Spring对JDBC的支持JdbcTemplate模板类
概述
Spring JDBC抽象框架core包提供了JDBC模板类,其中JdbcTemplate是core包的核心类,所以其他模板类都是基于它封装完成的,JDBC模板类是第一种工作模式。
JdbcTemplate类通过模板设计模式帮助我们消除了冗长的代码,只做需要做的事情(即可变部分),并且帮我们做哪些固定部分,如连接的创建及关闭。
JdbcTemplate类对可变部分采用回调接口方式实现,如ConnectionCallback通过回调接口返回给用户一个连接,从而可以使用该连接做任何事情、StatementCallback通过回调接口返回给用户一个Statement,从而可以使用该Statement做任何事情等等,还有其他一些回调接口
Spring除了提供JdbcTemplate核心类,还提供了基于JdbcTemplate实现的NamedParameterJdbcTemplate类用于支持命名参数绑定、 SimpleJdbcTemplate类用于支持Java5+的可变参数及自动装箱拆箱等特性。
JdbcTemplate
首先让我们来看下如何使用JdbcTemplate来实现增删改查。
1、首先创建表结构:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:spring-basic.xml")
@ActiveProfiles("dev")
public abstract class AbstractTestSupport {
protected transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Rule
public TestName name = new TestName();
@Before
public void setUp() {
String createTableSql = "create memory table test"
+ "(id int GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY, "
+ "name varchar(100))";
jdbcTemplate.update(createTableSql);
}
@After
public void tearDown() {
String dropTableSql = "drop table test";
jdbcTemplate.execute(dropTableSql);
}
@Resource
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
}
2、新增测试:
@Test
private void insert() {
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into test(name) values('name1')");
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into test(name) values('name2')");
Assert.assertEquals(2, jdbcTemplate.queryForInt("select count(*) from test"));
}
3、删除测试:
@Test
private void delete() {
jdbcTemplate.update("delete from test where name=?", new Object[]{"name2"});
Assert.assertEquals(1, jdbcTemplate.queryForInt("select count(*) from test"));
}
4、更新测试:
@Test
private void update() {
jdbcTemplate.update("update test set name='name3' where name=?", new Object[]{"name1"});
Assert.assertEquals(1, jdbcTemplate.queryForInt("select count(*) from test where name='name3'"));
}
5、查询测试:
@Test
private void select() {
jdbcTemplate.query("select * from test", new RowCallbackHandler() {
@Override
public void processRow(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
System.out.print("====id:" + rs.getInt("id"));
System.out.println(",name:" + rs.getString("name"));
}
});
}
看完以上示例,大家是否觉得JdbcTemplate简化了我们很多劳动力呢?接下来让我们深入学习一下JdbcTemplate提供的方法。
JdbcTemplate主要提供以下五类方法:
- execute方法:可以用于执行任何SQL语句,一般用于执行DDL语句;
- update方法:update方法用于执行新增、修改、删除等语句;
- batchUpdate方法:用于执行批处理相关语句;
- query方法及queryForXXX方法:用于执行查询相关语句;
- call方法:用于执行存储过程、函数相关语句。
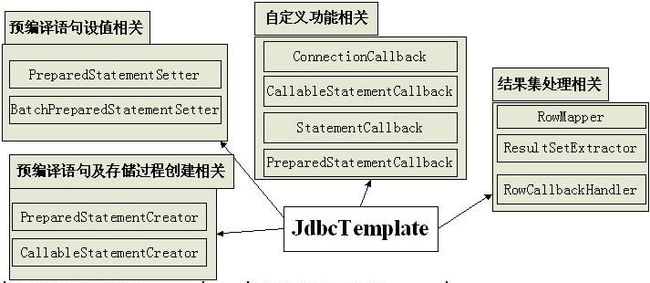
JdbcTemplate类支持的回调类:
- 预编译语句及存储过程创建回调:用于根据JdbcTemplate提供的连接创建相应的语句;
PreparedStatementCreator:通过回调获取JdbcTemplate提供的Connection,由用户使用该Conncetion创建相关的PreparedStatement;
CallableStatementCreator:通过回调获取JdbcTemplate提供的Connection,由用户使用该Conncetion创建相关的CallableStatement;
- 预编译语句设值回调:用于给预编译语句相应参数设值;
PreparedStatementSetter:通过回调获取JdbcTemplate提供的PreparedStatement,由用户来对相应的预编译语句相应参数设值;
BatchPreparedStatementSetter:;类似于PreparedStatementSetter,但用于批处理,需要指定批处理大小;
- 自定义功能回调:提供给用户一个扩展点,用户可以在指定类型的扩展点执行任何数量需要的操作;
ConnectionCallback:通过回调获取JdbcTemplate提供的Connection,用户可在该Connection执行任何数量的操作;
StatementCallback:通过回调获取JdbcTemplate提供的Statement,用户可以在该Statement执行任何数量的操作;
PreparedStatementCallback:通过回调获取JdbcTemplate提供的PreparedStatement,用户可以在该PreparedStatement执行任何数量的操作;
