Farm Irrigation zoj
Benny has a spacious farm land to irrigate. The farm land is a rectangle, and is divided into a lot of samll squares. Water pipes are placed in these squares. Different square has a different type of pipe. There are 11 types of pipes, which is marked from A to K, as Figure 1 shows.
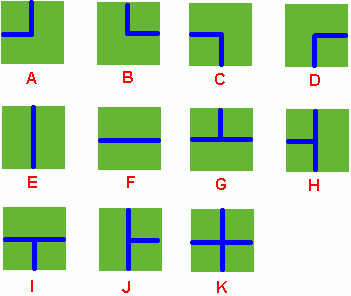
Figure 1
Benny has a map of his farm, which is an array of marks denoting the distribution of water pipes over the whole farm. For example, if he has a map
ADC FJK IHEthen the water pipes are distributed like
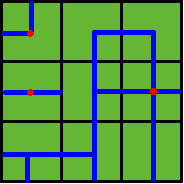
Figure 2
Several wellsprings are found in the center of some squares, so water can flow along the pipes from one square to another. If water flow crosses one square, the whole farm land in this square is irrigated and will have a good harvest in autumn.
Now Benny wants to know at least how many wellsprings should be found to have the whole farm land irrigated. Can you help him?
Note: In the above example, at least 3 wellsprings are needed, as those red points in Figure 2 show.
InputThere are several test cases! In each test case, the first line contains 2 integers M and N, then M lines follow. In each of these lines, there are N characters, in the range of 'A' to 'K', denoting the type of water pipe over the corresponding square. A negative M or N denotes the end of input, else you can assume 1 <= M, N <= 50.
Output
For each test case, output in one line the least number of wellsprings needed.
Sample Input
2 2 DK HF 3 3 ADC FJK IHE -1 -1Sample Output
2 3
这道题想麻烦了~ 看了网上的题解发现并没有开始想的那么复杂,在dfs的时候直接加入判断 每访问一个水源 就标记为1 最后搜完所有的水源 思路没错,但是for循环出错了~
坑~~~~~~~
code:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int channel[11][4] = {{0,0,1,1},{1,0,0,1},{0,1,1,0},{1,1,0,0},{0,1,0,1},
{1,0,1,0},{1,0,1,1},{0,1,1,1},{1,1,1,0},{1,1,0,1},{1,1,1,1}
};
int dir[4][2] = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
bool vis[55][55];
int map[55][55];
bool flag = false;
int n, m;
void dfs(int i, int j)
{
if (i <= 0 || i > m || j <= 0 || j > n)
return;
if (vis[i][j]) return;
flag = true;
vis[i][j] = true;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k)
{
if (channel[map[i][j]][k] && channel[map[i+dir[k][0]][j+dir[k][1]]][(k+2)%4])// 这种方法直接课可以判断是否有管道 比那么多判断好多了~~~~ orz~~~~
{
dfs(i+dir[k][0], j+dir[k][1]);
}
}
return;
}
int main(void)
{
while (cin>>m>>n)
{
if (m+n<0) break;
char ch;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j)
{
cin>>ch;
map[i][j] = ch-'A';
}
}
memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis));
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
for (int j = 1;j <= n; ++j)
{
flag = false;
if (!vis[i][j])
dfs(i, j);
if (flag)
cnt++;
}
}
cout<<cnt<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
第二种wa代码~ 有时间再改改~
思路 先记录访问过的水管 dfs一遍 即把所有与之相连的水管标记为1 同时在继续递归的时候 将第一次搜索到的水管加一~ 但是每一次dfs的时候 最后一个结点无法再标记 于是在加1的时候 先进行判断一下~ 如果和刚才搜索的相连 则在进行标记~ ~~~~~~
code:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int m,n;
int vis[1000][1000];
int map[1000][1000];
int sx,sy;
int ex,ey;
int dir[4][2]={0,1,0,-1,1,0,-1,0};
int channel[11][4]=
{
{1,0,0,1},
{1,1,0,0},
{0,0,1,1},
{0,1,1,0},
{1,0,1,0},
{0,1,0,1},
{1,1,0,1},
{1,0,1,1},
{0,1,1,1},
{1,1,1,0},
{1,1,1,1}
};
void dfs(int x,int y)
{
vis[x][y]=1;
ex=x;
ey=y;
for (int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
int nowx=x+dir[i][0];
int nowy=y+dir[i][1];
if (nowx<n&&nowy<m&&nowx>=0&&nowy>=0&&vis[nowx][nowy]==0)
{
if (nowy==y)
{
if (x<nowx&&channel[map[x][y]][1]==channel[map[nowx][nowy]][3])
{
dfs(nowx,nowy);
}
if (nowx<x&&channel[map[nowx][nowy]][1]==channel[map[x][y]][3])
{
dfs(nowx,nowy);
}
}
if (nowx==x)
{
if (y<nowy&&channel[map[x][y]][2]==channel[map[nowx][nowy]][0])
{
dfs(nowx,nowy);
}
if (y>nowy&&channel[map[nowx][nowy]][2]==channel[map[x][y]][0])
{
dfs(nowx,nowy);
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
char ch;
int ans=0;
while (cin>>m>>n)
{
if (m==-1&&n==-1)
break;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
memset(map,0,sizeof(map));
for (int i=0;i<m;i++)
for (int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
cin>>ch;
if(ch=='A')
map[i][j]=0;
if(ch=='B')
map[i][j]=1;
if(ch=='C')
map[i][j]=2;
if(ch=='D')
map[i][j]=3;
if(ch=='E')
map[i][j]=4;
if(ch=='F')
map[i][j]=5;
if(ch=='G')
map[i][j]=6;
if(ch=='H')
map[i][j]=7;
if(ch=='I')
map[i][j]=8;
if(ch=='J')
map[i][j]=9;
if(ch=='K')
map[i][j]=10;
}
ans=0;
int flag;
int cas=0;
while (1)
{
flag=0;
for (int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
int nowx=ex+dir[i][0];
int nowy=ey+dir[i][1];
if (nowx<n&&nowy<m&&nowx>=0&&nowy>=0&&vis[nowx][nowy]==0)
{
if (nowy==ey)
{
if (ex<nowx&&channel[map[nowx][nowy]][1]==channel[map[ex][ey]][3])
{
vis[nowx][nowy]=1;
break;
}
if (nowx<ex&&channel[map[ex][ey]][1]==channel[map[nowx][nowy]][3])
{
vis[nowx][nowy]=1;
break;
}
}
if (nowx==ex)
{
if (ey<nowy&&channel[map[nowx][nowy]][2]==channel[map[ex][ey]][0])
{
vis[nowx][nowy]=1;
break;
}
if (ey>nowy&&channel[map[ex][ey]][2]==channel[map[nowx][nowy]][0])
{
vis[nowx][nowy]=1;
break;
}
}
}
}
for (int i=0;i<m;i++)
for (int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if (vis[i][j])
vis[i][j]++;
if (vis[i][j]==0)
{
sx=i;
sy=j;
flag=1;
}
}
if (flag==1)
{
ans++;
dfs(sx,sy);
}
if (flag==0)
break;
}
cout<<ans+1<<endl;
}
return 0;
}