格
ApplicationInfo:一个可启动的应用
ApplicationsAdapter:gridview的adapter
BubbleTextView:一个定制了的textview
CellLayout:屏幕网格化
DeleteZone:UI的一部分
DragController,dragscroller, dragsource, droptarget:支持拖拽操作
DragLayer:内部支持拖拽的viewgroup
FastBitmapDrawable:工具
Folder:Icons的集合
FolderIcon:出现在workspace的icon代表了一个folder
FolderInfo: ItemInfo子类
HandleView:一个imageview。
InstallShortcutReceiver,UninstallShortcutReceiver:一个broadcastrecier
ItemInfo:代表Launcher中一个Item(例如folder)
Launcher: Launcher程序的主窗口
LauncherApplication:在VM中设置参数
LauncherAppWidgetHost,LauncherAppWidgetHostView,:Widget相关
LauncherModel:MVC中的M
LauncherProvider:一个contentprovider,为Launcher存储信息
LauncherSettings:设置相关的工具
LiveFolder,LiveFolderAdapter,LiveFolderIcon,LiveFolderInfo:livefolder相关
Search:搜索
UserFolder,UserFolderInfo:文件夹包含applications ,shortcuts
Utilities:小工具
WallpaperChooser:选择wallpaper的activity
Workspace:屏幕上的一块区域
widget :代表启动的widget实例,例如搜索
总结
1) Launcher中实现了MVC模式(M:launchermode , V:draglayer ,C: launcher),以此为主线,可以得到Launcher对各个组件管理的细节(如drag的实现)。
六 Launcher 起动过程
Android系统在启动时会安装应用程序,这些应用程序安装好之后,还需要有一个Home应用程序来负责把它们在桌面上展示出来,在Android系统中,这个默认的Home应用程序就是Launcher了,我将详细分析Launcher应用程序的启动过程。
Android系统的Home应用程序Launcher是由ActivityManagerService启动的,而ActivityManagerService和PackageManagerService一样,都是在开机时由SystemServer组件启动的,SystemServer组件首先是启动ePackageManagerServic,由它来负责安装系统的应用程序,系统中的应用程序安装好了以后,SystemServer组件接下来就要通过ActivityManagerService来启动Home应用程序Launcher了,Launcher在启动的时候便会通过PackageManagerServic把系统中已经安装好的应用程序以快捷图标的形式展示在桌面上,这样用户就可以使用这些应用程序了。
下面详细分析每一个步骤。
Step 1. SystemServer.main
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java文件中:
- publicclassSystemServer
- {
- ......
- nativepublicstaticvoidinit1(String[]args);
- ......
- publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){
- ......
- init1(args);
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- public class SystemServer
- {
- ......
- native public static void init1(String[] args);
- ......
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- ......
- init1(args);
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
Step 2. SystemServer.init1
这个函数是一个JNI方法,实现在frameworks/base/services/jni/com_android_server_SystemServer.cpp文件中:
- namespaceandroid{
- extern"C"intsystem_init();
- staticvoidandroid_server_SystemServer_init1(JNIEnv*env,jobjectclazz)
- {
- system_init();
- }
- /*
- *JNIregistration.
- */
- staticJNINativeMethodgMethods[]={
- /*name,signature,funcPtr*/
- {"init1","([Ljava/lang/String;)V",(void*)android_server_SystemServer_init1},
- };
- intregister_android_server_SystemServer(JNIEnv*env)
- {
- returnjniRegisterNativeMethods(env,"com/android/server/SystemServer",
- gMethods,NELEM(gMethods));
- }
- };//namespaceandroid
- namespace android {
- extern "C" int system_init();
- static void android_server_SystemServer_init1(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz)
- {
- system_init();
- }
- /*
- * JNI registration.
- */
- static JNINativeMethod gMethods[] = {
- /* name, signature, funcPtr */
- { "init1", "([Ljava/lang/String;)V", (void*) android_server_SystemServer_init1 },
- };
- int register_android_server_SystemServer(JNIEnv* env)
- {
- return jniRegisterNativeMethods(env, "com/android/server/SystemServer",
- gMethods, NELEM(gMethods));
- }
- }; // namespace android
Step 3.libsystem_server.system_init
函数system_init实现在libsystem_server库中,源代码位于frameworks/base/cmds/system_server/library/system_init.cpp文件中:
- extern"C"status_tsystem_init()
- {
- LOGI("Enteredsystem_init()");
- sp<ProcessState>proc(ProcessState::self());
- sp<IServiceManager>sm=defaultServiceManager();
- LOGI("ServiceManager:%p\n",sm.get());
- sp<GrimReaper>grim=newGrimReaper();
- sm->asBinder()->linkToDeath(grim,grim.get(),0);
- charpropBuf[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
- property_get("system_init.startsurfaceflinger",propBuf,"1");
- if(strcmp(propBuf,"1")==0){
- //StarttheSurfaceFlinger
- SurfaceFlinger::instantiate();
- }
- //Startthesensorservice
- SensorService::instantiate();
- //Onthesimulator,audioflingeretaldon'tgetstartedthe
- //samewayasonthedevice,andweneedtostartthemhere
- if(!proc->supportsProcesses()){
- //StarttheAudioFlinger
- AudioFlinger::instantiate();
- //Startthemediaplaybackservice
- MediaPlayerService::instantiate();
- //Startthecameraservice
- CameraService::instantiate();
- //Starttheaudiopolicyservice
- AudioPolicyService::instantiate();
- }
- //AndnowstarttheAndroidruntime.Wehavetodothisbit
- //ofnastinessbecausetheAndroidruntimeinitializationrequires
- //someofthecoresystemservicestoalreadybestarted.
- //AllotherserversshouldjuststarttheAndroidruntimeat
- //thebeginningoftheirprocesses'smain(),beforecalling
- //theinitfunction.
- LOGI("Systemserver:startingAndroidruntime.\n");
- AndroidRuntime*runtime=AndroidRuntime::getRuntime();
- LOGI("Systemserver:startingAndroidservices.\n");
- runtime->callStatic("com/android/server/SystemServer","init2");
- //Ifrunninginourownprocess,justgointothethread
- //pool.Otherwise,calltheinitializationfinished
- //functoletthisprocesscontinueitsinitilization.
- if(proc->supportsProcesses()){
- LOGI("Systemserver:enteringthreadpool.\n");
- ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
- IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
- LOGI("Systemserver:exitingthreadpool.\n");
- }
- returnNO_ERROR;
- }
- extern "C" status_t system_init()
- {
- LOGI("Entered system_init()");
- sp<ProcessState> proc(ProcessState::self());
- sp<IServiceManager> sm = defaultServiceManager();
- LOGI("ServiceManager: %p\n", sm.get());
- sp<GrimReaper> grim = new GrimReaper();
- sm->asBinder()->linkToDeath(grim, grim.get(), 0);
- char propBuf[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
- property_get("system_init.startsurfaceflinger", propBuf, "1");
- if (strcmp(propBuf, "1") == 0) {
- // Start the SurfaceFlinger
- SurfaceFlinger::instantiate();
- }
- // Start the sensor service
- SensorService::instantiate();
- // On the simulator, audioflinger et al don't get started the
- // same way as on the device, and we need to start them here
- if (!proc->supportsProcesses()) {
- // Start the AudioFlinger
- AudioFlinger::instantiate();
- // Start the media playback service
- MediaPlayerService::instantiate();
- // Start the camera service
- CameraService::instantiate();
- // Start the audio policy service
- AudioPolicyService::instantiate();
- }
- // And now start the Android runtime. We have to do this bit
- // of nastiness because the Android runtime initialization requires
- // some of the core system services to already be started.
- // All other servers should just start the Android runtime at
- // the beginning of their processes's main(), before calling
- // the init function.
- LOGI("System server: starting Android runtime.\n");
- AndroidRuntime* runtime = AndroidRuntime::getRuntime();
- LOGI("System server: starting Android services.\n");
- runtime->callStatic("com/android/server/SystemServer", "init2");
- // If running in our own process, just go into the thread
- // pool. Otherwise, call the initialization finished
- // func to let this process continue its initilization.
- if (proc->supportsProcesses()) {
- LOGI("System server: entering thread pool.\n");
- ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
- IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
- LOGI("System server: exiting thread pool.\n");
- }
- return NO_ERROR;
- }
Step 4. AndroidRuntime.callStatic
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp文件中:
- /*
- *CallastaticJavaProgrammingLanguagefunctionthattakesnoargumentsandreturnsvoid.
- */
- status_tAndroidRuntime::callStatic(constchar*className,constchar*methodName)
- {
- JNIEnv*env;
- jclassclazz;
- jmethodIDmethodId;
- env=getJNIEnv();
- if(env==NULL)
- returnUNKNOWN_ERROR;
- clazz=findClass(env,className);
- if(clazz==NULL){
- LOGE("ERROR:couldnotfindclass'%s'\n",className);
- returnUNKNOWN_ERROR;
- }
- methodId=env->GetStaticMethodID(clazz,methodName,"()V");
- if(methodId==NULL){
- LOGE("ERROR:couldnotfindmethod%s.%s\n",className,methodName);
- returnUNKNOWN_ERROR;
- }
- env->CallStaticVoidMethod(clazz,methodId);
- returnNO_ERROR;
- }
- /*
- * Call a static Java Programming Language function that takes no arguments and returns void.
