zoj 1377 || poj 1228 Grandpa's Estate
给你凸包上的一些点,求是否可以确定一个凸包。
开始木有理解哇,><,以为只要这个点等于求得凸包的点就可以了,后来发现不对。如果一个凸包的边只有两个点,那么如果外界还有一个点,可能这个凸包就不确定了,相当于,两个钉子之间有个皮筋,但是外面还有个钉子的话,皮筋就可以拉到那个钉子上,而且满足题意。
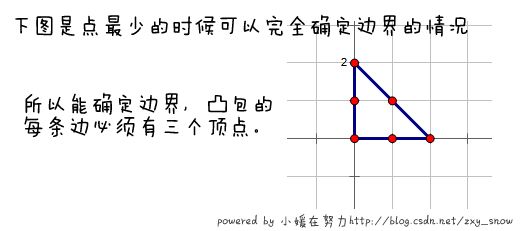
因此,需要满足凸包每条边必须有三个点,这样的话,如果外界还有点的话,拉的话,就不是凸多边形了,自己可以模拟下。
根据这个 ,看图
判断凸包上三点这个,我做的比较麻烦,分两种情况,如果在线段上(不在端点),可以,如果和这两点共线(不在端点),也可以。
后来想了下,既然题目已经给出的是凸包的点,那就不用graham算法了吧?改了改,不对。因为我需要按顺序去判断凸包的边,如果仅仅是排序,排不出来按顺时针或者逆时针的情况><。。。
测了下,数据弱了,不存在全部都共线的case。。。我还判断了呢。。。
#include <queue> #include <stack> #include <math.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <iostream> #include <limits.h> #include <string.h> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int MAX = 1010; const double eps = 1e-6; struct point{ double x,y;}; point p[MAX]; int stk[MAX]; int top; bool dy(double x,double y) { return x > y + eps;} // x > y bool xy(double x,double y) { return x < y - eps;} // x < y bool dyd(double x,double y) { return x > y - eps;} // x >= y bool xyd(double x,double y) { return x < y + eps;} // x <= y bool dd(double x,double y) { return fabs( x - y ) < eps;} // x == y double crossProduct(point a,point b,point c)//向量 ac 在 ab 的方向 { return (c.x - a.x)*(b.y - a.y) - (b.x - a.x)*(c.y - a.y); } double disp2p(point a,point b) { return sqrt( ( a.x - b.x ) * ( a.x - b.x ) + ( a.y - b.y ) * ( a.y - b.y ) ); } bool cmp(point a,point b) // 第一次排序 { if( dd(a.y ,b.y ) ) return xy(a.x, b.x); return xy(a.y,b.y); } bool cmp1(point a,point b) // 第二次排序 { double len = crossProduct(p[0],a,b); if( dd(len,0.0) ) return xy(disp2p(p[0],a),disp2p(p[0],b)); return xy(len,0.0); } bool is_polygon(point p[],int n) { if( n <= 2 ) return false; for(int i=2; i<n; i++) if( !dd(crossProduct(p[0],p[1],p[i]),0.0) ) return true; return false; } bool onSegment(point a, point b, point c) { double maxx = max(a.x,b.x); double maxy = max(a.y,b.y); double minx = min(a.x,b.x); double miny = min(a.y,b.y); if( dd(crossProduct(a,b,c),0.0) && dy(c.x,minx) && xy(c.x,maxx) && dy(c.y,miny) && xy(c.y,maxy) ) return true; return false; } bool Graham(point p[],int n) { sort(p,p+n,cmp); sort(p+1,p+n,cmp1); top = 0; stk[top++] = 0; stk[top++] = 1; stk[top++] = 2; top--; for(int i=3; i<n; i++) { while( top != 0 ) { point a,b; a = p[stk[top]]; b = p[stk[top-1]]; if( xyd( crossProduct(a,b,p[i]), 0.0 ) ) top--; else break; } stk[++top] = i; } top++; for(int i=0; i<top; i++) { bool flag = 0; for(int k=0; k<n; k++) if( k != stk[i] && k != stk[(i+1)%top] ) if( onSegment(p[stk[i]],p[stk[(i+1)%top]],p[k]) // 判断 在线段中间,或者和线段共线 || dd(crossProduct(p[stk[i]],p[stk[(i+1)%top]],p[k]),0.0) ) { flag = 1; break; } if( !flag ) return false; } return true; } int main() { int ncases; int n; scanf("%d",&ncases); while( ncases-- ) { scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=0; i<n; i++) scanf("%lf %lf",&p[i].x,&p[i].y); if( !is_polygon(p,n) || n <= 5 ) { printf("NO/n"); continue; } bool ans = Graham(p,n); if( ans ) printf("YES/n"); else printf("NO/n"); } return 0; }