hdu 4421 Bit Magic(2-sat,4级)
B - Bit Magic
Time Limit:2000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u
Description
Yesterday, my teacher taught me about bit operators: and (&), or (|), xor (^). I generated a number table a[N], and wrote a program to calculate the matrix table b[N][N] using three kinds of bit operator. I thought my achievement would get teacher's attention.
The key function is the code showed below.
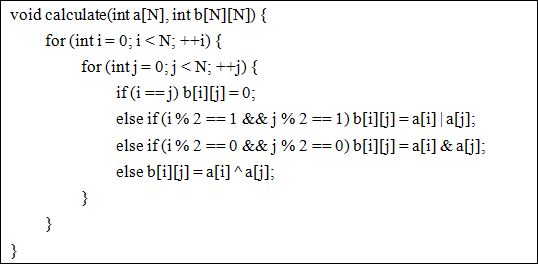
There is no doubt that my teacher raised lots of interests in my work and was surprised to my talented programming skills. After deeply thinking, he came up with another problem: if we have the matrix table b[N][N] at first, can you check whether corresponding number table a[N] exists?
The key function is the code showed below.
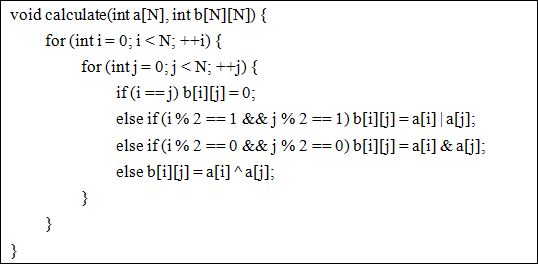
There is no doubt that my teacher raised lots of interests in my work and was surprised to my talented programming skills. After deeply thinking, he came up with another problem: if we have the matrix table b[N][N] at first, can you check whether corresponding number table a[N] exists?
Input
There are multiple test cases.
For each test case, the first line contains an integer N, indicating the size of the matrix. (1 <= N <= 500).
The next N lines, each line contains N integers, the jth integer in ith line indicating the element b[i][j] of matrix. (0 <= b[i][j] <= 2 31 - 1)
For each test case, the first line contains an integer N, indicating the size of the matrix. (1 <= N <= 500).
The next N lines, each line contains N integers, the jth integer in ith line indicating the element b[i][j] of matrix. (0 <= b[i][j] <= 2 31 - 1)
Output
For each test case, output "YES" if corresponding number table a[N] exists; otherwise output "NO".
Sample Input
2
0 4
4 0
3
0 1 24
1 0 86
24 86 0
Sample Output
YES
NO
思路:1:two-sat 确定每个数的每个比特位不是0就是1,所有位的每一位是独立可以分开算。
建立互斥关系就好了。
2:枚举每个比特位是0还是1,然后根据^的式子算出所有a的该比特位,验证一次就可以了。
two-sat
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#define FOR(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;++i)
#define clr(f,z) memset(f,z,sizeof(f))
#define ll(x) (1<<x)
using namespace std;
const int mm=502;
const int mp=mm*2;
const int me=mm*mm*4;
class Edge
{
public:int v,next;
};
class TWO_SAT
{
public:
int dfn[mp],e_to[mp],stack[mp];
Edge e[me];
int edge,head[mp],top,dfs_clock,bcc;
void clear()
{
edge=0;clr(head,-1);
}
void add(int u,int v)
{
e[edge].v=v;e[edge].next=head[u];head[u]=edge++;
}
void add_my(int x,int xval,int y,int yval)
{
x=x+x+xval;y=y+y+yval;
add(x,y);
}
void add_clause(int x,int xval,int y,int yval)
{///x or y
x=x+x+xval;
y=y+y+yval;
add(x^1,y);add(y^1,x);
}
void add_con(int x,int xval)
{
x=x+x+xval;
add(x^1,x);
}
int tarjan(int u)
{
int lowu,lowv;
lowu=dfn[u]=++dfs_clock;
int v; stack[top++]=u;
for(int i=head[u];~i;i=e[i].next)
{
v=e[i].v;
if(!dfn[v])
{
lowv=tarjan(v);
lowu=min(lowv,lowu);
}
else if(e_to[v]==-1)//in stack
lowu=min(lowu,dfn[v]);
}
if(dfn[u]==lowu)
{
++bcc;
do{
v=stack[--top];
e_to[v]=bcc;
}while(v!=u);
}
return lowu;
}
bool find_bcc(int n)
{ clr(e_to,-1);
clr(dfn,0);
bcc=dfs_clock=top=0;
FOR(i,0,2*n-1)
if(!dfn[i])
tarjan(i);
for(int i=0;i<2*n;i+=2)
if(e_to[i]==e_to[i^1])return 0;
return 1;
}
}two;
int n,m;
int g[mm][mm];
int main()
{ int a,b,c,d;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
bool ans=1;
FOR(i,0,n-1)FOR(j,0,n-1)
{
scanf("%d",&g[i][j]);
}
FOR(k,0,31)
{ two.clear();
FOR(i,0,n-1)FOR(j,0,n-1)
{
a=i;b=j;
if(i==j){if(g[i][j]!=0)ans=0;}
else if(i%2==1&&j%2==1)/// |
{
if(g[i][j]&ll(k))
two.add_clause(a,1,b,1);
else two.add_con(a,0),two.add_con(b,0);
}
else if(i%2==0&&j%2==0)/// &
{
if(g[i][j]&ll(k))
two.add_con(a,1),two.add_con(b,1);
else two.add_clause(a,0,b,0);
}
else ///^
{
if(g[i][j]&ll(k))
two.add_clause(a,1,b,1),two.add_clause(a,0,b,0);
else two.add_clause(a,1,b,0),two.add_clause(a,0,b,1);
}
}
if(!two.find_bcc(n))ans=0;
if(ans==0)break;
}
if(ans)printf("YES\n");
else printf("NO\n");
}
}
枚举验证
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 510;
int matrix[maxn][maxn],a[maxn];
bool judge(int bit,int n,int val)
{
a[0] = val;
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
int j;
if (i&1) j = 0;
else j = 1;
for(;j<n;j+=2)
{
if ((matrix[i][j]&(1LL<<bit)))
a[j] = a[i] ^ 1;
else a[j] = a[i];
}
}
//cout << a[0] << " " << a[1] << endl;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if (i == j) continue;
int b = (matrix[i][j]&(1LL<<bit)) > 0;
if (i%2==0&&j%2==0)
{
if ((a[i]&a[j]) != b) return false;
}
else if (i%2==1&&j%2==1)
{
if ((a[i]|a[j]) != b) return false;
}
else
{
if ((a[i]^a[j]) != b) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) == 1)
{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
scanf("%d",&matrix[i][j]);
bool ok = 1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
if (matrix[i][i] != 0)
{
ok = 0;
break;
}
if(!ok) {
puts("NO");
continue;
}
//cout << "bug" << endl;
for(int bit=0;bit<31;bit++)
{
bool flag1 = 1,flag2 = 1;
flag1 = judge(bit,n,0);
flag2 = judge(bit,n,1);
if (!flag1 && !flag2) {
ok = 0;
break;
}
}
puts(ok?"YES":"NO");
}
return 0;
}
/*
7
1 1 2 3 4 4 5
3
1 7
2 10
3 12
0
*/