- */
- status_t AndroidRuntime::callStatic(const char* className, const char* methodName)
- {
- JNIEnv* env;
- jclass clazz;
- jmethodID methodId;
- env = getJNIEnv();
- if (env == NULL)
- return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
- clazz = findClass(env, className);
- if (clazz == NULL) {
- LOGE("ERROR: could not find class '%s'\n", className);
- return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
- }
- methodId = env->GetStaticMethodID(clazz, methodName, "()V");
- if (methodId == NULL) {
- LOGE("ERROR: could not find method %s.%s\n", className, methodName);
- return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
- }
- env->CallStaticVoidMethod(clazz, methodId);
- return NO_ERROR;
- }
Step 5.SystemServer.init2
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java文件中:
- publicclassSystemServer
- {
- ......
- publicstaticfinalvoidinit2(){
- Slog.i(TAG,"EnteredtheAndroidsystemserver!");
- Threadthr=newServerThread();
- thr.setName("android.server.ServerThread");
- thr.start();
- }
- }
- public class SystemServer
- {
- ......
- public static final void init2() {
- Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!");
- Thread thr = new ServerThread();
- thr.setName("android.server.ServerThread");
- thr.start();
- }
- }
Step 6.ServerThread.run
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java文件中:
- classServerThreadextendsThread{
- ......
- @Override
- publicvoidrun(){
- ......
- IPackageManagerpm=null;
- ......
- //Criticalservices...
- try{
- ......
- Slog.i(TAG,"PackageManager");
- pm=PackageManagerService.main(context,
- factoryTest!=SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_OFF);
- ......
- }catch(RuntimeExceptione){
- Slog.e("System","Failurestartingcoreservice",e);
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- class ServerThread extends Thread {
- ......
- @Override
- public void run() {
- ......
- IPackageManager pm = null;
- ......
- // Critical services...
- try {
- ......
- Slog.i(TAG, "Package Manager");
- pm = PackageManagerService.main(context,
- factoryTest != SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_OFF);
- ......
- } catch (RuntimeException e) {
- Slog.e("System", "Failure starting core service", e);
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerServcie.java文件中:
- publicfinalclassActivityManagerServiceextendsActivityManagerNative
- implementsWatchdog.Monitor,BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback{
- ......
- publicstaticfinalContextmain(intfactoryTest){
- AThreadthr=newAThread();
- thr.start();
- synchronized(thr){
- while(thr.mService==null){
- try{
- thr.wait();
- }catch(InterruptedExceptione){
- }
- }
- }
- ActivityManagerServicem=thr.mService;
- mSelf=m;
- ActivityThreadat=ActivityThread.systemMain();
- mSystemThread=at;
- Contextcontext=at.getSystemContext();
- m.mContext=context;
- m.mFactoryTest=factoryTest;
- m.mMainStack=newActivityStack(m,context,true);
- m.mBatteryStatsService.publish(context);
- m.mUsageStatsService.publish(context);
- synchronized(thr){
- thr.mReady=true;
- thr.notifyAll();
- }
- m.startRunning(null,null,null,null);
- returncontext;
- }
- ......
- }
- public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
- implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
- ......
- public static final Context main(int factoryTest) {
- AThread thr = new AThread();
- thr.start();
- synchronized (thr) {
- while (thr.mService == null) {
- try {
- thr.wait();
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- }
- }
- }
- ActivityManagerService m = thr.mService;
- mSelf = m;
- ActivityThread at = ActivityThread.systemMain();
- mSystemThread = at;
- Context context = at.getSystemContext();
- m.mContext = context;
- m.mFactoryTest = factoryTest;
- m.mMainStack = new ActivityStack(m, context, true);
- m.mBatteryStatsService.publish(context);
- m.mUsageStatsService.publish(context);
- synchronized (thr) {
- thr.mReady = true;
- thr.notifyAll();
- }
- m.startRunning(null, null, null, null);
- return context;
- }
- ......
- }
Step 8.PackageManagerService.main
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/PackageManagerService.java文件中:
- classPackageManagerServiceextendsIPackageManager.Stub{
- ......
- publicstaticfinalIPackageManagermain(Contextcontext,booleanfactoryTest){
- PackageManagerServicem=newPackageManagerService(context,factoryTest);
- ServiceManager.addService("package",m);
- returnm;
- }
- ......
- }
- class PackageManagerService extends IPackageManager.Stub {
- ......
- public static final IPackageManager main(Context context, boolean factoryTest) {
- PackageManagerService m = new PackageManagerService(context, factoryTest);
- ServiceManager.addService("package", m);
- return m;
- }
- ......
- }
- classPackageManagerServiceextendsIPackageManager.Stub{
- ......
- publicPackageManagerService(Contextcontext,booleanfactoryTest){
- ......
