关于linux设备模型kobject,kset,ktype
--------------------------------------------------------
本文系本站原创,欢迎转载!
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/gdt_a20
--------------------------------------------------------
一、sysfs文件系统下的每个目录对应于一个kobj,kset是kobj的封装,内嵌了一个kobj,其代表kset自身,ktype代表属性操作集,但由于通用性,因此把ktype单独剥离出来,kobj,kset,ktype成为了各个驱动模型最底层的关联元素,并由此形成了sys下的各种拓扑结构。
二、关于kobject
首先看一下kobject的原型
- struct kobject {
- const char *name; //名字
- struct list_head entry; //连接到kset建立层次结构
- struct kobject *parent; //指向父节点,面向对象的层次架构
- struct kset *kset;
- struct kobj_type *ktype; //属性文件
- struct sysfs_dirent *sd;
- struct kref kref; //引用计数
- unsigned int state_initialized:1; //初始化状态...
- unsigned int state_in_sysfs:1;
- unsigned int state_add_uevent_sent:1;
- unsigned int state_remove_uevent_sent:1;
- unsigned int uevent_suppress:1;
- };
分析一下kobject的初始化过程
初始化函数为
- ---int kobject_init_and_add(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_type *ktype, //参数为kobject和属性结构体
- struct kobject *parent, const char *fmt, ...)
- {
- va_list args;
- int retval;
- kobject_init(kobj, ktype);
- va_start(args, fmt);
- retval = kobject_add_varg(kobj, parent, fmt, args);
- va_end(args);
- return retval;
- }
- ---void kobject_init(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_type *ktype)
- {
- char *err_str;
- if (!kobj) { //kobj为NULL错误退出
- err_str = "invalid kobject pointer!";
- goto error;
- }
- if (!ktype) { //ktype为NULL错误退出
- err_str = "must have a ktype to be initialized properly!/n";
- goto error;
- }
- if (kobj->state_initialized) { //如果初始化状态为1报错
- /* do not error out as sometimes we can recover */
- printk(KERN_ERR "kobject (%p): tried to init an initialized "
- "object, something is seriously wrong./n", kobj);
- dump_stack();
- }
- kobject_init_internal(kobj); //初始化kobj
- kobj->ktype = ktype; //关联obj和ktype
- return;
- error:
- printk(KERN_ERR "kobject (%p): %s/n", kobj, err_str);
- dump_stack();
- }
- -------static void kobject_init_internal(struct kobject *kobj)
- {
- if (!kobj)
- return;
- kref_init(&kobj->kref); //计数变成1
- INIT_LIST_HEAD(&kobj->entry); //都指向自己,prev和next
- kobj->state_in_sysfs = 0;
- kobj->state_add_uevent_sent = 0;
- kobj->state_remove_uevent_sent = 0;
- kobj->state_initialized = 1;
- }
- -------static int kobject_add_varg(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobject *parent,
- const char *fmt, va_list vargs)
- {
- int retval;
- retval = kobject_set_name_vargs(kobj, fmt, vargs); //设置名字,名字中不能有“/”
- if (retval) {
- printk(KERN_ERR "kobject: can not set name properly!/n");
- return retval;
- }
- kobj->parent = parent; //设置parent,其父节点
- return kobject_add_internal(kobj);
- }
- ----static int kobject_add_internal(struct kobject *kobj)
- {
- int error = 0;
- struct kobject *parent;
- if (!kobj)
- return -ENOENT;
- if (!kobj->name || !kobj->name[0]) { //名字不能为空
- WARN(1, "kobject: (%p): attempted to be registered with empty "
- "name!/n", kobj);
- return -EINVAL;
- }
- parent = kobject_get(kobj->parent); //如果parent为真,则增加kobj->kref计数,也就是父节点的引用计数
- /* join kset if set, use it as parent if we do not already have one */
- if (kobj->kset) {
- if (!parent)
- parent = kobject_get(&kobj->kset->kobj); //如果kobj-parent父节点为NULL那么就用kobj->kset->kobj
- // 作其父节点,并增加其引用计数
- kobj_kset_join(kobj); //把kobj的entry成员添加到kobj->kset>list的尾部,现在的层次就是
- kobj->parent = parent; //kobj->kset->list指向kobj->parent
- } // ->parent 指向kset->kobj
- pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: parent: '%s', set: '%s'/n",
- kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__,
- parent ? kobject_name(parent) : "<NULL>",
- kobj->kset ? kobject_name(&kobj->kset->kobj) : "<NULL>");
- error = create_dir(kobj); //利用kobj创建目录和属性文件,其中会判断,如果parent为NULL那么就在sysfs_root下创建
- if (error) {
- kobj_kset_leave(kobj);
- kobject_put(parent);
- kobj->parent = NULL;
- /* be noisy on error issues */
- if (error == -EEXIST)
- printk(KERN_ERR "%s failed for %s with "
- "-EEXIST, don't try to register things with "
- "the same name in the same directory./n",
- __func__, kobject_name(kobj));
- else
- printk(KERN_ERR "%s failed for %s (%d)/n",
- __func__, kobject_name(kobj), error);
- dump_stack();
- } else
- kobj->state_in_sysfs = 1;
- return error;
- }
- ---static int create_dir(struct kobject *kobj)
- {
- int error = 0;
- if (kobject_name(kobj)) {
- error = sysfs_create_dir(kobj); //创建目录
- if (!error) {
- error = populate_dir(kobj); //创建属性文件
- if (error)
- sysfs_remove_dir(kobj);
- }
- }
- return error;
- }
三、关于 kset
首先看一下kset的原型
- struct kset {
- struct list_head list; //连接着他下面的kobj成员,与kobj-entry关联
- spinlock_t list_lock;
- struct kobject kobj; //代表kset自己
- const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops;
- };
再来看一下kset的初始化操作,kset表现为更高级一点的kobj,其初始化操作仍然是围绕其内部的kobj展开的。
- struct kset *kset_create_and_add(const char *name,
- const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops,
- struct kobject *parent_kobj)
- {
- struct kset *kset;
- int error;
- kset = kset_create(name, uevent_ops, parent_kobj); //创建kset,关联操作函数和其父节点
- if (!kset)
- return NULL;
- error = kset_register(kset);
- if (error) {
- kfree(kset);
- return NULL;
- }
- return kset;
- }
- ---static struct kset *kset_create(const char *name,
- const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops,
- struct kobject *parent_kobj)
- {
- struct kset *kset;
- int retval;
- kset = kzalloc(sizeof(*kset), GFP_KERNEL); //申请结构体内存
- if (!kset)
- return NULL;
- retval = kobject_set_name(&kset->kobj, name); //设置名字
- if (retval) {
- kfree(kset);
- return NULL;
- }
- kset->uevent_ops = uevent_ops; //关联操作函数
- kset->kobj.parent = parent_kobj; //关联父节点
- /*
- * The kobject of this kset will have a type of kset_ktype and belong to
- * no kset itself. That way we can properly free it when it is
- * finished being used.
