android 群英传笔记----Android scroll
现在流行的app中都存在大量的滑动操作,但是一直没有去研究过,实在是不应该,正好这本书有讲解,就参考本书学习一下
- 滑动产生的原因
- 如何实现、处理滑动效果
1 . 滑动产生的原因
滑动一个View,本质上来说就是移动一个View。改变其当前所处位置,它的原理与动画效果非常相似,都是通过不断改变View的坐标来实现这一效果。所以,要实现View的滑动,就必须监听用户的触摸事件,从而实现View跟随用户触摸的滑动而滑动。
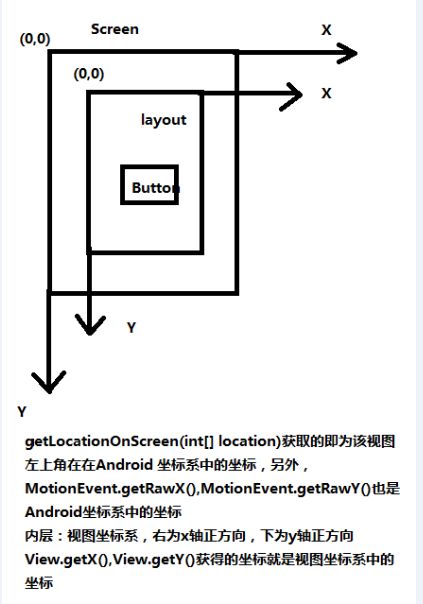
1.1 坐标系
1.2 常见的获取坐标方法
2 .实现滑动的7中方法
要实现的效果:让自定义View随着手指在屏幕上的滑动而滑动
- layout()方法
public class DragViewLayout extends View {
private int lastX;
private int lastY;
public DragViewLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public DragViewLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public DragViewLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int action = event.getAction();
int x = (int) event.getX();
int y = (int) event.getY();
switch (action){
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
lastX = x;
lastY = y;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
int offsetX = x - lastX;
int offsetY = y-lastY;
layout(getLeft()+offsetX,getTop()+offsetY,getRight()+offsetX,getBottom()+offsetY);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
break;
default:
break;
}
return true;
}
}- offsetLeftAndrRight()与offsetTopAndBottom()
public class DragViewOffset extends View {
private int lastX;
private int lastY;
public DragViewOffset(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public DragViewOffset(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public DragViewOffset(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int action = event.getAction();
int x = (int) event.getX();
int y = (int) event.getY();
switch (action){
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
lastX = x;
lastY = y;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
int offsetX = x - lastX;
int offsetY = y-lastY;
offsetLeftAndRight(offsetX);
offsetTopAndBottom(offsetY);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
break;
default:
break;
}
return true;
}
}- LayoutParams
public class DragViewMargin extends View {
private int lastX;
private int lastY;
private ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams params;
public DragViewMargin(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public DragViewMargin(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public DragViewMargin(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int action = event.getAction();
int x = (int) event.getX();
int y = (int) event.getY();
switch (action){
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
lastX = x;
lastY = y;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
int offsetX = x - lastX;
int offsetY = y-lastY;
params = (ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams) getLayoutParams();
params.leftMargin = getLeft()+offsetX;
params.topMargin = getTop()+offsetY;
setLayoutParams(params);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
break;
default:
break;
}
return true;
}
}
- scrollTo 与scrollby,注意参考系的不同
/** * 如果是View使用Scrollby,移动的是view的内容,TextView,content是他的文本,ImageView,content是他的drawable * 如果是ViewGroup,移动的是所有子View */
public class DragViewScrollBy extends View {
private int lastX;
private int lastY;
private ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams params;
public DragViewScrollBy(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public DragViewScrollBy(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public DragViewScrollBy(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int action = event.getAction();
int x = (int) event.getX();
int y = (int) event.getY();
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
lastX = x;
lastY = y;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
int offsetX = x - lastX;
int offsetY = y - lastY;
//此处,是用-offset
((ViewGroup) getParent()).scrollBy(-offsetX, -offsetY);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
break;
default:
break;
}
return true;
}
}
- Scroller,实现平滑移动效果
/** * Created by acer on 2015/11/5. * 松开手指,回到原位置 * */
public class DragViewScroller extends View {
private int lastX;
private int lastY;
private Scroller mscroller;
public DragViewScroller(Context context) {
super(context);
init(context);
}
public DragViewScroller(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init(context);
}
public DragViewScroller(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init(context);
}
private void init(Context context) {
mscroller = new Scroller(context);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int action = event.getAction();
int x = (int) event.getX();
int y = (int) event.getY();
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
lastX = x;