- synchronized(mInstallLock){
- synchronized(mPackages){
- ......
- FiledataDir=Environment.getDataDirectory();
- mAppDataDir=newFile(dataDir,"data");
- mSecureAppDataDir=newFile(dataDir,"secure/data");
- mDrmAppPrivateInstallDir=newFile(dataDir,"app-private");
- ......
- mFrameworkDir=newFile(Environment.getRootDirectory(),"framework");
- mDalvikCacheDir=newFile(dataDir,"dalvik-cache");
- ......
- //Findbaseframeworks(resourcepackageswithoutcode).
- mFrameworkInstallObserver=newAppDirObserver(
- mFrameworkDir.getPath(),OBSERVER_EVENTS,true);
- mFrameworkInstallObserver.startWatching();
- scanDirLI(mFrameworkDir,PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
- |PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR,
- scanMode|SCAN_NO_DEX,0);
- //Collectallsystempackages.
- mSystemAppDir=newFile(Environment.getRootDirectory(),"app");
- mSystemInstallObserver=newAppDirObserver(
- mSystemAppDir.getPath(),OBSERVER_EVENTS,true);
- mSystemInstallObserver.startWatching();
- scanDirLI(mSystemAppDir,PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
- |PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR,scanMode,0);
- //Collectallvendorpackages.
- mVendorAppDir=newFile("/vendor/app");
- mVendorInstallObserver=newAppDirObserver(
- mVendorAppDir.getPath(),OBSERVER_EVENTS,true);
- mVendorInstallObserver.startWatching();
- scanDirLI(mVendorAppDir,PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
- |PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR,scanMode,0);
- mAppInstallObserver=newAppDirObserver(
- mAppInstallDir.getPath(),OBSERVER_EVENTS,false);
- mAppInstallObserver.startWatching();
- scanDirLI(mAppInstallDir,0,scanMode,0);
- mDrmAppInstallObserver=newAppDirObserver(
- mDrmAppPrivateInstallDir.getPath(),OBSERVER_EVENTS,false);
- mDrmAppInstallObserver.startWatching();
- scanDirLI(mDrmAppPrivateInstallDir,PackageParser.PARSE_FORWARD_LOCK,
- scanMode,0);
- ......
- }
- }
- }
- ......
- }
- class PackageManagerService extends IPackageManager.Stub {
- ......
- public PackageManagerService(Context context, boolean factoryTest) {
- ......
- synchronized (mInstallLock) {
- synchronized (mPackages) {
- ......
- File dataDir = Environment.getDataDirectory();
- mAppDataDir = new File(dataDir, "data");
- mSecureAppDataDir = new File(dataDir, "secure/data");
- mDrmAppPrivateInstallDir = new File(dataDir, "app-private");
- ......
- mFrameworkDir = new File(Environment.getRootDirectory(), "framework");
- mDalvikCacheDir = new File(dataDir, "dalvik-cache");
- ......
- // Find base frameworks (resource packages without code).
- mFrameworkInstallObserver = new AppDirObserver(
- mFrameworkDir.getPath(), OBSERVER_EVENTS, true);
- mFrameworkInstallObserver.startWatching();
- scanDirLI(mFrameworkDir, PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
- | PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR,
- scanMode | SCAN_NO_DEX, 0);
- // Collect all system packages.
- mSystemAppDir = new File(Environment.getRootDirectory(), "app");
- mSystemInstallObserver = new AppDirObserver(
- mSystemAppDir.getPath(), OBSERVER_EVENTS, true);
- mSystemInstallObserver.startWatching();
- scanDirLI(mSystemAppDir, PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
- | PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR, scanMode, 0);
- // Collect all vendor packages.
- mVendorAppDir = new File("/vendor/app");
- mVendorInstallObserver = new AppDirObserver(
- mVendorAppDir.getPath(), OBSERVER_EVENTS, true);
- mVendorInstallObserver.startWatching();
- scanDirLI(mVendorAppDir, PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
- | PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR, scanMode, 0);
- mAppInstallObserver = new AppDirObserver(
- mAppInstallDir.getPath(), OBSERVER_EVENTS, false);
- mAppInstallObserver.startWatching();
- scanDirLI(mAppInstallDir, 0, scanMode, 0);
- mDrmAppInstallObserver = new AppDirObserver(
- mDrmAppPrivateInstallDir.getPath(), OBSERVER_EVENTS, false);
- mDrmAppInstallObserver.startWatching();
- scanDirLI(mDrmAppPrivateInstallDir, PackageParser.PARSE_FORWARD_LOCK,
- scanMode, 0);
- ......
- }
- }
- }
- ......
- }
/system/framework
/system/app
/vendor/app
/data/app
/data/app-private
Step 9.ActivityManagerService.setSystemProcess
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerServcie.java文件中:
- publicfinalclassActivityManagerServiceextendsActivityManagerNative
- implementsWatchdog.Monitor,BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback{
- ......
- publicstaticvoidsetSystemProcess(){
- try{
- ActivityManagerServicem=mSelf;
- ServiceManager.addService("activity",m);
- ServiceManager.addService("meminfo",newMemBinder(m));
- if(MONITOR_CPU_USAGE){
- ServiceManager.addService("cpuinfo",newCpuBinder(m));
- }
- ServiceManager.addService("permission",newPermissionController(m));
- ApplicationInfoinfo=
- mSelf.mContext.getPackageManager().getApplicationInfo(
- "android",STOCK_PM_FLAGS);
- mSystemThread.installSystemApplicationInfo(info);
- synchronized(mSelf){
- ProcessRecordapp=mSelf.newProcessRecordLocked(
- mSystemThread.getApplicationThread(),info,
- info.processName);
- app.persistent=true;
- app.pid=MY_PID;
- app.maxAdj=SYSTEM_ADJ;
- mSelf.mProcessNames.put(app.processName,app.info.uid,app);
- synchronized(mSelf.mPidsSelfLocked){
- mSelf.mPidsSelfLocked.put(app.pid,app);
- }
- mSelf.updateLruProcessLocked(app,true,true);
- }
- }catch(PackageManager.NameNotFoundExceptione){
- thrownewRuntimeException(
- "Unabletofindandroidsystempackage",e);
- }
- }
- ......
- }
- public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
- implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
- ......
- public static void setSystemProcess() {
- try {
- ActivityManagerService m = mSelf;
- ServiceManager.addService("activity", m);
- ServiceManager.addService("meminfo", new MemBinder(m));
- if (MONITOR_CPU_USAGE) {
- ServiceManager.addService("cpuinfo", new CpuBinder(m));
- }
- ServiceManager.addService("permission", new PermissionController(m));
- ApplicationInfo info =
- mSelf.mContext.getPackageManager().getApplicationInfo(
- "android", STOCK_PM_FLAGS);
- mSystemThread.installSystemApplicationInfo(info);
- synchronized (mSelf) {
- ProcessRecord app = mSelf.newProcessRecordLocked(
- mSystemThread.getApplicationThread(), info,
- info.processName);
- app.persistent = true;
- app.pid = MY_PID;
- app.maxAdj = SYSTEM_ADJ;
- mSelf.mProcessNames.put(app.processName, app.info.uid, app);
- synchronized (mSelf.mPidsSelfLocked) {
- mSelf.mPidsSelfLocked.put(app.pid, app);
- }
- mSelf.updateLruProcessLocked(app, true, true);
- }
- } catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(
- "Unable to find android system package", e);
- }
- }
- ......
- }
Step 10. ActivityManagerService.systemReady
这个函数是在上面的Step 6中的ServerThread.run函数在将系统中的一系列服务都初始化完毕之后才调用的,它定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerServcie.java文件中:
- publicfinalclassActivityManagerServiceextendsActivityManagerNative
- implementsWatchdog.Monitor,BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback{
- ......
- publicvoidsystemReady(finalRunnablegoingCallback){
- ......
- synchronized(this){
- ......
- mMainStack.resumeTopActivityLocked(null);
- }
- }
- ......
- }
- public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
- implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
- ......
- public void systemReady(final Runnable goingCallback) {
- ......
- synchronized (this) {
- ......
- mMainStack.resumeTopActivityLocked(null);
- }
- }
- ......
- }
Step 11. ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityLocked
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java文件中:
- publicclassActivityStack{
- ......
- finalbooleanresumeTopActivityLocked(ActivityRecordprev){
- //Findthefirstactivitythatisnotfinishing.
- ActivityRecordnext=topRunningActivityLocked(null);
- ......
- if(next==null){
- //Therearenomoreactivities!Let'sjuststartupthe
- //Launcher...
- if(mMainStack){
- returnmService.startHomeActivityLocked();
- }
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- public class ActivityStack {
- ......
- final boolean resumeTopActivityLocked(ActivityRecord prev) {
- // Find the first activity that is not finishing.
- ActivityRecord next = topRunningActivityLocked(null);
- ......
- if (next == null) {
- // There are no more activities! Let's just start up the
- // Launcher...
- if (mMainStack) {
- return mService.startHomeActivityLocked();
- }
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
Step 12.ActivityManagerService.startHomeActivityLocked
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerServcie.java文件中:
- publicfinalclassActivityManagerServiceextendsActivityManagerNative
- implementsWatchdog.Monitor,BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback{
- ......
- booleanstartHomeActivityLocked(){
- ......
