Android开发常用工具总结
目录:
什么是AIDL以及如何使用
获取总内存及可用内存
dp、px转换
程序的安装与卸载
根据URI获取真实路径
关闭开启网络
还原短信
横竖屏切换
获取mac地址
获取SD卡状态
获取状态栏和标题栏的高度
获取各种窗体高度
获取内外置存储卡路径
捕获Application全局异常
禁止Home键
开机启动
控制对话框位置
模拟器错误
挪动dialog的位置
屏幕适配
设置APN
调节屏幕亮度
重启
拍照、录音、录像
隐藏软键盘
隐藏以及显示软键盘以及不自动弹出键盘的方法
BitMap、Drawable、inputStream及byte[] 互转
drawable转bitmap
Android目录结构
Android下的Linux指令
Android中特有的指令
刷模拟器,rom写文件(su)
修改字体
修改开机动画
删除锁屏密码
关于9path
上传代码到github
什么是AIDL以及如何使用
①aidl是Android interface definition Language 的英文缩写,意思Android 接口定义语言。
②使用aidl可以帮助我们发布以及调用远程服务,实现跨进程通信。
③将服务的aidl放到对应的src目录,工程的gen目录会生成相应的接口类
我们通过bindService(Intent,ServiceConnect,int)方法绑定远程服务,在bindService中有一个ServiceConnec接口,我们需要覆写该类的onServiceConnected(ComponentName,IBinder)方法,这个方法的第二个参数IBinder对象其实就是已经在aidl中定义的接口,因此我们可以将IBinder对象强制转换为aidl中的接口类。
我们通过IBinder获取到的对象(也就是aidl文件生成的接口)其实是系统产生的代理对象,该代理对象既可以跟我们的进程通信,又可以跟远程进程通信,作为一个中间的角色实现了进程间通信
获取总内存及可用内存
private String getAvailMemory() {// 获取android当前可用内存大小
ActivityManager am = (ActivityManager) getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
MemoryInfo mi = new MemoryInfo();
am.getMemoryInfo(mi);//mi.availMem; 当前系统的可用内存
return Formatter.formatFileSize(getBaseContext(), mi.availMem);// 将获取的内存大小规格化
}
private String getTotalMemory() {
String str1 = "/proc/meminfo";// 系统内存信息文件
String str2;
String[] arrayOfString;
long initial_memory = 0;
try {
FileReader localFileReader = new FileReader(str1);
BufferedReader localBufferedReader = new BufferedReader(
localFileReader, 8192);
str2 = localBufferedReader.readLine();// 读取meminfo第一行,系统总内存大小
arrayOfString = str2.split("\\s+");
for (String num : arrayOfString) {
Log.i(str2, num + "\t");
}
initial_memory = Integer.valueOf(arrayOfString[1]).intValue() * 1024;// 获得系统总内存,单位是KB,乘以1024转换为Byte
localBufferedReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
return Formatter.formatFileSize(getBaseContext(), initial_memory);// Byte转换为KB或者MB,内存大小规格化
}
dp、px转换
/** * 根据手机的分辨率从 dip 的单位 转成为 px(像素) */
public static int dip2px(Context context, float dpValue) {
final float scale = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;
return (int) (dpValue * scale + 0.5f);
}
/** * 根据手机的分辨率从 px(像素) 的单位 转成为 dp */
public static int px2dip(Context context, float pxValue) {
final float scale = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;
return (int) (pxValue / scale + 0.5f);
} 程序的安装与卸载
安装:
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
intent.setDataAndType(Uri.fromFile(new File("/sdcard/xxx.apk")),
"application/vnd.android.package-archive");
MainActivity.this.startActivity(intent);
卸载:
Uri uri = Uri.parse("package:com.xxx.xxx(包名)");
Intent intent2 = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_DELETE, uri);
MainActivity.this.startActivity(intent2); 根据URI获取真实路径
public static String getRealFilePath( final Context context, final Uri uri ) {
if ( null == uri ) return null;
final String scheme = uri.getScheme();
String data = null;
if ( scheme == null )
data = uri.getPath();
else if ( ContentResolver.SCHEME_FILE.equals( scheme ) ) {
data = uri.getPath();
} else if ( ContentResolver.SCHEME_CONTENT.equals( scheme ) ) {
Cursor cursor = context.getContentResolver().query( uri, new String[] { ImageColumns.DATA }, null, null, null );
if ( null != cursor ) {
