iOS开发之表视图爱上CoreData
在接触到CoreData时,感觉就是苹果封装的一个ORM。CoreData负责在Model的实体和sqllite建立关联,数据模型的实体类就相当于Java中的JavaBean, 而CoreData的功能和JavaEE中的Hibernate的功能类似,最基本是两者都有通过对实体的操作来实现对数据库的CURD操作。CoreData中的上下文(managedObjectContext)就相当于Hibernate中的session对象, CoreData中的save操作就和Hibernate中的commit,还有一些相似之处,在这就不一一列举了。(上面是笔者自己为了更好的理解CoreData而做的简单类比,如果学过PHP的ThinkPHP框架的小伙伴们也可以和TP中的ORM类比)。
那么TableView为什么会爱上CoreData呢?下面会通个代码给出他们相爱的原因。就举一个IOS开发中的经典的demo:通讯录来说明问题。
1.在TableView没遇到CoreData的时候我们怎么通过动态表视图来显示我们的通讯录的内容呢?也就是说我们通讯录的数据结构该如何组织呢?
为了在TableView中显示我们的信息我们这样设计我们的数据结构:
1.整个TableView是一个可变的数组tableArray;
2.tableArray中的每个元素又是一个存放分组的字典sectionDictionary;
3.在sectionDictionary中我们存放着两个键值对 header和items, header中存放的时section中的名字,items中存放的时每个section中的用户信息
4.items中又是一个数组rowsArray, rowsArray中存放的又是一个字典userInfoDictionary, 在userInfoDictionary中存放着我们要显示的信息
千字不如一图,看到上面对我们要设计的数据结构的描述会有点迷糊,下面来张图吧:
2.数据结构我们设计好了,那么如何用代码生成我们的测试数据(数据的组织形式如上图所示),下面的代码就是生成我们要在tableView中显示的数据,生成的数组存储在tableArray中,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
/*
*手动创建我们在动态表视图上显示的数据格式
*整个数据存储在一个数组中
*数组中每一个元素是一个自动,字典的key是sectionHeader的值,value是该section中以数组形式存的数据
*section中的每一行对应着一个数组元素,数组元素中又存储着一个字典,字典中存储着用户的具体数据。
*/
//为我们的数组分配存储空间, 代表着有20个section
self.telBook = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:26];
//为我们的section设置不同的header
char
header =
'A'
;
//计数
static
int
number = 0;
for
(
int
i = 0; i < 26; i ++) {
//新建字典来存储我们每个section中的数据, 假设每个section中有1个数组
NSMutableDictionary *sectionDic = [NSMutableDictionary dictionaryWithCapacity:1];
//创建字典中的数组,数组中以键值对的形式来储存用户的信息
NSMutableArray *rowArray = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:3];
for
(
int
j = 0; j < 3; j ++)
{
//创建存储用户信息的字典
NSMutableDictionary *user = [NSMutableDictionary dictionaryWithCapacity:2];
//生成测试数据
NSString *name = [NSString stringWithFormat:@
"User%03d"
, number];
NSString *tel = [NSString stringWithFormat:@
"12345%03d"
, number++];
//加入字典中
[user setObject:name forKey:@
"name"
];
[user setObject:tel forKey:@
"tel"
];
//把字典加入数组
[rowArray addObject:user];
}
//把rowArray添加到section字典中
NSString *key = [NSString stringWithFormat:@
"%c"
,(header+i)];
[sectionDic setObject:key forKey:@
"header"
];
[sectionDic setObject:rowArray forKey:@
"items"
];
//把section添加到总的数组中
[self.telBook addObject:sectionDic];
}
|
3.把我们用代码创建的模拟数据在我们的TableView中进行显示,在相应的函数中根据我们生成的数据返回相应的值显示在TableView中,显示代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
#pragma mark - Table view data source
//返回Section的个数,即我们telBook数组元素的个数
- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView
{
return
self.telBook.count;
}
//返回每个section中的行数,即section中的数组元素的个数
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section
{
NSArray *rowArray = self.telBook[section][@
"items"
];
return
rowArray.count;
}
//给每个分组设置header
-(NSString *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView titleForHeaderInSection:(NSInteger)section
{
//获取每个section中的header
NSString *title = self.telBook[section][@
"header"
];
return
title;
}
//获取cell并添加完数据发挥
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:@
"Cell"
forIndexPath:indexPath];
//获取secion中的数据数组
NSArray *items = self.telBook[indexPath.section][@
"items"
];
//获取数组中的每一项的一个字典
NSString *name = items[indexPath.row][@
"name"
];
NSString *tel = items[indexPath.row][@
"tel"
];
//给sel设置值
cell.textLabel.text = name;
cell.detailTextLabel.text = tel;
return
cell;
}
|
4.上面给出的时关键代码,至于怎么配置TableView的Cell模板或者如何把TableViewController和Storyboard中的ViewController绑定,在前面的博客中都有介绍,在这小编就不做赘述。运行结果和上面的图片是一样的。
上面的东西只是这篇博文的引子,为了显示上面的数据结构我们这样做是不是太麻烦了,而且上面的数据是不能被持久化存储的。如果给我们的数据都要转换成上面的数据组织形式,想必由于所给数据结构的不确定,所以转换起来是相当的复杂的。TableView之所以会爱上CoreData,是因为我们的CoreData会简化我们对数据的操作,并且会持久化到sqlite中。CoreData相当于TableView和sqllite的纽带,说的专业一些就是映射,那么我们CoreData如何使用才会简化我们的操作呢?下面将要介绍的才是这篇博客中的重点:我们如何使用CoreData才会让TableView爱上它呢?