- Intentintent=newIntent(
- mTopAction,
- mTopData!=null?Uri.parse(mTopData):null);
- intent.setComponent(mTopComponent);
- if(mFactoryTest!=SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL){
- intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME);
- }
- ActivityInfoaInfo=
- intent.resolveActivityInfo(mContext.getPackageManager(),
- STOCK_PM_FLAGS);
- if(aInfo!=null){
- intent.setComponent(newComponentName(
- aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName,aInfo.name));
- //Don'tdothisifthehomeappiscurrentlybeing
- //instrumented.
- ProcessRecordapp=getProcessRecordLocked(aInfo.processName,
- aInfo.applicationInfo.uid);
- if(app==null||app.instrumentationClass==null){
- intent.setFlags(intent.getFlags()|Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
- mMainStack.startActivityLocked(null,intent,null,null,0,aInfo,
- null,null,0,0,0,false,false);
- }
- }
- returntrue;
- }
- ......
- }
- public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
- implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
- ......
- boolean startHomeActivityLocked() {
- ......
- Intent intent = new Intent(
- mTopAction,
- mTopData != null ? Uri.parse(mTopData) : null);
- intent.setComponent(mTopComponent);
- if (mFactoryTest != SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
- intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME);
- }
- ActivityInfo aInfo =
- intent.resolveActivityInfo(mContext.getPackageManager(),
- STOCK_PM_FLAGS);
- if (aInfo != null) {
- intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(
- aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, aInfo.name));
- // Don't do this if the home app is currently being
- // instrumented.
- ProcessRecord app = getProcessRecordLocked(aInfo.processName,
- aInfo.applicationInfo.uid);
- if (app == null || app.instrumentationClass == null) {
- intent.setFlags(intent.getFlags() | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
- mMainStack.startActivityLocked(null, intent, null, null, 0, aInfo,
- null, null, 0, 0, 0, false, false);
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
- ......
- }
- <manifest
- xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- package="com.android.launcher"
- android:sharedUserId="@string/sharedUserId"
- >
- ......
- <application
- android:name="com.android.launcher2.LauncherApplication"
- android:process="@string/process"
- android:label="@string/application_name"
- android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher_home">
- <activity
- android:name="com.android.launcher2.Launcher"
- android:launchMode="singleTask"
- android:clearTaskOnLaunch="true"
- android:stateNotNeeded="true"
- android:theme="@style/Theme"
- android:screenOrientation="nosensor"
- android:windowSoftInputMode="stateUnspecified|adjustPan">
- <intent-filter>
- <actionandroid:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"/>
- <categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.HOME"/>
- <categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
- <categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.MONKEY"/>
- </intent-filter>
- </activity>
- ......
- </application>
- </manifest>
- <manifest
- xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- package="com.android.launcher"
- android:sharedUserId="@string/sharedUserId"
- >
- ......
- <application
- android:name="com.android.launcher2.LauncherApplication"
- android:process="@string/process"
- android:label="@string/application_name"
- android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher_home">
- <activity
- android:name="com.android.launcher2.Launcher"
- android:launchMode="singleTask"
- android:clearTaskOnLaunch="true"
- android:stateNotNeeded="true"
- android:theme="@style/Theme"
- android:screenOrientation="nosensor"
- android:windowSoftInputMode="stateUnspecified|adjustPan">
- <intent-filter>
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.HOME" />
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.MONKEY"/>
- </intent-filter>
- </activity>
- ......
- </application>
- </manifest>
因此,这里就返回com.android.launcher2.Launcher这个Activity了。由于是第一次启动这个Activity,接下来调用函数getProcessRecordLocked返回来的ProcessRecord值为null,于是,就调用mMainStack.startActivityLocked函数启动com.android.launcher2.Launcher这个Activity了,这里的mMainStack是一个ActivityStack类型的成员变量。
Step 13. ActivityStack.startActivityLocked
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java文件中
Step 14.Launcher.onCreate
这个函数定义在packages/apps/Launcher2/src/com/android/launcher2/Launcher.java文件中:
- publicfinalclassLauncherextendsActivity
- implementsView.OnClickListener,OnLongClickListener,LauncherModel.Callbacks,AllAppsView.Watcher{
- ......
- @Override
- protectedvoidonCreate(BundlesavedInstanceState){
- ......
- if(!mRestoring){
- mModel.startLoader(this,true);
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- public final class Launcher extends Activity
- implements View.OnClickListener, OnLongClickListener, LauncherModel.Callbacks, AllAppsView.Watcher {
- ......
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- ......
- if (!mRestoring) {
- mModel.startLoader(this, true);
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
Step 15.LauncherModel.startLoader
这个函数定义在packages/apps/Launcher2/src/com/android/launcher2/LauncherModel.java文件中:
- publicclassLauncherModelextendsBroadcastReceiver{
- ......
