android开发之布局优化之include、ViewStub、merge使用与源码分析
在开发中UI布局是我们都会遇到的问题,随着UI越来越多,布局的重复性、复杂度也会随之增长。Android官方给了几个优化的方法,但是网络上的资料基本上都是对官方资料的翻译,这些资料都特别的简单,经常会出现问题而不知其所以然。这篇文章就是对这些问题的更详细的说明,也欢迎大家多留言交流。
一、include
1.概述:
首先用得最多的应该是include,按照官方的意思,include就是为了解决重复定义相同布局的问题。例如你有五个界面,这五个界面的顶部都有布局一模一样的一个返回按钮和一个文本控件,在不使用include的情况下你在每个界面都需要重新在xml里面写同样的返回按钮和文本控件的顶部栏,这样的重复工作会相当的恶心。使用include标签,我们只需要把这个会被多次使用的顶部栏独立成一个xml文件,然后在需要使用的地方通过include标签引入即可。其实就相当于C语言、C++中的include头文件一样,我们把一些常用的、底层的API封装起来,然后复用,需要的时候引入它即可,而不必每次都自己写一遍。
2.示例如下 :
my_title_layout.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:id="@+id/my_title_parent_id" android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<ImageButton android:id="@+id/back_btn" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher" />
<TextView android:id="@+id/title_tv" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:layout_marginLeft="20dp" android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/back_btn" android:gravity="center" android:text="我的title" android:textSize="18sp" />
</RelativeLayout>include布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" >
<include android:id="@+id/my_title_ly" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" layout="@layout/my_title_layout" />
<!-- 代码省略 -->
</LinearLayout>这样我们就可以使用my_title_layout了。
3.注意事项:
- 使用include最常见的问题就是findViewById查找不到目标控件,其正确的使用形式如下:
View titleView = findViewById(R.id.my_title_ly) ;
TextView titleTextView = (TextView)titleView.findViewById(R.id.title_tv) ;
titleTextView.setText("new Title");首先找到include的id, 例如这里include设置的id为“my_title_ly”,然后再对获取到的titleView.findViewById来查找目标布局中的子控件,例如title_tv就是my_title_layout.xml中定义的子控件。因此我们如果需要查找控件的话,可以设置include标签的id,通过这个id获取include对应的view以后,再通过对这个view进行findViewById才能正确查找。如果你设置了include标签的id,然后通过被include的布局的root view的id来查找子元素的话,则会报错,如下 :(其实,如果include中没有设置Id, 而被include的布局的根元素设置了id,那么通过该根元素的id来查找该view即可,也就是说以下的方式也没有错!)
View titleView = findViewById(R.id.my_title_parent_id) ;
TextView titleTextView = (TextView)titleView.findViewById(R.id.title_tv) ;
titleTextView.setText("new Title");这样会报空指针异常,因为titleView没有找到,会报空指针。那么这是怎么回事呢? 我们来分析它的源码看看吧。对于布局文件的解析,最终都会调用到LayoutInflater的inflate方法,该方法最终又会调用rInflate方法,我们看看这个方法。
05-24 19:42:53.333: E/AndroidRuntime(3744): Caused by: java.lang.NullPointerException
05-24 19:42:53.333: E/AndroidRuntime(3744): at com.zanelove.toastdemo.MainActivity.onCreate(MainActivity.java:40)4.源码分析:
/** * Recursive method used to descend down the xml hierarchy and instantiate * views, instantiate their children, and then call onFinishInflate(). */
void rInflate(XmlPullParser parser, View parent, final AttributeSet attrs,
boolean finishInflate) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
final int depth = parser.getDepth();
int type;
// 迭代xml中的所有元素,挨个解析
while (((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_TAG ||
parser.getDepth() > depth) && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
continue;
}
final String name = parser.getName();
if (TAG_REQUEST_FOCUS.equals(name)) {
parseRequestFocus(parser, parent);
} else if (TAG_INCLUDE.equals(name)) {// 如果xml中的节点是include节点,则调用parseInclude方法
if (parser.getDepth() == 0) {
throw new InflateException("<include /> cannot be the root element");
}
parseInclude(parser, parent, attrs);
} else if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
throw new InflateException("<merge /> must be the root element");
} else if (TAG_1995.equals(name)) {
final View view = new BlinkLayout(mContext, attrs);
final ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) parent;
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
rInflate(parser, view, attrs, true);
viewGroup.addView(view, params);
} else {
final View view = createViewFromTag(parent, name, attrs);
final ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) parent;
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
rInflate(parser, view, attrs, true);
viewGroup.addView(view, params);
}