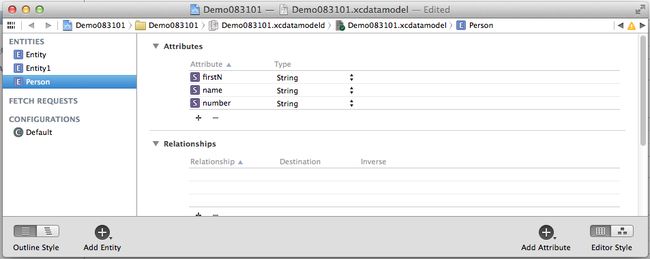
1.新建一个Empty Application, 在新建工程的时候,不要忘了把Use Core Data给选中,选中Use Core Data会自动引入Core Data框架库和在AppDelegate.h和AppDelegate.m中进行相应的配置,并且同时还自动生成一个以本应用名命名的Data Model文件,我们可以在Data Model文件中添加我们的数据模型, 添加好的数据模型我们会在生成数据实体类时使用(和JavaBean类似)
(1)AppDelegata.m中多出的部分代码如下,从多出的部分代码就可以看出,CoreData会把我们的数据实体和sqllite建立起一一对应的关系:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
// Returns the managed object model for the application.
// If the model doesn't already exist, it is created from the application's model.
- (NSManagedObjectModel *)managedObjectModel
{
if
(_managedObjectModel != nil) {
return
_managedObjectModel;
}
NSURL *modelURL = [[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@
"Demo083101"
withExtension:@
"momd"
];
_managedObjectModel = [[NSManagedObjectModel alloc] initWithContentsOfURL:modelURL];
return
_managedObjectModel;
}
// Returns the persistent store coordinator for the application.
// If the coordinator doesn't already exist, it is created and the application's store added to it.
- (NSPersistentStoreCoordinator *)persistentStoreCoordinator
{
if
(_persistentStoreCoordinator != nil) {
return
_persistentStoreCoordinator;
}
NSURL *storeURL = [[self applicationDocumentsDirectory] URLByAppendingPathComponent:@
"Demo083101.sqlite"
];
NSError *error = nil;
_persistentStoreCoordinator = [[NSPersistentStoreCoordinator alloc] initWithManagedObjectModel:[self managedObjectModel]];
if
(![_persistentStoreCoordinator addPersistentStoreWithType:NSSQLiteStoreType configuration:nil URL:storeURL options:nil error:&error]) {
NSLog(@
"Unresolved error %@, %@"
, error, [error userInfo]);
abort
();
}
return
_persistentStoreCoordinator;
}
|
(2)我们可以通过 projectName.xcdatamodeld中创建我们的数据实体模型,如下图所示
(3)通过创建好的数据实体模型来创建我们的实体类(和JavaBean类似的东西)创建过程如下图,点击下一步以后,选中创建的实体模型即可:
2.CoreData准备的差不多啦,该我们的TableView出场啦,在Empty Application中默认的时没有storyboard, 如果你又想通过storyboard来简化你的操作,得给应用创建一个storybaord才对,创建过程如下:
(1)第一步创建一个storyboard文件,命名为Main,如下图所示
(2)第二步:设置从storyboard来启动, 在Main InterFace中选中我们创建的storyboard即可
(3) 第三步修改AppDelegate.m中的函数如下所示,把初始化的工作交给我们创建的storyboard进行:
|
1
2
3
4
|
- (
BOOL
)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions
{
return
YES;
}
|
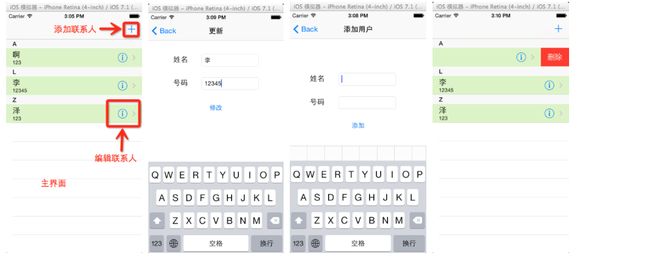
3.配置工作完成接下来就是TableView和CoreData相爱的过程啦,如何在storyboard中对TableView的cell进行配置在这儿就不赘述了,下面给出我们要通过TableView和CoreData来实现什么功能。
(1)我们要实现对通讯录的增删改查,主要需求入下图所示:
(2)实现添加功能,点击右上角的添加按钮时会跳转到添加页面,在添加页面中有两个TextField来接受用户的输入,点击添加按钮进行数据添加。AddViewController.m中的主要代码如下。
a.需要用到的属性如下, 用NSManagedObejectContext的对象来操作CoreData中的数据,和Hibernate中的session的对象相似
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