- publicvoidstartLoader(Contextcontext,booleanisLaunching){
- ......
- synchronized(mLock){
- ......
- //Don'tbothertostartthethreadifweknowit'snotgoingtodoanything
- if(mCallbacks!=null&&mCallbacks.get()!=null){
- //Ifthereisalreadyonerunning,tellittostop.
- LoaderTaskoldTask=mLoaderTask;
- if(oldTask!=null){
- if(oldTask.isLaunching()){
- //don'tdowngradeisLaunchingifwe'realreadyrunning
- isLaunching=true;
- }
- oldTask.stopLocked();
- }
- mLoaderTask=newLoaderTask(context,isLaunching);
- sWorker.post(mLoaderTask);
- }
- }
- }
- ......
- }
- public class LauncherModel extends BroadcastReceiver {
- ......
- public void startLoader(Context context, boolean isLaunching) {
- ......
- synchronized (mLock) {
- ......
- // Don't bother to start the thread if we know it's not going to do anything
- if (mCallbacks != null && mCallbacks.get() != null) {
- // If there is already one running, tell it to stop.
- LoaderTask oldTask = mLoaderTask;
- if (oldTask != null) {
- if (oldTask.isLaunching()) {
- // don't downgrade isLaunching if we're already running
- isLaunching = true;
- }
- oldTask.stopLocked();
- }
- mLoaderTask = new LoaderTask(context, isLaunching);
- sWorker.post(mLoaderTask);
- }
- }
- }
- ......
- }
Step 16. LoaderTask.run
这个函数定义在packages/apps/Launcher2/src/com/android/launcher2/LauncherModel.java文件中:
- publicclassLauncherModelextendsBroadcastReceiver{
- ......
- privateclassLoaderTaskimplementsRunnable{
- ......
- publicvoidrun(){
- ......
- keep_running:{
- ......
- //secondstep
- if(loadWorkspaceFirst){
- ......
- loadAndBindAllApps();
- }else{
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- public class LauncherModel extends BroadcastReceiver {
- ......
- private class LoaderTask implements Runnable {
- ......
- public void run() {
- ......
- keep_running: {
- ......
- // second step
- if (loadWorkspaceFirst) {
- ......
- loadAndBindAllApps();
- } else {
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
Step 17.LoaderTask.loadAndBindAllApps
这个函数定义在packages/apps/Launcher2/src/com/android/launcher2/LauncherModel.java文件中:
- publicclassLauncherModelextendsBroadcastReceiver{
- ......
- privateclassLoaderTaskimplementsRunnable{
- ......
- privatevoidloadAndBindAllApps(){
- ......
- if(!mAllAppsLoaded){
- loadAllAppsByBatch();
- if(mStopped){
- return;
- }
- mAllAppsLoaded=true;
- }else{
- onlyBindAllApps();
- }
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- public class LauncherModel extends BroadcastReceiver {
- ......
- private class LoaderTask implements Runnable {
- ......
- private void loadAndBindAllApps() {
- ......
- if (!mAllAppsLoaded) {
- loadAllAppsByBatch();
- if (mStopped) {
- return;
- }
- mAllAppsLoaded = true;
- } else {
- onlyBindAllApps();
- }
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
Step 18.LoaderTask.loadAllAppsByBatch
这个函数定义在packages/apps/Launcher2/src/com/android/launcher2/LauncherModel.java文件中:
- publicclassLauncherModelextendsBroadcastReceiver{
- ......
- privateclassLoaderTaskimplementsRunnable{
- ......
- privatevoidloadAllAppsByBatch(){
- ......
- finalIntentmainIntent=newIntent(Intent.ACTION_MAIN,null);
- mainIntent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_LAUNCHER);
- finalPackageManagerpackageManager=mContext.getPackageManager();
- List<ResolveInfo>apps=null;
- intN=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
- intstartIndex;
- inti=0;
- intbatchSize=-1;
- while(i<N&&!mStopped){
- if(i==0){
- mAllAppsList.clear();
- ......
- apps=packageManager.queryIntentActivities(mainIntent,0);
- ......
- N=apps.size();
- ......
- if(mBatchSize==0){
- batchSize=N;
- }else{
- batchSize=mBatchSize;
- }
- ......
- Collections.sort(apps,
- newResolveInfo.DisplayNameComparator(packageManager));
- }
- startIndex=i;
- for(intj=0;i<N&&j<batchSize;j++){
- //Thisbuildstheiconbitmaps.
