HBase源代码调试(4)
protected class Connection extends Thread
今天学习了一下RPC架构
When new a HTable object, it will create a special ServerName
ServerName("HBCKServerName", -1, -1)
///** HBCK special code name used as server name when manipulating ZK nodes */
specify hard code Non-User Dir
[.logs, .oldlogs, .corrupt, .META., -ROOT-, splitlog, .hbck]
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
In HConnectionManager.java
function
HRegionInterface getHRegionConnection(final String hostname, final int port,
final InetSocketAddress isa, final boolean master)
server = (HRegionInterface) HBaseRPC.waitForProxy(
serverInterfaceClass, HRegionInterface.VERSION,
address, this.conf,
this.maxRPCAttempts, this.rpcTimeout, this.rpcTimeout);
In HBaseRPC.java
public static VersionedProtocol getProxy(
Class<? extends VersionedProtocol> protocol,
long clientVersion, InetSocketAddress addr, User ticket,
Configuration conf, SocketFactory factory, int rpcTimeout)
throws IOException {
VersionedProtocol proxy =
getProtocolEngine(protocol,conf)
.getProxy(protocol, clientVersion, addr, ticket, conf, factory, Math.min(rpcTimeout, HBaseRPC.getRpcTimeout()));
long serverVersion = proxy.getProtocolVersion(protocol.getName(),
clientVersion);
if (serverVersion == clientVersion) {
return proxy;
}
throw new VersionMismatch(protocol.getName(), clientVersion,
serverVersion);
}
getProtocolEngine will return a WritableRpcEngine object
In WritableRpcEngine.java
public VersionedProtocol getProxy(
Class<? extends VersionedProtocol> protocol, long clientVersion,
InetSocketAddress addr, User ticket,
Configuration conf, SocketFactory factory, int rpcTimeout)
throws IOException {
VersionedProtocol proxy =
(VersionedProtocol) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
protocol.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { protocol },
new Invoker(protocol, addr, ticket, conf, factory, rpcTimeout));
if (proxy instanceof VersionedProtocol) {
long serverVersion = ((VersionedProtocol)proxy)
.getProtocolVersion(protocol.getName(), clientVersion);
if (serverVersion != clientVersion) {
throw new HBaseRPC.VersionMismatch(protocol.getName(), clientVersion,
serverVersion);
}
}
return proxy;
}
private static class Invoker implements InvocationHandler {
private Class<? extends VersionedProtocol> protocol;
private InetSocketAddress address;
private User ticket;
private HBaseClient client;
private boolean isClosed = false;
final private int rpcTimeout;
public Invoker(Class<? extends VersionedProtocol> protocol,
InetSocketAddress address, User ticket,
Configuration conf, SocketFactory factory, int rpcTimeout) {
this.protocol = protocol;
this.address = address;
this.ticket = ticket;
this.client = CLIENTS.getClient(conf, factory);
this.rpcTimeout = rpcTimeout;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
final boolean logDebug = LOG.isDebugEnabled();
long startTime = 0;
if (logDebug) {
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
HbaseObjectWritable value = (HbaseObjectWritable)
client.call(new Invocation(method, protocol, args), address,
protocol, ticket, rpcTimeout);
if (logDebug) {
// FIGURE HOW TO TURN THIS OFF!
long callTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
LOG.debug("Call: " + method.getName() + " " + callTime);
}
return value.get();
}
/* close the IPC client that's responsible for this invoker's RPCs */
synchronized protected void close() {
if (!isClosed) {
isClosed = true;
CLIENTS.stopClient(client);
}
}
}
protocol is org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc.HRegionInterface
set in configuration file "hbase.regionserver.class" default value is "HConstants.DEFAULT_REGION_SERVER_CLASS"
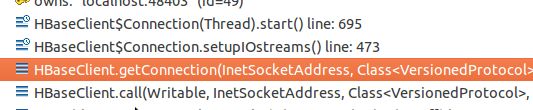
最后都会调用到Invoker.invoke, 然后到client.call ()
in HBaseClient.java
public Writable call(Writable param, InetSocketAddress addr,
Class<? extends VersionedProtocol> protocol,
User ticket, int rpcTimeout)
throws InterruptedException, IOException {
Call call = new Call(param);
Connection connection = getConnection(addr, protocol, ticket, rpcTimeout, call);
connection.sendParam(call);
protected class Call {
final int id; // call id
final Writable param; // parameter
Writable value; // value, null if error
IOException error; // exception, null if value
boolean done; // true when call is done
long startTime;
protected Call(Writable param) {
this.param = param;
this.startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
synchronized (HBaseClient.this) {
this.id = counter++;
}
}
//Call 又是一个内部类
所以当我们在
HConnectionManager.java里面调用如
regionInfoRow = server.getClosestRowBefore(
metaLocation.getRegionInfo().getRegionName(), metaKey,
HConstants.CATALOG_FAMILY);
我们并非在client端调用某个类的getClosestRowBefore, 而是把"getClosestRowBefore"这个方法的名字等信息
封装成一个Invocation object, 进而传递给Call 类的构造函数, connection.sendParam(call)发送一个请求.