@property (strong, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *nameTextField;
@property (strong, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *numberTextField;
//声明CoreData的上下文
@property (strong, nonatomic) NSManagedObjectContext *managedObjectContext;
|
b.获取UIApplication的单例application, 然后再通过application获取delegate, 最后通过delegate来获取上下文,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
|
//通过application对象的代理对象获取上下文
UIApplication *application = [UIApplication sharedApplication];
id delegate = application.delegate;
self.managedObjectContext = [delegate managedObjectContext];
|
c.编辑点击button要回调的方法,在点击添加按钮时首先得通过上下文获取我们的实体对象,获取完实体对象后再给实体对象的属性赋上相应的值,最后调用上下文的save方法来存储一下我们的实体对象。添加完以后还要通过navigationController来返回到上一层视图,代码如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
- (IBAction)tapAdd:(id)sender {
//获取Person的实体对象
Person *person = [NSEntityDescription insertNewObjectForEntityForName:NSStringFromClass([Person
class
]) inManagedObjectContext:self.managedObjectContext];
//给person赋值
person.name = self.nameTextField.text;
person.number = self.numberTextField.text;
person.firstN = [NSString stringWithFormat:@
"%c"
, pinyinFirstLetter([person.name characterAtIndex:0])-32];
//通过上下文存储实体对象
NSError *error;
if
(![self.managedObjectContext save:&error]) {
NSLog(@
"%@"
, [error localizedDescription]);
}
//返回上一层的view
[self.navigationController popToRootViewControllerAnimated:YES];
}
|
(3)实现上面的代码只是通过CoreData往sqlite中添加数据,要想在我们的TableView中显示还需要通过CoreData把我们的存储在sqlite中的数据来查询出来,再用CoreData给我们提供的方法把查询结果做一个转换,转换成适合TableView显示的数据,下面给出相应的获取数据的代码。
a.在TableViewController我们需要声明如下两个属性,一个用于获取上下文,一个用于存储返回结果
|
1
2
3
4
|
//声明通过CoreData读取数据要用到的变量
@property (strong, nonatomic) NSManagedObjectContext *managedObjectContext;
//用来存储查询并适合TableView来显示的数据
@property (strong, nonatomic) NSFetchedResultsController *fetchedResultsController;
|
b.在viewDidLoad中获取上下文
|
1
2
3
4
|
//通过application对象的代理对象获取上下文
UIApplication *application = [UIApplication sharedApplication];
id delegate = application.delegate;
self.managedObjectContext = [delegate managedObjectContext];
|
c.在viewDidLoad中通过上下文来查询数据,并存储在fetchedResultsController中, 在获取数据的过程中我们需要定义UIFetchRequest 和排序规则,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
/*********
通过CoreData获取sqlite中的数据
*********/
//通过实体名获取请求
NSFetchRequest *request = [[NSFetchRequest alloc] initWithEntityName:NSStringFromClass([Person
class
])];
//定义分组和排序规则
NSSortDescriptor *sortDescriptor = [[NSSortDescriptor alloc] initWithKey:@
"firstN"
ascending:YES];
//把排序和分组规则添加到请求中
[request setSortDescriptors:@[sortDescriptor]];
//把请求的结果转换成适合tableView显示的数据