- mAllAppsList.add(newApplicationInfo(apps.get(i),mIconCache));
- i++;
- }
- finalbooleanfirst=i<=batchSize;
- finalCallbackscallbacks=tryGetCallbacks(oldCallbacks);
- finalArrayList<ApplicationInfo>added=mAllAppsList.added;
- mAllAppsList.added=newArrayList<ApplicationInfo>();
- mHandler.post(newRunnable(){
- publicvoidrun(){
- finallongt=SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
- if(callbacks!=null){
- if(first){
- callbacks.bindAllApplications(added);
- }else{
- callbacks.bindAppsAdded(added);
- }
- ......
- }else{
- ......
- }
- }
- });
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- public class LauncherModel extends BroadcastReceiver {
- ......
- private class LoaderTask implements Runnable {
- ......
- private void loadAllAppsByBatch() {
- ......
- final Intent mainIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MAIN, null);
- mainIntent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_LAUNCHER);
- final PackageManager packageManager = mContext.getPackageManager();
- List<ResolveInfo> apps = null;
- int N = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
- int startIndex;
- int i=0;
- int batchSize = -1;
- while (i < N && !mStopped) {
- if (i == 0) {
- mAllAppsList.clear();
- ......
- apps = packageManager.queryIntentActivities(mainIntent, 0);
- ......
- N = apps.size();
- ......
- if (mBatchSize == 0) {
- batchSize = N;
- } else {
- batchSize = mBatchSize;
- }
- ......
- Collections.sort(apps,
- new ResolveInfo.DisplayNameComparator(packageManager));
- }
- startIndex = i;
- for (int j=0; i<N && j<batchSize; j++) {
- // This builds the icon bitmaps.
- mAllAppsList.add(new ApplicationInfo(apps.get(i), mIconCache));
- i++;
- }
- final boolean first = i <= batchSize;
- final Callbacks callbacks = tryGetCallbacks(oldCallbacks);
- final ArrayList<ApplicationInfo> added = mAllAppsList.added;
- mAllAppsList.added = new ArrayList<ApplicationInfo>();
- mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
- public void run() {
- final long t = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
- if (callbacks != null) {
- if (first) {
- callbacks.bindAllApplications(added);
- } else {
- callbacks.bindAppsAdded(added);
- }
- ......
- } else {
- ......
- }
- }
- });
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- finalIntentmainIntent=newIntent(Intent.ACTION_MAIN,null);
- mainIntent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_LAUNCHER);
- final Intent mainIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MAIN, null);
- mainIntent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_LAUNCHER);
- finalPackageManagerpackageManager=mContext.getPackageManager();
- final PackageManager packageManager = mContext.getPackageManager();
下一步就是通过这个PackageManagerService.queryIntentActivities接口来取回所有Action类型为Intent.ACTION_MAIN,并且Category类型为Intent.CATEGORY_LAUNCHER的Activity了。
我们先进入到PackageManagerService.queryIntentActivities函数中看看是如何获得这些Activity的,然后再回到这个函数中来看其余操作。
Step 19.PackageManagerService.queryIntentActivities
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/PackageManagerService.java文件中:
- classPackageManagerServiceextendsIPackageManager.Stub{
- ......
- publicList<ResolveInfo>queryIntentActivities(Intentintent,
- StringresolvedType,intflags){
- ......
- synchronized(mPackages){
- StringpkgName=intent.getPackage();
- if(pkgName==null){
- return(List<ResolveInfo>)mActivities.queryIntent(intent,
- resolvedType,flags);
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- class PackageManagerService extends IPackageManager.Stub {
- ......
- public List<ResolveInfo> queryIntentActivities(Intent intent,
- String resolvedType, int flags) {
- ......
- synchronized (mPackages) {
- String pkgName = intent.getPackage();
- if (pkgName == null) {
- return (List<ResolveInfo>)mActivities.queryIntent(intent,
- resolvedType, flags);
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
系统在启动PackageManagerService时,会把系统中的应用程序都解析一遍,然后把解析得到的Activity都保存在mActivities变量中,这里通过这个mActivities变量的queryIntent函数返回符合条件intent的Activity,这里要返回的便是Action类型为Intent.ACTION_MAIN,并且Category类型为Intent.CATEGORY_LAUNCHER的Activity了。
回到Step 18中的LoaderTask.loadAllAppsByBatch函数中,从queryIntentActivities函数调用处返回所要求的Activity后,便调用函数tryGetCallbacks(oldCallbacks)得到一个返CallBack接口,这个接口是由Launcher类实现的,接着调用这个接口的.bindAllApplications函数来进一步操作。注意,这里又是通过消息来处理加载应用程序的操作的。
Step 20.Launcher.bindAllApplications
这个函数定义在packages/apps/Launcher2/src/com/android/launcher2/Launcher.java文件中:
- publicfinalclassLauncherextendsActivity
- implementsView.OnClickListener,OnLongClickListener,LauncherModel.Callbacks,AllAppsView.Watcher{