在此之前
Connection connection=getConnection(addr, ...)会启动一个线程来接受服务器的response
Connection是一个HBaseClient的内部类
protected class Connection extends Thread
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
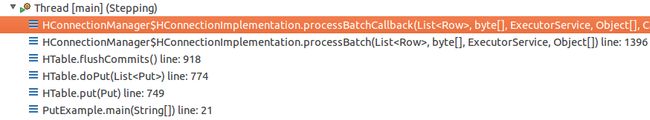
in processBatcchCallback function
public <R> void processBatchCallback(
List<? extends Row> list,
byte[] tableName,
ExecutorService pool,
Object[] results,
Batch.Callback<R> callback)
throws IOException, InterruptedException{
for (Entry<HRegionLocation, MultiAction<R>> e: actionsByServer.entrySet()) {
futures.put(e.getKey(), pool.submit(createCallable(e.getKey(), e.getValue(), tableName)));
}
// step 3: collect the failures and successes and prepare for retry
for (Entry<HRegionLocation, Future<MultiResponse>> responsePerServer
: futures.entrySet()) {
HRegionLocation loc = responsePerServer.getKey();
try {
Future<MultiResponse> future = responsePerServer.getValue();
MultiResponse resp = future.get();
let's look at createCallable function
private <R> Callable<MultiResponse> createCallable(final HRegionLocation loc,
final MultiAction<R> multi, final byte [] tableName) {
// TODO: This does not belong in here!!! St.Ack HConnections should
// not be dealing in Callables; Callables have HConnections, not other
// way around.
final HConnection connection = this;
return new Callable<MultiResponse>() {
public MultiResponse call() throws IOException {
ServerCallable<MultiResponse> callable =
new ServerCallable<MultiResponse>(connection, tableName, null) {
public MultiResponse call() throws IOException {
return server.multi(multi);
}
@Override
public void connect(boolean reload) throws IOException {
server = connection.getHRegionConnection(loc.getHostname(), loc.getPort());
}
};
return callable.withoutRetries();
}
};
}
When we call
MultiResponse resp = future.get();
it will call
callable.withoutRetries();
The definition for withoutRetries
public T withoutRetries()
throws IOException, RuntimeException {
try {
beforeCall();
connect(false);
return call();
} catch (Throwable t) {
Throwable t2 = translateException(t);
if (t2 instanceof IOException) {
throw (IOException)t2;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException(t2);
}
} finally {
afterCall();
}
}
then call its definition for connect(false) and call()
public MultiResponse call() throws IOException {
return server.multi(multi);
}
@Override
public void connect(boolean reload) throws IOException {
server = connection.getHRegionConnection(loc.getHostname(), loc.getPort());
}
--------------------------------------------------------------------
In WritableRpcEngine.java
Construct a HBaseClient object
protected synchronized HBaseClient getClient(Configuration conf,
SocketFactory factory) {
// Construct & cache client. The configuration is only used for timeout,
// and Clients have connection pools. So we can either (a) lose some
// connection pooling and leak sockets, or (b) use the same timeout for
// all configurations. Since the IPC is usually intended globally, not
// per-job, we choose (a).
HBaseClient client = clients.get(factory);
if (client == null) {
// Make an hbase client instead of hadoop Client.
client = new HBaseClient(HbaseObjectWritable.class, conf, factory);
clients.put(factory, client);
} else {
client.incCount();
}
return client;
}
HbaseObjectWritable will be the 'valueClass' of object
so In
protected void receiveResponse() { //in HBaseClient$Connection
Writable value = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(valueClass, conf); //the 'value' will be a new object of Class HbaseObjectWritable
also in Connection, there is a var 'calls', it contains all the request to the server, and the return value will also be writen to calls (identified by id)
// currently active calls
protected final ConcurrentSkipListMap<Integer, Call> calls = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<Integer, Call>();
public Writable call(Writable param, InetSocketAddress addr,
Class<? extends VersionedProtocol> protocol,
User ticket, int rpcTimeout)
throws InterruptedException, IOException {
Call call = new Call(param);
Connection connection = getConnection(addr, protocol, ticket, rpcTimeout, call);//Add request 'call' to 'calls' and start a thread to get response by function 'receiveResponse', the return value be written to new HbaseObjectWritable object, and assign to call
connection.sendParam(call); //sent request to server?
-------------------------------
HRegion
可以单独调试学习, 只要在debug configurations里面
main class 指定为HRegion
arguments 指定一个catalog table
The so called Catalog table is '.META.' & '-ROOT-'
when start up , read default block size through
public long getDefaultBlockSize() {
// default to 32MB: large enough to minimize the impact of seeks
return getConf().getLong("fs.local.block.size", 32 * 1024 * 1024);
}