self.fetchedResultsController = [[NSFetchedResultsController alloc] initWithFetchRequest:request managedObjectContext:self.managedObjectContext sectionNameKeyPath:@
"firstN"
cacheName:nil];
//执行fetchedResultsController
NSError *error;
if
([self.fetchedResultsController performFetch:&error]) {
NSLog(@
"%@"
, [error localizedDescription]);
}
|
d.把查询到的数据显示在TableView中代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
#pragma mark - Table view data source
- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView
{
//我们的数据中有多少个section, fetchedResultsController中的sections方法可以以数组的形式返回所有的section
//sections数组中存的是每个section的数据信息
NSArray *sections = [self.fetchedResultsController sections];
return
sections.count;
}
//通过获取section中的信息来获取header和每个secion中有多少数据
-(NSString *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView titleForHeaderInSection:(NSInteger)section
{
NSArray *sections = [self.fetchedResultsController sections];
//获取对应section的sectionInfo
id<NSFetchedResultsSectionInfo> sectionInfo = sections[section];
//返回header
return
[sectionInfo name];
}
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section
{
NSArray *sections = [self.fetchedResultsController sections];
id<NSFetchedResultsSectionInfo> sectionInfo = sections[section];
//返回每个section中的元素个数
return
[sectionInfo numberOfObjects];
}
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:@
"Cell"
forIndexPath:indexPath];
//获取实体对象
Person *person = [self.fetchedResultsController objectAtIndexPath:indexPath];
cell.textLabel.text = person.name;
cell.detailTextLabel.text = person.number;
// Configure the cell...
return
cell;
}
|
(4) 经上面的代码,我们就可以通过CoreData查询sqlite, 然后把查询测数据结果显示到TableView中,可是上面的代码有个问题,就是当通过CoreData来修改或着添加数据时,TableView上的内容是不跟着CoreData的变化而变化的,接下来要做的就是要绑定TableView和CoreData的关系。即通过CoreData修改数据的同时TableView也会跟着改变。
a.要想实现TableView和CoreData的同步,我们需要让TableView对应的Controller实现协议NSFetchedResultsControllerDelegate, 然后再ViewDidLoad中进行注册,在添加上相应的回调代码即可。实现协议的代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
@interface MyTableViewController : UITableViewController<NSFetchedResultsControllerDelegate>
@end
|
b.进行委托回调的注册,在viewDidLoad中添加
|
1
2
|
//注册回调,使同步生效
self.fetchedResultsController.delegate = self;
|
c.添加相应的委托回调的方法,我们可以到Help中的API中去复制, 查询NSFetchedResultsControllerDelegate,找到相应的回调代码复制过来然后再做简单的修改即可, 实现回调的方法代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
|
/*
Assume self has a property 'tableView' -- as is the case for an instance of a UITableViewController
subclass -- and a method configureCell:atIndexPath: which updates the contents of a given cell
with information from a managed object at the given index path in the fetched results controller.
