UVA 10173 Smallest Bounding Rectangle(旋转卡壳求最小面积外接矩形)
神呐。。。终于过了 T T 。。。
一个卡壳卡两天啊啊啊啊 !!!至少两天啊啊啊啊 !!!T T 。。。
这两天都是,不想复习了,就在纸上画画卡壳。。。画画凸包。。。然后想这个题怎么实现比较好。。。
我开始还是枚举旋转最小角度,代码十分之繁琐。。。其实我写差不多了,但是应该是有问题的,如果凸包是三角形,怎么都枚举不对T T 。。
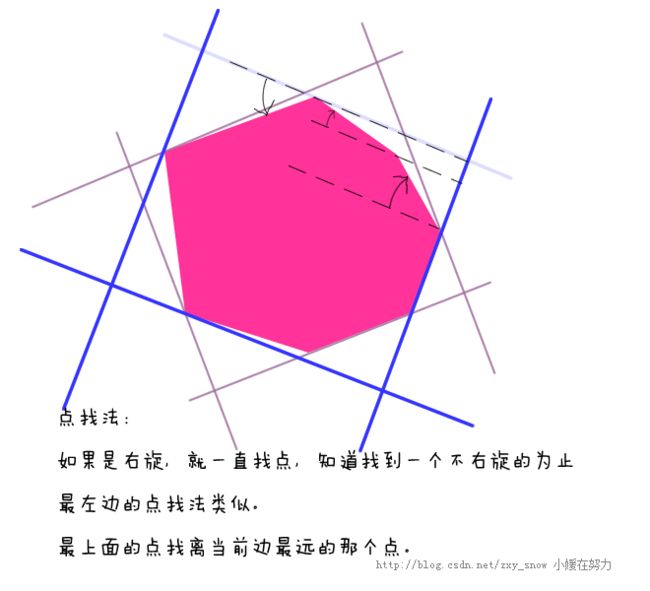
丫丫的,索性今天下午想了想,改成每次枚举每条边重合,然后找另外三个点。其实这三个点也很好找,最初找的x最大 x最小 y最大 y最小,只需要这些点旋转下即可,可以自己画下图。算了,我画下吧。
rank28 哇咔咔。。
#include <queue> #include <stack> #include <math.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <iostream> #include <limits.h> #include <string.h> #include <string> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int MAX = 1005; const double inf = 1e20*1.0; struct point{ double x,y;}; point c[MAX]; const double eps = 1e-6; bool dy(double x,double y) { return x > y + eps;} // x > y bool xy(double x,double y) { return x < y - eps;} // x < y bool dyd(double x,double y) { return x > y - eps;} // x >= y bool xyd(double x,double y) { return x < y + eps;} // x <= y bool dd(double x,double y) { return fabs( x - y ) < eps;} // x == y double crossProduct(point a,point b,point c)//向量 ac 在 ab 的方向 { return (c.x - a.x)*(b.y - a.y) - (b.x - a.x)*(c.y - a.y); } double disp2p(point a,point b) { return sqrt((a.x - b.x)*(a.x - b.x) + (a.y - b.y)*(a.y - b.y)); } bool cmp(point a,point b) // 排序 { double len = crossProduct(c[0],a,b); if( dd(len,0.0) ) return xy(disp2p(c[0],a),disp2p(c[0],b)); return xy(len,0.0); } double disp2seg(point a,point l1,point l2) { return fabs(crossProduct(a,l1,l2))/disp2p(l1,l2); } point foot_line(point a,point l1,point l2) // 求一个点,使得ab垂直于l1l2 { point c; l2.x -= l1.x; l2.y -= l1.y; c.x = a.x - l1.x - l2.y + l1.x; c.y = a.y - l1.y + l2.x + l1.y; return c; } double rota_angle(point a1,point a2,point b1,point b2) //判断向量a1a2与b1b2的位置 { //返回b1b2在a1a2的方向 point t; t.x = b2.x - (b1.x - a1.x); t.y = b2.y - (b1.y - a1.y); return crossProduct(a1,a2,t); } double RC_minareaRectangle(point p[],int n) { int r[4]; // 0 == ymin, 1 == xmin, 2 == ymax ,3 == xmax; memset(r,0,sizeof(r)); for(int i=0; i<n; i++) { if( xy(p[i].y,p[r[0]].y) ) r[0] = i; if( xy(p[i].x,p[r[1]].x) ) r[1] = i; if( dy(p[i].y,p[r[2]].y) ) r[2] = i; if( dy(p[i].x,p[r[3]].x) ) r[3] = i; } int tp = r[0]; double area = inf; do { point t = foot_line(p[r[0]],p[r[0]],p[(r[0]+1)%n]); while( dy(rota_angle(t,p[r[0]],p[r[1]],p[(r[1]+1)%n]),0.0) ) r[1]++, r[1] %= n; while( dy(rota_angle(p[r[0]],t,p[r[3]],p[(r[3]+1)%n]),0.0) ) r[3]++, r[3] %= n; while( dy(disp2seg(p[(r[2]+1)%n],p[r[0]],p[(r[0]+1)%n]), disp2seg(p[r[2]],p[r[0]],p[(r[0]+1)%n])) ) r[2]++, r[2] %= n; double a = disp2seg(p[r[2]],p[r[0]],p[(r[0]+1)%n]); t = foot_line(p[r[3]],p[r[0]],p[(r[0]+1)%n]); double b = disp2seg(p[r[1]],p[r[3]],t); area = min( area, a*b ); r[0]++; r[0] %= n; }while( r[0] != tp ); return area; } point stk[MAX]; int top; double Graham(int n) { int tmp = 0; for(int i=1; i<n; i++) if( xy(c[i].x,c[tmp].x) || dd(c[i].x,c[tmp].x) && xy(c[i].y,c[tmp].y) ) tmp = i; swap(c[0],c[tmp]); sort(c+1,c+n,cmp); stk[0] = c[0]; stk[1] = c[1]; top = 1; for(int i=2; i<n; i++) { while( xyd( crossProduct(stk[top],stk[top-1],c[i]), 0.0 ) && top >= 1 ) top--; stk[++top] = c[i]; } return RC_minareaRectangle(stk,top+1); } int main() { int n; while( ~scanf("%d",&n) && n ) { for(int i=0; i<n; i++) scanf("%lf%lf",&c[i].x,&c[i].y); if( n <= 2 ) { printf("0.0000/n"); continue; } double ans = Graham(n); printf("%.4lf/n",ans); } return 0; }