}
if (finishInflate) parent.onFinishInflate();
}这个方法其实就是遍历xml中的所有元素,然后挨个进行解析。例如解析到一个标签,那么就根据用户设置的一些layout_width、layout_height、id等属性来构造一个TextView对象,然后添加到父控件(ViewGroup类型)中。标签也是一样的,我们看到遇到include标签时,会调用parseInclude函数,这就是对标签的解析,我们看看吧。
private void parseInclude(XmlPullParser parser, View parent, AttributeSet attrs)
throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
int type;
if (parent instanceof ViewGroup) {
final int layout = attrs.getAttributeResourceValue(null, "layout", 0);
if (layout == 0) {// include标签中没有设置layout属性,会抛出异常
final String value = attrs.getAttributeValue(null, "layout");
if (value == null) {
throw new InflateException("You must specifiy a layout in the"
+ " include tag: <include layout=\"@layout/layoutID\" />");
} else {
throw new InflateException("You must specifiy a valid layout "
+ "reference. The layout ID " + value + " is not valid.");
}
} else {
final XmlResourceParser childParser =
getContext().getResources().getLayout(layout);
try {// 获取属性集,即在include标签中设置的属性
final AttributeSet childAttrs = Xml.asAttributeSet(childParser);
while ((type = childParser.next()) != XmlPullParser.START_TAG &&
type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
// Empty.
}
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
throw new InflateException(childParser.getPositionDescription() +
": No start tag found!");
}
// 1、解析include中的第一个元素
final String childName = childParser.getName();
// 如果第一个元素是merge标签,那么调用rInflate函数解析
if (TAG_MERGE.equals(childName)) {
// Inflate all children.
rInflate(childParser, parent, childAttrs, false);
} else {// 2、我们例子中的情况会走到这一步,首先根据include的属性集创建被include进来的xml布局的根view
// 这里的根view对应为my_title_layout.xml中的RelativeLayout
final View view = createViewFromTag(parent, childName, childAttrs);
final ViewGroup group = (ViewGroup) parent;// include标签的parent view
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = null;
try {// 获3、取布局属性
params = group.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
params = group.generateLayoutParams(childAttrs);
} finally {
if (params != null) {// 被inlcude进来的根view设置布局参数
view.setLayoutParams(params);
}
}
// 4、Inflate all children. 解析所有子控件
rInflate(childParser, view, childAttrs, true);
// Attempt to override the included layout's android:id with the
// one set on the <include /> tag itself.
TypedArray a = mContext.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,
com.android.internal.R.styleable.View, 0, 0);
int id = a.getResourceId(com.android.internal.R.styleable.View_id, View.NO_ID);
// While we're at it, let's try to override android:visibility.
int visibility = a.getInt(com.android.internal.R.styleable.View_visibility, -1);
a.recycle();
/** * 5、将include中设置的id设置给根view,因此实际上my_title_layout.xml中的 * RelativeLayout的id会变成include标签中的id,include不设置id, * 那么也可以通过relative的找到. * / if (id != View.NO_ID) { view.setId(id); } switch (visibility) { case 0: view.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); break; case 1: view.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); break; case 2: view.setVisibility(View.GONE); break; } // 6、将根view添加到父控件中 group.addView(view); } } finally { childParser.close(); } } } else { throw new InflateException("<include /> can only be used inside of a ViewGroup"); } final int currentDepth = parser.getDepth(); while (((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_TAG || parser.getDepth() > currentDepth) && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) { // Empty } }整个过程就是根据不同的标签解析不同的元素,首先会解析include元素,然后再解析被include进来的布局的root view元素。在我们的例子中对应的root view就是id为my_title_parent_id的RelativeLayout,然后再解析root view下面的所有元素,这个过程是从上面注释的2~4的过程,然后是设置布局参数。我们注意看注释5处,这里就解释了为什么include标签和被引入的布局的根元素都设置了id的情况下,通过被引入的根元素的id来查找子控件会找不到的情况。我们看到,注释5处的会判断include标签的id如果不是View.NO_ID的话会把该id设置给被引入的布局根元素的id,即此时在我们的例子中被引入的id为my_title_parent_id的根元素RelativeLayout的id被设置成了include标签中的id,即RelativeLayout的id被动态修改成了”my_title_ly”。因此此时我们再通过“my_title_parent_id”这个id来查找根元素就会找不到了!