*/
//当CoreData的数据正在发生改变是,FRC产生的回调
- (
void
)controllerWillChangeContent:(NSFetchedResultsController *)controller {
[self.tableView beginUpdates];
}
//分区改变状况
- (
void
)controller:(NSFetchedResultsController *)controller didChangeSection:(id <NSFetchedResultsSectionInfo>)sectionInfo
atIndex:(NSUInteger)sectionIndex forChangeType:(NSFetchedResultsChangeType)type {
switch
(type) {
case
NSFetchedResultsChangeInsert:
[self.tableView insertSections:[NSIndexSet indexSetWithIndex:sectionIndex]
withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationFade];
break
;
case
NSFetchedResultsChangeDelete:
[self.tableView deleteSections:[NSIndexSet indexSetWithIndex:sectionIndex]
withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationFade];
break
;
}
}
//数据改变状况
- (
void
)controller:(NSFetchedResultsController *)controller didChangeObject:(id)anObject
atIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath forChangeType:(NSFetchedResultsChangeType)type
newIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)newIndexPath {
UITableView *tableView = self.tableView;
switch
(type) {
case
NSFetchedResultsChangeInsert:
//让tableView在newIndexPath位置插入一个cell
[tableView insertRowsAtIndexPaths:[NSArray arrayWithObject:newIndexPath]
withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationFade];
break
;
case
NSFetchedResultsChangeDelete:
[tableView deleteRowsAtIndexPaths:[NSArray arrayWithObject:indexPath]
withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationFade];
break
;
case
NSFetchedResultsChangeUpdate:
//让tableView刷新indexPath位置上的cell
[tableView reloadRowsAtIndexPaths:@[indexPath] withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationFade];
break
;
case
NSFetchedResultsChangeMove:
[tableView deleteRowsAtIndexPaths:[NSArray arrayWithObject:indexPath]
withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationFade];
[tableView insertRowsAtIndexPaths:[NSArray arrayWithObject:newIndexPath]
withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationFade];
break
;
}
}
//当CoreData的数据完成改变是,FRC产生的回调
- (
void
)controllerDidChangeContent:(NSFetchedResultsController *)controller {
[self.tableView endUpdates];
}
|
(5)经过上面的代码就可以实现CoreData和TableView的同步啦,到此会感觉到TableView结合着CoreData是如此的顺手,虽然配置起来较为麻烦,但还是比较中规中矩的,只要按部就班的来,是不难实现的。因此TableView深爱着CoreData. 上面我们完成了通过CoreData来对数据的插入和查询并同步到TableView中,下面将会介绍到如何对我们的Cell进行删除。
a.想通过TableView来删除数据的话得开启我们的TableView的编辑功能
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
//开启编辑
// Override to support conditional editing of the table view.
- (
BOOL
)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView canEditRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
// Return NO if you do not want the specified item to be editable.
return
YES;
}
|
b.开启编辑功能以后我们就可以在tableView的对应的方法中来实现删除功能啦,当点击删除时,我们需呀获取cell对应的索引在CoreData中的实体对象,然后通过上下文进行删除,在save一下即可。因为CoreData和TableView已经进行了同步,所以删除后TableView会自动更新,删除代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
// Override to support editing the table view.
- (
void
)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView commitEditingStyle:(UITableViewCellEditingStyle)editingStyle forRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
if
(editingStyle == UITableViewCellEditingStyleDelete)
{
//通过coreData删除对象
//通过indexPath获取我们要删除的实体
Person * person = [self.fetchedResultsController objectAtIndexPath:indexPath];
//通过上下文移除实体
[self.managedObjectContext deleteObject:person];
//保存
NSError *error;
if
([self.managedObjectContext save:&error]) {
NSLog(@
"%@"
, [error localizedDescription]);
}
}
}
|
c.默认的删除按钮上显示的是Delete, 可以通过下面的方法进行修改,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
//设置删除的名字
-(NSString *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView titleForDeleteConfirmationButtonForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
return
@
"删除"
;
}
|
(6)到这一步删除功能算是完成了,还有最后一个功能点,就是更新我们的数据。更新数据通过点击相应的cell,把cell上的数据传到UpdateView的页面上,然后进行更新即可。
a.下面的代码是获取数据我们选中的数据并通过KVC把参数传到目的视图中
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
#pragma mark - Navigation
//把对应的cell上的值传到修改的页面上
// In a storyboard-based application, you will often want to do a little preparation before navigation
