POJ 3084 Panic Room //最小割
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 909 | Accepted: 427 |
Description
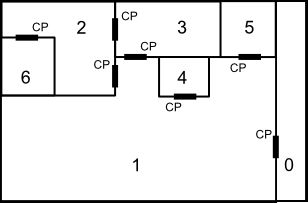
with rooms numbered 0-6 and control panels marked with the letters "CP" (each next to the door it can unlock and in the room that it is accessible from), then one could say that the minimum number of locks to perform to secure room 2 from room 1 is two; one has to lock the door between room 2 and room 1 and the door between room 3 and room 1. Note that it is impossible to secure room 2 from room 3, since one would always be able to use the control panel in room 3 that unlocks the door between room 3 and room 2.
Input
- Start line – a single line "m n" (1 <=m<= 20; 0 <=n<= 19) where m indicates the number of rooms in the house and n indicates the room to secure (the panic room).
- Room list – a series of m lines. Each line lists, for a single room, whether there is an intruder in that room ("I" for intruder, "NI" for no intruder), a count of doors c (0 <= c <= 20) that lead to other rooms and have a control panel in this room, and a list of rooms that those doors lead to. For example, if room 3 had no intruder, and doors to rooms 1 and 2, and each of those doors' control panels were accessible from room 3 (as is the case in the above layout), the line for room 3 would read "NI 2 1 2". The first line in the list represents room 0. The second line represents room 1, and so on until the last line, which represents room m - 1. On each line, the rooms are always listed in ascending order. It is possible for rooms to be connected by multiple doors and for there to be more than one intruder!
Output
Sample Input
3 7 2 NI 0 I 3 0 4 5 NI 2 1 6 NI 2 1 2 NI 0 NI 0 NI 0 7 2 I 0 NI 3 0 4 5 NI 2 1 6 I 2 1 2 NI 0 NI 0 NI 0 4 3 I 0 NI 1 2 NI 1 0 NI 4 1 1 2 2
Sample Output
2 PANIC ROOM BREACH 1
Source
这个题真是晦涩啊
读懂了,应该可以明白是最小割的题目
构图我觉得很巧妙吧
首先当然是对于有侵略者的房间的处理,把侵略者看成流,所以要建立一个超级源点,让超级源点与有侵略者的房间相连
那么这个边长应该是多少呢?
由于只要是有门开着,侵略者都可以走,而不会受门的数量限制,所以源点与房间的边长为正无穷
接着将那个要保护的房间作为汇点
巧妙的构造就是那个有门连接的两个房间的处理上
1号房间用门连向2号房间,门可以在1号房间打开
那么就构造从1号房间连向2号房间的边,边长为正无穷,再构造从2号房间连向一号房间的边,边长为1
为什么这么构造,就是因为最小割
因为如果是一号房间到2号房间,要是一号房间有侵略者,那么无论你怎么关这个门,是阻止不了侵略者进入的
所以这条边从一号房间到2号房间是最小割不能割到的
但是这个门,如果侵略者在2号房间的话,关上这个门就可以了,付出的代价为1.
接着又怎么证明这个最小割就对应着所有能走的门都被关上了呢
可以使用反证法,如果还存在边长为1的边,并且通过这个门能到达T,那么就还存在增广路。。。。。。。。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
const int N=50;
const int M=20001;
const int inf=0x7ffffff;
int head[N];
struct Edge
{
int v,next,w;
} edge[M];
int cnt,n,s,t;
void addedge(int u,int v,int w)
{
edge[cnt].v=v;
edge[cnt].w=w;
edge[cnt].next=head[u];
head[u]=cnt++;
edge[cnt].v=u;
edge[cnt].w=0;
edge[cnt].next=head[v];
head[v]=cnt++;
}
int sap()
{
int pre[N],cur[N],dis[N],gap[N];
int flow=0,aug=inf,u;
bool flag;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
cur[i]=head[i];
gap[i]=dis[i]=0;
}
gap[s]=n;
u=pre[s]=s;
while(dis[s]<n)
{
flag=0;
for(int &j=cur[u]; j!=-1; j=edge[j].next)
{
int v=edge[j].v;
if(edge[j].w>0&&dis[u]==dis[v]+1)
{
flag=1;
if(edge[j].w<aug) aug=edge[j].w;
pre[v]=u;
u=v;
if(u==t)
{
flow+=aug;
while(u!=s)
{
u=pre[u];
edge[cur[u]].w-=aug;
edge[cur[u]^1].w+=aug;
}
aug=inf;
}
break;
}
}
if(flag) continue;
int mindis=n;
for(int j=head[u]; j!=-1; j=edge[j].next)
{
int v=edge[j].v;
if(edge[j].w>0&&dis[v]<mindis)
{
mindis=dis[v];
cur[u]=j;
}
}
if((--gap[dis[u]])==0)
break;
gap[dis[u]=mindis+1]++;
u=pre[u];
}
return flow;
}
int main()
{
int T,m;
char str[10];
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
s=0;
t=m+1;
cnt=0;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int k;
scanf("%s",str);
if(str[0]=='I') addedge(s,i,inf);
scanf("%d",&k);
for(int j=1;j<=k;j++)
{
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
x++;
addedge(i,x,inf);
addedge(x,i,1);
}
}
n=n+1;
int t=sap();
if(t>=inf) printf("PANIC ROOM BREACH/n");
else printf("%d/n",t);
}
return 0;
}