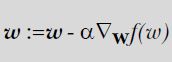1. sigmoid 函数:
梯度上升(Gradient Ascent)与 梯度下降(Gradient Descent):
2. 循环迭代的梯度上升计算系数w:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
def
loadDataSet():
dataMat
=
[]; labelMat
=
[]
fr
=
open
(
'testSet.txt'
)
for
line
in
fr.readlines():
lineArr
=
line.strip().split()
dataMat.append([
1.0
,
float
(lineArr[
0
]),
float
(lineArr[
1
])])
# here set x0=1.0
labelMat.append(
int
(lineArr[
2
]))
return
dataMat,labelMat
def
sigmoid(inX):
return
1.0
/
(
1
+
exp(
-
inX))
def
gradAscent(dataMatIn, classLabels):
dataMatrix
=
mat(dataMatIn)
#convert to NumPy matrix
labelMat
=
mat(classLabels).transpose()
#convert to NumPy matrix
m,n
=
shape(dataMatrix)
alpha
=
0.001
maxCycles
=
500
weights
=
ones((n,
1
))
for
k
in
range
(maxCycles):
#heavy on matrix operations
h
=
sigmoid(dataMatrix
*
weights)
#matrix mult
error
=
(labelMat
-
h)
#vector subtraction
#weights = weights + alpha * dataMatrix.transpose()* error
weights
=
weights
+
alpha
*
dataMatrix.transpose()
*
error
/
m
#matrix mult
return
weights
|
3. 画出上面2计算出来的分类结果:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
def
plotBestFit(weights):
import
matplotlib.pyplot as plt
dataMat,labelMat
=
loadDataSet()
dataArr
=
array(dataMat)
n
=
shape(dataArr)[
0
]
xcord1
=
[]; ycord1
=
[]
xcord2
=
[]; ycord2
=
[]
for
i
in
range
(n):
if
int
(labelMat[i])
=
=
1
:
xcord1.append(dataArr[i,
1
]); ycord1.append(dataArr[i,
2
])
else
:
xcord2.append(dataArr[i,
1
]); ycord2.append(dataArr[i,
2
])
fig
=
plt.figure()
ax
=
fig.add_subplot(
111
)
ax.scatter(xcord1, ycord1, s
=
30
, c
=
'red'
, marker
=
's'
)
ax.scatter(xcord2, ycord2, s
=
30
, c
=
'green'
)
x
=
arange(
-
3.0
,
3.0
,
0.1
)
y
=
(
-
weights[
0
]
-
weights[
1
]
*
x)
/
weights[
2
]
#for sigmoid,input=0 is the classifier line for 0 and 1, so the classifier is w0x0+w1x1+w2x2=0
ax.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel(
'X1'
); plt.ylabel(
'X2'
);
plt.show()
|
4.随机梯度上升(stochastic gradient ascent)
由于上述的梯度上升算法,每次迭代都是用到全部的数据集,当数据量特别大,并且特征维数特别高时,计算量将会非常巨大;因此一种替代方法就是每次迭代更新都是用一个新样本来完成,即随机梯度上升法。
随机梯度上升法(1)步长a可变 (2)每次迭代,随机选取样本来更新系数w
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
def
stocGradAscent1(dataMatrix, classLabels, numIter
=
150
):
m,n
=
shape(dataMatrix)
weights
=
ones(n)
#initialize to all ones
for
j
in
range
(numIter):
dataIndex
=
range
(m)
for
i
in
range
(m):
alpha
=
4
/
(
1.0
+
j
+
i)
+
0.0001
#apha decreases with iteration, does not
randIndex
=
int
(random.uniform(
0
,
len
(dataIndex)))
#go to 0 because of the constant
h
=
sigmoid(
sum
(dataMatrix[randIndex]
*
weights))
error
=
classLabels[randIndex]
-
h
weights
=
weights
+
alpha
*
error
*
dataMatrix[randIndex]
del
(dataIndex[randIndex])
return
weights
|
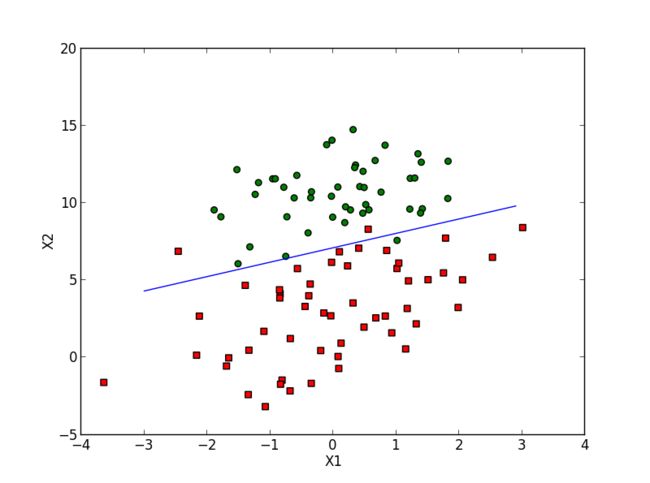
这样可以用比较少次数的迭代,就会得到和2里相类似的结果,下图是numIter=5次随机梯度结果:
#coding:utf-8#===================================#Logistic回归#author:zhang haibo#time: 2013-7-12#===================================import mathfrom numpy import *#加载数据集def loadDataSet ():dataMat = []; labelMat = []fr = open ( 'testSet.txt' )for line in fr . readlines ():lineArr = line . strip () . split ()dataMat . append ([ 1.0 , float ( lineArr [ 0 ]), float ( lineArr [ 1 ])])labelMat . append ( int ( lineArr [ 2 ]))return dataMat , labelMat#sigmod函数def sigmoid ( inX ):return 1.0 / ( 1 + exp ( - inX ))#Logistic回归梯度上升优化算法:用全部的样本进行训练,大量的乘法def gradAscent ( dataMatIn , classLabels ):dataMatrix = mat ( dataMatIn )labelMat = mat ( classLabels ) . transpose ()m , n = shape ( dataMatrix )alpha = 0.001maxCycles = 500weights = ones (( n , 1 ))for k in range ( maxCycles ):h = sigmoid ( dataMatrix * weights )error = ( labelMat - h )weights = weights + alpha * dataMatrix . transpose () * errorreturn weights#随机梯度上升算法:在线学习算法,每次仅用一个样本进行训练def stocGradAscent0 ( dataMatrix , classLabels ):m , n = shape ( dataMatrix )alpha = 0.01weights = ones ( n )for i in range ( m ):h = sigmoid ( sum ( dataMatrix [ i ] * weights ))error = classLabels [ i ] - hweights += alpha * error * dataMatrix [ i ]return weights#改进的随机梯度上升算法def stocGradAscent1 ( dataMatrix , classLabels , numIter = 150 ):m , n = shape ( dataMatrix )weights = ones ( n )for j in range ( numIter ):dataIndex = range ( m )for i in range ( m ):alpha = 4 / ( 1.0 + j + i ) + 0.01randIndex = int ( random . uniform ( 0 , len ( dataIndex )))h = sigmoid ( sum ( dataMatrix [ dataIndex [ randIndex ]] * weights ))error = classLabels [ dataIndex [ randIndex ]] - hweights += alpha * error * dataMatrix [ dataIndex [ randIndex ]]del ( dataIndex [ randIndex ])return weights#Logistic回归分类函数def classifyVector ( inX , weights ):prob = sigmoid ( sum ( inX * weights ))if prob > 0.5 :return 1.0else :return 0.0#示例:预测病马的死亡率def colicTest ():frTrain = open ( 'horseColicTraining.txt' )frTest = open ( 'horseColicTest.txt' )trainingSet = []; trainingLabels = []for line in frTrain . readlines ():currLine = line . strip () . split ( ' \t ' )lineArr = []for i in range ( 21 ):lineArr . append ( float ( currLine [ i ]))trainingSet . append ( lineArr )trainingLabels . append ( float ( currLine [ 21 ]))trainWeights = stocGradAscent1 ( array ( trainingSet ), trainingLabels , 500 )errorCount = 0 ; numTestVec = 0.0for line in frTest . readlines ():numTestVec += 1.0currLine = line . strip () . split ( ' \t ' )lineArr = []for i in range ( 21 ):lineArr . append ( float ( currLine [ i ]))if int ( classifyVector ( array ( lineArr ), trainWeights )) != int ( currLine [ 21 ]):errorCount += 1errorRate = ( float ( errorCount ) / numTestVec )print "the error rate of this test is: %f " % errorRatereturn errorRatedef multiTest ():numTests = 10 ; errorSum = 0.0for k in range ( numTests ):errorSum += colicTest ()print "after %d iterations the average error rate is: %f " % ( numTests , errorSum / float ( numTests ))#=============测试代码=====================dataArr , labelMat = loadDataSet ()print gradAscent ( dataArr , labelMat )print stocGradAscent1 ( array ( dataArr ), labelMat )multiTest ()