- (
void
)prepareForSegue:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue sender:(id)sender
{
//参数sender是点击的对应的cell
//判断sender是否为TableViewCell的对象
if
([sender isKindOfClass:[UITableViewCell
class
]]) {
//做一个类型的转换
UITableViewCell *cell = (UITableViewCell *)sender;
//通过tableView获取cell对应的索引,然后通过索引获取实体对象
NSIndexPath *indexPath = [self.tableView indexPathForCell:cell];
//用frc通过indexPath来获取Person
Person *person = [self.fetchedResultsController objectAtIndexPath:indexPath];
//通过segue来获取我们目的视图控制器
UIViewController *nextView = [segue destinationViewController];
//通过KVC把参数传入目的控制器
[nextView setValue:person forKey:@
"person"
];
}
}
|
b.在UpdateViewController中把传过来的实体对象进行更新,再保存。更新部分的代码和添加部分的代码差不多,在这就不往上贴啦。
经过上面的艰苦的历程后我们的tableView就会深深的爱上CoreData, 可能上面的内容有些多,有疑问的可以留言交流。
上面所做的功能里我们的真正的通讯录还有些差距,看过上面的代码的小伙伴会有个疑问:添加的页面和更新的页面能不能使用同一个呢? 当然啦,为了遵循Don`t Repeat Yourself的原则,下面我们就把两个相似的页面合并在一起,同时给我们每条记录加上头像和给整个tableView加上索引。
1.把更新页面删掉,做如下修改,点击添加和修改都跳转到我们的编辑页面,同时添加一个自定义Button,点击Button时,我们会调用ImagePickerController来从手机相册获取图片:
2.为了把头像持久化存储,我们还得修改数据模型,从新生成Person类,添加一个存储image的选项,是通过二进制的形式存储的
3.在之前保存的ViewController中如果Person为空,说明是执行的添加记录的方法我们就生成一个新的person, 如果Person不为空则不新建Person对象,直接更新完保存。
(1)为了获取图片,我们需要添加ImagePickerController对象,并在viewDidLoad中做相应的配置,代码如下
|
1
2
|
//声明ImagePicker
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIImagePickerController *picker;
|
进行相关配置
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
//初始化并配置ImagePicker
self.picker = [[UIImagePickerController alloc] init];
//picker是否可以编辑
self.picker.allowsEditing = YES;
//注册回调
self.picker.delegate = self;
|
(2)点头像会跳转到我们定义好的ImagePickerController中,我们就可在图片库中选取相应的照片啦。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
//点击图片按钮设置图片
- (IBAction)tapImageButton:(id)sender {
//跳转到ImagePickerView来获取按钮
[self presentViewController:self.picker animated:YES completion:^{}];
}
|
(3)在ImagePickerController中点击取消按钮触发的事件,跳转到原来编辑的界面
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
//回调图片选择取消
-(
void
)imagePickerControllerDidCancel:(UIImagePickerController *)picker
{
//在ImagePickerView中点击取消时回到原来的界面
[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:YES completion:^{}];
}
|
(4)选完图片把头像设置成用户选中的按钮,并dismiss到原来界面
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
//实现图片回调方法,从相册获取图片
-(
void
) imagePickerController:(UIImagePickerController *)picker didFinishPickingMediaWithInfo:(NSDictionary *)info
{
//获取到编辑好的图片
UIImage * image = info[UIImagePickerControllerEditedImage];
//把获取的图片设置成用户的头像
[self.imageButton setImage:image forState:UIControlStateNormal];
//返回到原来View
[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:YES completion:^{}];
}
|
(5)把我们点击保存按钮回调的方法作如下修改,如果person为空,我们会新建一个新的person.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
- (IBAction)tapSave:(id)sender
{
//如果person为空则新建,如果已经存在则更新
if
(self.person == nil)
{
self.person = [NSEntityDescription insertNewObjectForEntityForName:NSStringFromClass([Person
class
]) inManagedObjectContext:self.managedObjectContext];
}
//赋值
self.person.name = self.nameTextField.text;
self.person.tel = self.telTextField.text;
self.person.firstN = [NSString stringWithFormat:@
"%c"
, pinyinFirstLetter([self.person.name characterAtIndex:0])-32];
//把button上的图片存入对象
UIImage *buttonImage = [self.imageButton imageView].image;
self.person.imageData = UIImagePNGRepresentation(buttonImage);
//保存
NSError *error;
if
(![self.managedObjectContext save:&error]) {
NSLog(@
"%@"
, [error localizedDescription]);
}
//保存成功后POP到表视图
[self.navigationController popToRootViewControllerAnimated:YES];
}
|
(6)因为是何更新页面公用的所以我们要在viewDidLoad对TextField和Button的背景进行初始化,如果person中的imageData有值我们有用传过来的图片,否则用默认的图片,添加数据初始化代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
self.nameTextField.text = self.person.name;
self.telTextField.text = self.person.tel;
if
(self.person.imageData != nil)
{
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageWithData:self.person.imageData];
[self.imageButton setImage:image forState:UIControlStateNormal];
}
|
4.上面的代码就可以插入头像了,我们需要在tableView中进行显示即可,在tableView中从person对象中获取相应的头像,然后显示即可,下面我们要加上索引。
(1)在cell中显示头像的代码如下:
|
1
2
3
|