lastY = y;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
int offsetX = x - lastX;
int offsetY = y - lastY;
((View) getParent()).scrollBy(-offsetX, -offsetY);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
//手指离开,开始滑动回原位置
View viewGroup = (View) getParent();
mscroller.startScroll(viewGroup.getScrollX(), viewGroup.getScrollY(), -viewGroup.getScrollX(), -viewGroup.getScrollY());
invalidate();
break;
default:
break;
}
return true;
}
/** *computeScroll()方法不会自动调用, *只能通过invalidate()---draw()--computeScroll()来间接调用 * */
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
if (mscroller.computeScrollOffset()) {
((View) getParent()).scrollTo(mscroller.getCurrX(), mscroller.getCurrY());
//通过重绘,不断调用computeScrol
invalidate();
}
}
}- ViewGragHelper 强大的滑动控制类,实现各种不同的滑动,拖放需求
public class LearnViewDragHelper extends FrameLayout {
private ViewDragHelper mHelper;
private View mMenuView;
private View mMainView;
private int mWidth;
public LearnViewDragHelper(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public LearnViewDragHelper(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public LearnViewDragHelper(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP)
public LearnViewDragHelper(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
init();
}
/** * 加载布局文件完成后调用 */
@Override
public void onFinishInflate(){
super.onFinishInflate();
mMenuView = getChildAt(0);
mMainView = getChildAt(1);
}
@Override
public void onSizeChanged(int w,int h,int oldw,int oldh){
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
mWidth = mMenuView.getMeasuredWidth();
}
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
return mHelper.shouldInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
//将触摸事件传递给ViewDragHelper,此操作必不可少
mHelper.processTouchEvent(event);
return true;
}
private void init() {
mHelper = ViewDragHelper.create(this, callback);
}
/** * 核心回調 **/
private ViewDragHelper.Callback callback = new ViewDragHelper.Callback() {
/** * 开始检测触摸事件 * @param child * @param pointerId * @return */
@Override
public boolean tryCaptureView(View child, int pointerId) {
//如果当前触摸的child是mMainView时开始检测
return mMainView==child;
}
/** * 用户触摸到View后回调 * @param capturedChild * @param activePointerId */
@Override
public void onViewCaptured(View capturedChild, int activePointerId) {
super.onViewCaptured(capturedChild, activePointerId);
}
/** * view拖拽状态改变时回调 * @param state */
@Override
public void onViewDragStateChanged(int state) {
super.onViewDragStateChanged(state);
}
/** * view position改变时回调,常用于更改scale进行缩放等效果 * @param changedView * @param left * @param top * @param dx * @param dy */
@Override
public void onViewPositionChanged(View changedView, int left, int top, int dx, int dy) {
super.onViewPositionChanged(changedView, left, top, dx, dy);
}
/** * * 通常情况下,只需要返回top 和 left即可,但是当需要更加精确的计算padding等属性的时候,就需要对left进行一些处理,并返回合适大小的值 * */
/** * 水平方向滑动 * @param child * @param left 在水平方向child移动的距离 * @param dx 较前一次的增量 * @return 默认返回0 */
@Override
public int clampViewPositionHorizontal(View child, int left, int dx) {
return left;
}
/** * 竖直方向滑动 * @param child * @param top 在竖直方向child移动的距离 * @param dy 较前一次移动的距离 * @return 默认返回0 */
@Override
public int clampViewPositionVertical(View child, int top, int dy) {
return super.clampViewPositionVertical(child,top,dy);
}
/** * 拖动结束后调用 * @param releasedChild * @param xvel * @param yvel */
@Override
public void onViewReleased(View releasedChild, float xvel, float yvel) {
super.onViewReleased(releasedChild, xvel, yvel);
//手指抬起后,缓慢移动到指定位置
if(mMainView.getLeft()<500){
//关闭菜单,相当于Scroller.startScroll
mHelper.smoothSlideViewTo(mMainView,0,0);
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(LearnViewDragHelper.this);
}else{
//打开菜单
mHelper.smoothSlideViewTo(mMainView,300,0);
/** *Cause an invalidate to happen on the next animation time *step, typically the next display frame * */ ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(LearnViewDragHelper.this);
}
}
};
/** * Move the captured settling view by the appropriate amount for the current time. * If <code>continueSettling</code> returns true, the caller should call it again * on the next frame to continue. * * @param deferCallbacks true if state callbacks should be deferred via posted message. * Set this to true if you are calling this method from * {@link android.view.View#computeScroll()} or similar methods * invoked as part of layout or drawing. * @return true if settle is still in progress */
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
if (mHelper.continueSettling(true)) {
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(this);
}
}
}
滑动效果图如下:
DragViewHelper效果图如下: