Nginx之环境准备
1. 操作系统
-
CentOS 6.4 x86_64
2.软件版本
-
Nginx 1.4.2
3.实验拓扑
注,实验拓扑见下文。
4.安装yum源
|
1
2
3
|
[root@nginx ~]
# rpm -ivh http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
[root@web1 ~]
# rpm -ivh http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
[root@web2 ~]
# rpm -ivh http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
|
5.各节点时间同步
|
1
2
3
|
[root@nginx ~]
# ntpdate 202.120.2.101
[root@web1 ~]
# ntpdate 202.120.2.101
[root@web2 ~]
# ntpdate 202.120.2.101
|
6.关闭防火墙与SELinux
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
[root@nginx ~]
# service iptables stop
[root@nginx ~]
# chkconfig iptables off
[root@nginx ~]
# getenforce
Disabled
[root@web1 ~]
# service iptables stop
[root@web1 ~]
# chkconfig iptables off
[root@web1 ~]
# getenforce
Disabled
[root@web2 ~]
# service iptables stop
[root@web2 ~]
# chkconfig iptables off
[root@web2 ~]
# getenforce
Disabled
|
三、安装Nginx
1.解压
|
1
|
[root@nginx src]
# tar xf nginx-1.4.2.tar.gz
|
2.新建nginx用户与组
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@nginx src]
# groupadd -g 108 -r nginx
[root@nginx src]
# useradd -u 108 -r -g 108 nginx
[root@nginx src]
# id nginx
uid=108(nginx) gid=108(nginx) 组=108(nginx)
|
3.准备编译配置文件
|
1
2
|
[root@nginx src]
# yum install -y pcre-devel openssl-devel
[root@nginx nginx-1.4.2]
# ./configure --prefix=/usr --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --pid-path=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid --lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/client/ --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/proxy/ --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/fcgi/ --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/uwsgi --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/scgi --with-pcre
|
4.编译并安装
|
1
|
[root@nginx nginx-1.4.2]
# make && make install
|
5.为nginx提供SysV init脚本
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
|
[root@nginx ~]
# cat /etc/init.d/nginx
#!/bin/sh
#
# nginx - this script starts and stops the nginx daemon
#
# chkconfig: - 85 15
# description: Nginx is an HTTP(S) server, HTTP(S) reverse \
# proxy and IMAP/POP3 proxy server
# processname: nginx
# config: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
# config: /etc/sysconfig/nginx
# pidfile: /var/run/nginx.pid
# Source function library.
.
/etc/rc
.d
/init
.d
/functions
# Source networking configuration.
.
/etc/sysconfig/network
# Check that networking is up.
[
"$NETWORKING"
=
"no"
] &&
exit
0
nginx=
"/usr/sbin/nginx"
prog=$(
basename
$nginx)
NGINX_CONF_FILE=
"/etc/nginx/nginx.conf"
[ -f
/etc/sysconfig/nginx
] && .
/etc/sysconfig/nginx
lockfile=
/var/lock/subsys/nginx
make_dirs() {
# make required directories
user=`nginx -V 2>&1 |
grep
"configure arguments:"
|
sed
's/[^*]*--user=\([^ ]*\).*/\1/g'
-`
options=`$nginx -V 2>&1 |
grep
'configure arguments:'
`
for
opt
in
$options;
do
if
[ `
echo
$opt |
grep
'.*-temp-path'
` ];
then
value=`
echo
$opt |
cut
-d
"="
-f 2`
if
[ ! -d
"$value"
];
then
# echo "creating" $value
mkdir
-p $value &&
chown
-R $user $value
fi
fi
done
}
start() {
[ -x $nginx ] ||
exit
5
[ -f $NGINX_CONF_FILE ] ||
exit
6
make_dirs
echo
-n $
"Starting $prog: "
daemon $nginx -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE
retval=$?
echo
[ $retval -
eq
0 ] &&
touch
$lockfile
return
$retval
}
stop() {
echo
-n $
"Stopping $prog: "
killproc $prog -QUIT
retval=$?
echo
[ $retval -
eq
0 ] &&
rm
-f $lockfile
return
$retval
}
restart() {
configtest ||
return
$?
stop
sleep
1
start
}
reload() {
configtest ||
return
$?
echo
-n $
"Reloading $prog: "
killproc $nginx -HUP
RETVAL=$?
echo
}
force_reload() {
restart
}
configtest() {
$nginx -t -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE
}
rh_status() {
status $prog
}
rh_status_q() {
rh_status >
/dev/null
2>&1
}
case
"$1"
in
start)
rh_status_q &&
exit
0
$1
;;
stop)
rh_status_q ||
exit
0
$1
;;
restart|configtest)
$1
;;
reload)
rh_status_q ||
exit
7
$1
;;
force-reload)
force_reload
;;
status)
rh_status
;;
condrestart|try-restart)
rh_status_q ||
exit
0
;;
*)
echo
$
"Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|restart|condrestart|try-restart|reload|force-reload|configtest}"
exit
2
esac
|
6.为此脚本赋予执行权限
|
1
|
[root@nginx ~]
# chmod +x /etc/init.d/nginx
|
7.添加至服务管理列表,并让其开机自动启动
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@nginx ~]
# chkconfig --add nginx
[root@nginx ~]
# chkconfig nginx on
[root@nginx ~]
# chkconfig nginx --list
nginx 0:关闭 1:关闭 2:启用 3:启用 4:启用 5:启用 6:关闭
|
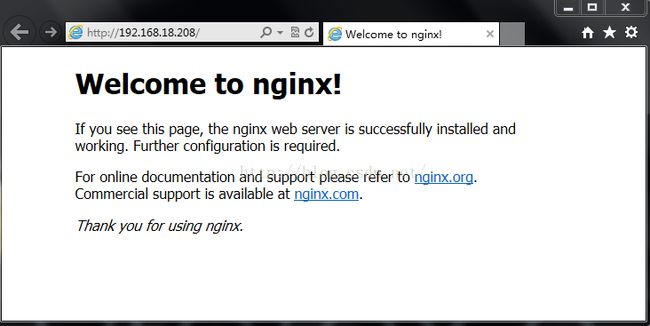
8.启动nginx
|
1
2
|
[root@nginx ~]
# service nginx start
正在启动 nginx: [确定]
|
9.查看一下端口