5.结论:
如果include中设置了id,那么就通过include的id来查找被include布局根元素的View;如果include中没有设置Id, 而被include的布局的根元素设置了id,那么通过该根元素的id来查找该view即可。拿到根元素后查找其子控件都是一样的。
二、ViewStub
我们先看看官方的说明:
ViewStub is a lightweight view with no dimension and doesn’t draw anything or participate in the layout. As such, it’s cheap to inflate and cheap to leave in a view hierarchy. Each ViewStub simply needs to include the android:layout attribute to specify the layout to inflate.
1.概述:
其实ViewStub就是一个宽高都为0的一个View,它默认是不可见的,只有通过调用setVisibility函数或者Inflate函数才会将其要装载的目标布局给加载出来,从而达到延迟加载的效果,这个要被加载的布局通过android:layout属性来设置。例如我们通过一个ViewStub来惰性加载一个消息流的评论列表,因为一个帖子可能并没有评论,此时我可以不加载这个评论的ListView,只有当有评论时我才把它加载出来,这样就去除了加载ListView带来的资源消耗以及延时。
2.示例如下 :
<ViewStub android:id="@+id/stub_import" android:inflatedId="@+id/stub_comm_lv" android:layout="@layout/my_comment_layout" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="bottom" />my_comment_layout.xml如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<ListView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:id="@+id/my_comm_lv" android:layout_height="match_parent" >
</ListView> 在运行时,我们只需要控制id为stub_import的ViewStub的可见性或者调用inflate()函数来控制是否加载这个评论列表即可。示例如下 :
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
public void onCreate(Bundle b){
// main.xml中包含上面的ViewStub
setContentView(R.layout.main);
// 方式1,获取ViewStub,
ViewStub listStub = (ViewStub) findViewById(R.id.stub_import);
// 加载评论列表布局
listStub.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
// 获取到评论ListView,注意这里是通过ViewStub的inflatedId来获取
ListView commLv = findViewById(R.id.stub_comm_lv);
if ( listStub.getVisibility() == View.VISIBLE ) {
// 已经加载, 否则还没有加载
}
}
}通过setVisibility(View.VISIBILITY)来加载评论列表,此时你要获取到评论ListView对象的话,则需要通过findViewById来查找,而这个id并不是就是ViewStub的id,这是为什么呢 ?