CallableStatementCallback:通过回调获取JdbcTemplate提供的CallableStatement,用户可以在该CallableStatement执行任何数量的操作;
- 结果集处理回调:通过回调处理ResultSet或将ResultSet转换为需要的形式;
RowMapper:用于将结果集每行数据转换为需要的类型,用户需实现方法mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum)来完成将每行数据转换为相应的类型。
RowCallbackHandler:用于处理ResultSet的每一行结果,用户需实现方法processRow(ResultSet rs)来完成处理,在该回调方法中无需执行rs.next(),该操作由JdbcTemplate来执行,用户只需按行获取数据然后处理即可。
ResultSetExtractor:用于结果集数据提取,用户需实现方法extractData(ResultSet rs)来处理结果集,用户必须处理整个结果集;
接下来让我们看下具体示例吧,在示例中不可能介绍到JdbcTemplate全部方法及回调类的使用方法,我们只介绍代表性的,其余的使用都是类似的;
- 预编译语句及存储过程创建回调、自定义功能回调使用:
@Test
public void testPpreparedStatement1() {
int count = jdbcTemplate.execute(new PreparedStatementCreator() {
@Override
public PreparedStatement createPreparedStatement(Connection conn)
throws SQLException {
return conn.prepareStatement("select count(*) from test");
}}, new PreparedStatementCallback<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer doInPreparedStatement(PreparedStatement pstmt)
throws SQLException, DataAccessException {
pstmt.execute();
ResultSet rs = pstmt.getResultSet();
rs.next();
return rs.getInt(1);
}});
Assert.assertEquals(0, count);
}
首先使用PreparedStatementCreator创建一个预编译语句,其次由JdbcTemplate通过PreparedStatementCallback回调传回,由用户决定如何执行该PreparedStatement。此处我们使用的是execute方法。
- 预编译语句设值回调使用:
@Test
public void testPreparedStatement2() {
String insertSql = "insert into test(name) values (?)";
int count = jdbcTemplate.update(insertSql, new PreparedStatementSetter() {
@Override
public void setValues(PreparedStatement pstmt) throws SQLException {
pstmt.setObject(1, "name4");
}});
Assert.assertEquals(1, count);
String deleteSql = "delete from test where name=?";
count = jdbcTemplate.update(deleteSql, new Object[] {"name4"});
Assert.assertEquals(1, count);
}
通过JdbcTemplate的int update(String sql, PreparedStatementSetter pss)执行预编译sql,其中sql参数为“insert into test(name) values (?) ”,该sql有一个占位符需要在执行前设值,PreparedStatementSetter实现就是为了设值,使用setValues(PreparedStatement pstmt)回调方法设值相应的占位符位置的值。JdbcTemplate也提供一种更简单的方式“update(String sql, Object... args)”来实现设值,所以只要当使用该种方式不满足需求时才应使用PreparedStatementSetter。
- 结果集处理回调:
@Test
public void testResultSet1() {
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into test(name) values('name5')");
String listSql = "select * from test";
List result = jdbcTemplate.query(listSql, new RowMapper<Map>() {
@Override
public Map mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Map row = new HashMap();
row.put(rs.getInt("id"), rs.getString("name"));
return row;
}});
Assert.assertEquals(1, result.size());
jdbcTemplate.update("delete from test where name='name5'");
}
RowMapper接口提供
mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum)方法将结果集的每一行转换为一个Map,当然可以转换为其他类,如表的对象画形式。
@Test
public void testResultSet2() {
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into test(name) values('name5')");
String listSql = "select * from test";
final List result = new ArrayList();
jdbcTemplate.query(listSql, new RowCallbackHandler() {
@Override
public void processRow(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
Map row = new HashMap();
row.put(rs.getInt("id"), rs.getString("name"));
result.add(row);
}});
Assert.assertEquals(1, result.size());