- */
- kset->kobj.ktype = &kset_ktype; //关联属性文件
- kset->kobj.kset = NULL;
- return kset;
- }
- ----int kset_register(struct kset *k)
- {
- int err;
- if (!k)
- return -EINVAL;
- kset_init(k);
- err = kobject_add_internal(&k->kobj); //调用kobj操作函数
- if (err)
- return err;
- kobject_uevent(&k->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);
- return 0;
- }
- ----void kset_init(struct kset *k)
- {
- kobject_init_internal(&k->kobj); //调用kobj操作函数
- INIT_LIST_HEAD(&k->list);
- spin_lock_init(&k->list_lock);
- }
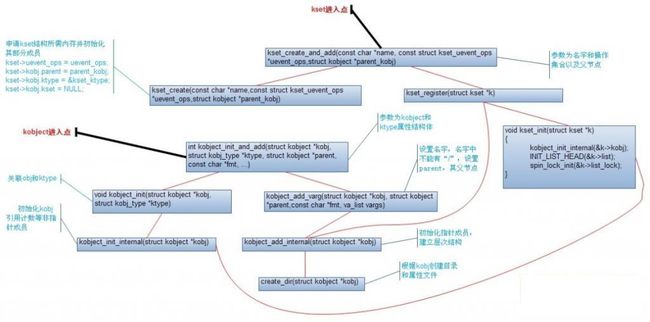
四、上面给出了kobj,kset的初始化过程,以及相互产生关联的关键点,下面给出整体的一个流程图:
總算有點了解 sysfs 了
昨天寫了一整天的 sysfs 的 code,因為我一直想要把這個東西搞清楚。但過程真的滿辛苦的,因為文件並不是很多,所以我一氣之下,決定直接看 sysfs.h, kobject.h, device.h, sysdev.h 來找 sysfs 提供的 API。
我 trace 的程式是 cpufreq,推薦一下這個程式,裡面有完整的 kobject initial、如何套到一個 sys_device 上、ktype的宣告等。裡面也有一些不錯的寫程式技巧,減低了重覆宣告 kyte 的 attribute 和 ops(這些技巧在kernel code中常出現,想必是不錯的撰寫風格),想了解 sysfs 的話,我想 cpufreq 算是不錯的範例格式。
果然皇天不負苦心人,更清楚了解 kobject, ktype, kset, sub-system, attribute 的用處。
kobject: 最小的 device model unit。單純地宣告一個 kobject 並沒什麼用處,他最神奇的地方是內嵌在 Kernel 的 device 資料結構中,例如 character device(cdev), block device(blkdev)。這些資料結構中都會內嵌一個 kobject,所以,您知道知道做了吧 :-)
ktype: kobject 的集合。但它比較偏向收集相同 operation 的 kobject 的一個集合,也就是說它是負責管理這一群 kobjects 的 operation. (show,store)。kobject 會利用它了辨識自已是屬於那一個類型,然後在 /sys 下建立正確的目錄位置。
kset: kobject 的集合。這也是一個集合,不同於ktype,它不管理 kobject 的 ops,最重要的是建立上層(sub-system)和下層的(kobject)的關聯性。kobject 也會利用它了辨識自已是屬於那一個類型,然後在 /sys 下建立正確的目錄位置。而 kset 的優先權比較高,kobject 會利用自已的 *kset 找到自已所屬的kset,並把 *ktype 指定成該kset下的ktype,當然,你也是可以搞鬼,設定了kset,但用不同的ktype的operation(...有些code是這樣)。除非沒有定義kset,才會用 ktype 來建立關聯。
subsystem:如果說 kset 是管理 kobject 的集合,同理、sussystem 就是管理 kset 的集合。
attribute: 建立了 kobject 並成功註冊之後,你會發現出現該 kobj 對應的目錄竟然是空的(這是當然的啦 XD),要如何產生資訊檔案,就是利用 attribute 這個資料結構。
struct attribute {
char *name; // 以該變數為檔名出現在 kobj 的目錄下
struct module *owner; // THIS_MODULE
mode_t mode; //permission, "S_IRUGO" or "S_IWUSR" or "0660"
};
應該是的出來 attribute 的功用,建立好attribute之後,讀取/寫入該檔案會呼叫 ktype 對應的 operation.
至於動態建立 node 並非 sysfs 的工作(still depends on him), 是由 hotplug 接收 kset 中的hotplug ops 來傳送信號並傳送給 udev 來建立 device node的(這又是一篇懸疑小說了),以後有空再寫。