3.源码分析:
@SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"})
public ViewStub(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.ViewStub,
defStyle, 0);
// 获取inflatedId属性
mInflatedId = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.ViewStub_inflatedId, NO_ID);
mLayoutResource = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.ViewStub_layout, 0);
a.recycle();
a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.View, defStyle, 0);
mID = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.View_id, NO_ID);
a.recycle();
initialize(context);
}
private void initialize(Context context) {
mContext = context;
setVisibility(GONE);// 设置不可教案
setWillNotDraw(true);// 设置不绘制
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(0, 0);// 宽高都为0
}
@Override
public void setVisibility(int visibility) {
if (mInflatedViewRef != null) {// 如果已经加载过则只设置Visibility属性
View view = mInflatedViewRef.get();
if (view != null) {
view.setVisibility(visibility);
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("setVisibility called on un-referenced view");
}
} else {// 如果未加载,这加载目标布局
super.setVisibility(visibility);
if (visibility == VISIBLE || visibility == INVISIBLE) {
inflate();// 调用inflate来加载目标布局
}
}
}
/** * Inflates the layout resource identified by {@link #getLayoutResource()} * and replaces this StubbedView in its parent by the inflated layout resource. * * @return The inflated layout resource. * */
public View inflate() {
final ViewParent viewParent = getParent();
if (viewParent != null && viewParent instanceof ViewGroup) {
if (mLayoutResource != 0) {
final ViewGroup parent = (ViewGroup) viewParent;// 获取ViewStub的parent view,也是目标布局根元素的parent view
final LayoutInflater factory = LayoutInflater.from(mContext);
final View view = factory.inflate(mLayoutResource, parent,
false);// 1、加载目标布局
// 2、如果ViewStub的inflatedId不是NO_ID则把inflatedId设置为目标布局根元素的id,即评论ListView的id
if (mInflatedId != NO_ID) {
view.setId(mInflatedId);
}
final int index = parent.indexOfChild(this);
parent.removeViewInLayout(this);// 3、将ViewStub自身从parent中移除
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = getLayoutParams();
if (layoutParams != null) {
parent.addView(view, index, layoutParams);// 4、将目标布局的根元素添加到parent中,有参数
} else {
parent.addView(view, index);// 4、将目标布局的根元素添加到parent中
}
mInflatedViewRef = new WeakReference<View>(view);
if (mInflateListener != null) {
mInflateListener.onInflate(this, view);
}
return view;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("ViewStub must have a valid layoutResource");
}
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("ViewStub must have a non-null ViewGroup viewParent");
}
}可以看到,其实最终加载目标布局的还是inflate()函数,在该函数中将加载目标布局,获取到根元素后,如果mInflatedId不为NO_ID则把mInflatedId设置为根元素的id,这也是为什么我们在获取评论ListView时会使用findViewById(R.id.stub_comm_lv)来获取,其中的stub_comm_lv就是ViewStub的inflatedId。当然如果你没有设置inflatedId的话还是可以通过评论列表的id来获取的,例如findViewById(R.id.my_comm_lv)。然后就是ViewStub从parent中移除、把目标布局的根元素添加到parent中。最后会把目标布局的根元素返回,因此我们在调用inflate()函数时可以直接获得根元素,省掉了findViewById的过程。
还有一种方式加载目标布局的就是直接调用ViewStub的inflate()方法,示例如下 :
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
// 把commLv2设置为类的成员变量
ListView commLv2 = null;
public void onCreate(Bundle b){
// main.xml中包含上面的ViewStub
setContentView(R.layout.main);
// 方式二
ViewStub listStub2 = (ViewStub) findViewById(R.id.stub_import) ;
// 成员变量commLv2为空则代表未加载
if ( commLv2 == null ) {
// 加载评论列表布局, 并且获取评论ListView,inflate函数直接返回ListView对象
commLv2 = (ListView)listStub2.inflate();
} else {
// ViewStub已经加载
}
}
} 4.注意事项:
- 判断是否已经加载过, 如果通过setVisibility来加载,那么通过判断可见性即可;如果通过inflate()来加载是不可以通过判断可见性来处理的,而需要使用方式2来进行判断。
- findViewById的问题,注意ViewStub中是否设置了inflatedId,如果设置了则需要通过inflatedId来查找目标布局的根元素。
三、Merge
1.概述:
首先我们看官方的说明:
The tag helps eliminate redundant view groups in your view hierarchy when including one layout within another. For example, if your main layout is a vertical LinearLayout in which two consecutive views can be re-used in multiple layouts, then the re-usable layout in which you place the two views requires its own root view. However, using another LinearLayout as the root for the re-usable layout would result in a vertical LinearLayout inside a vertical LinearLayout. The nested LinearLayout serves no real purpose other than to slow down your UI performance.