jdbcTemplate.update("delete from test where name='name5'");
}
RowCallbackHandler
接口也提供方法processRow(ResultSet rs),能将结果集的行转换为需要的形式。
@Test
public void testResultSet3() {
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into test(name) values('name5')");
String listSql = "select * from test";
List result = jdbcTemplate.query(listSql, new ResultSetExtractor<List>() {
@Override
public List extractData(ResultSet rs)
throws SQLException, DataAccessException {
List result = new ArrayList();
while(rs.next()) {
Map row = new HashMap();
row.put(rs.getInt("id"), rs.getString("name"));
result.add(row);
}
return result;
}});
Assert.assertEquals(0, result.size());
jdbcTemplate.update("delete from test where name='name5'");
}
ResultSetExtractor
使用回调方法extractData(ResultSet rs)提供给用户整个结果集,让用户决定如何处理该结果集
当然JdbcTemplate提供更简单的queryForXXX方法,来简化开发:
//1.查询一行数据并返回int型结果
jdbcTemplate.queryForInt("select count(*) from test");
//2. 查询一行数据并将该行数据转换为Map返回
jdbcTemplate.queryForMap("select * from test where name='name5'");
//3.查询一行任何类型的数据,最后一个参数指定返回结果类型
jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select count(*) from test", Integer.class);
//4.查询一批数据,默认将每行数据转换为Map
jdbcTemplate.queryForList("select * from test");
//5.只查询一列数据列表,列类型是String类型,列名字是name
jdbcTemplate.queryForList("
select name from test where name=?", new Object[]{"name5"}, String.class);
//6.查询一批数据,返回为SqlRowSet,类似于ResultSet,但不再绑定到连接上
SqlRowSet rs = jdbcTemplate.queryForRowSet("select * from test");
存储过程及函数回调:
MySQL
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:spring-basic.xml")
@ActiveProfiles("dev")
public abstract class AbstractTestSupport {
protected transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Rule
public TestName name = new TestName();
@Before
public void setUp() {
// 2.创建自定义函数
String createFunctionSql = "CREATE FUNCTION FUNCTION_TEST(str VARCHAR(100)) "
+ "returns INT return LENGTH(str)";
String dropFunctionSql = "DROP FUNCTION IF EXISTS FUNCTION_TEST";
jdbcTemplate.update(dropFunctionSql);
jdbcTemplate.update(createFunctionSql);
// 3.准备sql,mysql支持{?= call …}
final String callFunctionSql = "{?= call FUNCTION_TEST(?)}";
// 4.定义参数
List<SqlParameter> params = new ArrayList<SqlParameter>();
params.add(new SqlOutParameter("result", Types.INTEGER));
params.add(new SqlParameter("str", Types.VARCHAR));
Map<String, Object> outValues = jdbcTemplate.call(new CallableStatementCreator() {
@Override
public CallableStatement createCallableStatement(Connection conn) throws SQLException {
CallableStatement cstmt = conn.prepareCall(callFunctionSql);
cstmt.registerOutParameter(1, Types.INTEGER);
cstmt.setString(2, "test");
return cstmt;
}
}, params);
Assert.assertEquals(4, outValues.get("result"));
}
@After
public void tearDown() {
}
@Resource
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
}
@Test
public void testCallableStatementCreator3() {
final String callProcedureSql = "{call PROCEDURE_TEST(?, ?)}";
List<SqlParameter> params = new ArrayList<SqlParameter>();
params.add(new SqlInOutParameter("inOutName", Types.VARCHAR));
params.add(new SqlOutParameter("outId", Types.INTEGER));
Map<String, Object> outValues = jdbcTemplate.call(
new CallableStatementCreator() {
@Override
public CallableStatement createCallableStatement(Connection conn) throws SQLException {