其实就是减少在include布局文件时的层级。标签是这几个标签中最让我费解的,大家可能想不到,标签竟然会是一个Activity,里面有一个LinearLayout对象。
/** * Exercise <merge /> tag in XML files. */
public class Merge extends Activity {
private LinearLayout mLayout;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle icicle) {
super.onCreate(icicle);
mLayout = new LinearLayout(this);
mLayout.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);
LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.merge_tag, mLayout);
setContentView(mLayout);
}
public ViewGroup getLayout() {
return mLayout;
}
} 使用merge来组织子元素可以减少布局的层级。例如我们在复用一个含有多个子控件的布局时,肯定需要一个ViewGroup来管理。
2.使用include引用资源文件时一般资源文件与使用merge进行包裹的资源文件的层级结构区别:
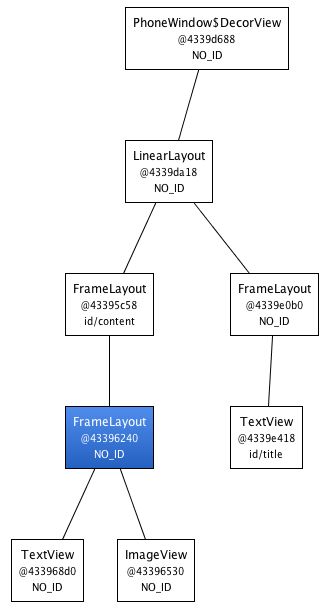
- 将该布局通过include引入时就会多引入了一个FrameLayout层级。此时结构如下 :
示例如下 :
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<ImageView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:scaleType="center" android:src="@drawable/golden_gate" />
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginBottom="20dip" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal|bottom" android:padding="12dip" android:background="#AA000000" android:textColor="#ffffffff" android:text="Golden Gate" />
</FrameLayout>- 使用merge标签就会消除上图中蓝色的FrameLayout层级。此时结构如下 :
示例如下 :
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<ImageView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:scaleType="center" android:src="@drawable/golden_gate" />
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginBottom="20dip" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal|bottom" android:padding="12dip" android:background="#AA000000" android:textColor="#ffffffff" android:text="Golden Gate" />
</merge>那么它是如何实现的呢,我们还是看源码吧。相关的源码也是在LayoutInflater的inflate()函数中。
3.源码分析:
public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
synchronized (mConstructorArgs) {
final AttributeSet attrs = Xml.asAttributeSet(parser);
Context lastContext = (Context)mConstructorArgs[0];
mConstructorArgs[0] = mContext;
View result = root;
try {
// Look for the root node.
int type;
while ((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.START_TAG &&
type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
// Empty
}
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
throw new InflateException(parser.getPositionDescription()
+ ": No start tag found!");
}
final String name = parser.getName();
// m如果是erge标签,那么调用rInflate进行解析
if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
throw new InflateException("<merge /> can be used only with a valid "
+ "ViewGroup root and attachToRoot=true");
}
// 解析merge标签
rInflate(parser, root, attrs, false);
} else {
// 代码省略
}
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
// 代码省略
}
return result;
}
}
void rInflate(XmlPullParser parser, View parent, final AttributeSet attrs,
boolean finishInflate) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
final int depth = parser.getDepth();
int type;
while (((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_TAG ||
parser.getDepth() > depth) && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
continue;
}
final String name = parser.getName();
if (TAG_REQUEST_FOCUS.equals(name)) {
parseRequestFocus(parser, parent);
} else if (TAG_INCLUDE.equals(name)) {
// 代码省略
parseInclude(parser, parent, attrs);
} else if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
throw new InflateException("<merge /> must be the root element");
} else if (TAG_1995.equals(name)) {
final View view = new BlinkLayout(mContext, attrs);
final ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) parent;
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
rInflate(parser, view, attrs, true);
viewGroup.addView(view, params);
} else { // 我们的例子会进入这里
final View view = createViewFromTag(parent, name, attrs);
// 获取merge标签的parent
final ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) parent;
// 获取布局参数
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
// 递归解析每个子元素
rInflate(parser, view, attrs, true);
// 将子元素直接添加到merge标签的parent view中
viewGroup.addView(view, params);
}
}
if (finishInflate) parent.onFinishInflate();
}其实就是如果是merge标签,那么直接将其中的子元素添加到merge标签parent中,这样就保证了不会引入额外的层级。