CallableStatement cstmt = conn.prepareCall(callProcedureSql);
cstmt.registerOutParameter(1, Types.VARCHAR);
cstmt.registerOutParameter(2, Types.INTEGER);
cstmt.setString(1, "test");
return cstmt;
}}, params);
Assert.assertEquals("Hello,test", outValues.get("inOutName"));
Assert.assertEquals(0, outValues.get("outId"));
}
- {call PROCEDURE_TEST(?, ?)}:定义存储过程sql;
- params:定义存储过程参数;SqlInOutParameter描述INOUT类型参数、SqlOutParameter描述OUT类型参数;
- CallableStatementCreator:用于创建CallableStatement,并设值及注册OUT参数类型;
- outValues:通过SqlInOutParameter及SqlOutParameter参数定义的name来获取存储过程结果。
Oracel
@Resource
private CallableStatementCallback<Map<String, String>> tranchkCallableStatementCallback;
@Resource
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
public void testCall(){
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map = jdbcTemplate.execute("{call SP_BMPS_CHKBANKFILE(" + 9999 + "," + 1 + ",?)}",
tranchkCallableStatementCallback);
String line = map.get("outLine");
System.out.println(line);
}
存储过程
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE "SP_BMPS_CHKBANKFILE" (iv_chlcode IN VARCHAR2, --通道号
iv_checktype IN VARCHAR2, -- 0 信息流 1 资金流
out_line OUT INT) IS
CURSOR lc_checkdate IS select * from tcor_chk_bankfile_tmp;
lr_bankfile tcor_chk_bankfile_tmp%ROWTYPE;
ln_bankfilecnt number;
ln_checkkeycnt number;
BEGIN
dbms_output.put_line('IN PROCEDURE SP_BACS_POSCHECK: PROCEDURE START [存储过程处理开始!] ');
out_line :=0;
dbms_output.put_line(out_line);
OPEN lc_checkdate;
LOOP
FETCH lc_checkdate INTO lr_bankfile;
EXIT WHEN lc_checkdate%NOTFOUND;
select count(1) into ln_bankfilecnt
from tcor_chk_bankfile t
where t.check_key = lr_bankfile.check_key
and nvl(t.tran_amount, 0) = nvl(lr_bankfile.tran_amount, 0)
and t.do_date < = to_char(sysdate, 'yyyy-mm-dd')
and t.do_date > = to_char(sysdate - 10, 'yyyy-mm-dd')
and t.tran_tp = lr_bankfile.tran_tp
and t.check_type = lr_bankfile.check_type;
select count(*) into ln_checkkeycnt
from tcor_chk_bankfile a
where a.check_key = nvl(lr_bankfile.check_key, ' ')
and a.check_type = lr_bankfile.check_type and a.tran_tp = lr_bankfile.tran_tp;
if ln_bankfilecnt = 0 then
--有更新 没有插入
if ln_checkkeycnt = 1 then
update TCOR_CHK_BANKFILE set TPL_NO = nvl(lr_bankfile.tpl_no, ''),
FILE_NAME = nvl(lr_bankfile.file_name, ''),
BANK_CODE=nvl(lr_bankfile.bank_code, ''),
SUPPLIER_BILL_NO = nvl(lr_bankfile.supplier_bill_no, ''))
where CHECK_KEY = nvl(lr_bankfile.check_key, '') and CHECK_TYPE = nvl(lr_bankfile.check_type, '');
out_line := sql%rowcount;
--同时存在消费:消费撤销对应的两条记录的过滤掉不入库
elsif (ln_checkkeycnt < 1) then
insert into TCOR_CHK_BANKFILE
(CHK_NO,
TPL_NO,
FILE_NAME,
BANK_CODE,
SUPPLIER_BILL_NO)
values
(SEQ_BANKFILE.NEXTVAL,
lr_bankfile.tpl_no,
lr_bankfile.file_name,
lr_bankfile.bank_code,
lr_bankfile.supplier_bill_no);
out_line := out_line + sql%rowcount;
end if;
end if;
END LOOP;
delete from tcor_chk_bankfile_tmp; --结束后删除临时表
commit;
IF lc_checkdate%ISOPEN THEN
CLOSE lc_checkdate;
END IF;
dbms_output.put_line('IN PROCEDURE SP_BACS_POSCHECK: PROCEDURE END [存储过程处理结束!] ');
EXCEPTION
WHEN OTHERS THEN
IF lc_checkdate%ISOPEN THEN
CLOSE lc_checkdate;
END IF;
ROLLBACK;
delete from tcor_chk_bankfile_tmp; --结束后删除临时表
out_line :=0;
commit;
end SP_BMPS_CHKBANKFILE;