if ( cursor.moveToFirst() ) {
int index = cursor.getColumnIndex( ImageColumns.DATA );
if ( index > -1 ) {
data = cursor.getString( index );
}
}
cursor.close();
}
}
return data;
}关闭开启网络
public static void setDataConnectionState(Context cxt, boolean state) {
ConnectivityManager connectivityManager = null;
Class connectivityManagerClz = null;
try {
connectivityManager = (ConnectivityManager) cxt
.getSystemService("connectivity");
connectivityManagerClz = connectivityManager.getClass();
Method method = connectivityManagerClz.getMethod(
"setMobileDataEnabled", new Class[] { boolean.class });
method.invoke(connectivityManager, state);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}还原短信
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("address", "123456789");
values.put("body", "haha");
values.put("date", "135123000000");
getContentResolver().insert(Uri.parse("content://sms/sent"), values);横竖屏切换
< activity android:name="MyActivity"
android:configChanges="orientation|keyboardHidden">
public void onConfigurationChanged(Configuration newConfig) {
super.onConfigurationChanged(newConfig);
if (this.getResources().getConfiguration().orientation == Configuration.ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE) {
//加入横屏要处理的代码
}else if (this.getResources().getConfiguration().orientation == Configuration.ORIENTATION_PORTRAIT) {
//加入竖屏要处理的代码
}
} 获取mac地址
1、<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE"/>
2、private String getLocalMacAddress() {
WifiManager wifi = (WifiManager) getSystemService(Context.WIFI_SERVICE);
WifiInfo info = wifi.getConnectionInfo();
return info.getMacAddress();
} 获取SD卡状态
/** 获取存储卡路径 */
File sdcardDir=Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory();
/** StatFs 看文件系统空间使用情况 */
StatFs statFs=new StatFs(sdcardDir.getPath());
/** Block 的 size*/
Long blockSize=statFs.getBlockSize();
/** 总 Block 数量 */
Long totalBlocks=statFs.getBlockCount();
/** 已使用的 Block 数量 */
Long availableBlocks=statFs.getAvailableBlocks(); 获取状态栏和标题栏的高度
1.Android获取状态栏高度:
decorView是window中的最顶层view,可以从window中获取到decorView,然后decorView有个getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame方法可以获取到程序显示的区域,包括标题栏,但不包括状态栏。
于是,我们就可以算出状态栏的高度了。
Rect frame = new Rect();
getWindow().getDecorView().getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(frame);
int statusBarHeight = frame.top;
2.获取标题栏高度:
getWindow().findViewById(Window.ID_ANDROID_CONTENT)这个方法获取到的view就是程序不包括标题栏的部分,然后就可以知道标题栏的高度了。
int contentTop = getWindow().findViewById(Window.ID_ANDROID_CONTENT).getTop();
//statusBarHeight是上面所求的状态栏的高度
int titleBarHeight = contentTop - statusBarHeight
例子代码:
package com.cn.lhq;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.Window;
import android.widget.ImageView;
public class Main extends Activity {
ImageView iv;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
iv = (ImageView) this.findViewById(R.id.ImageView01);
iv.post(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
viewInited();
}
});
Log.v("test", "== ok ==");
}
private void viewInited() {
Rect rect = new Rect();
Window window = getWindow();
iv.getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(rect);
int statusBarHeight = rect.top;
int contentViewTop = window.findViewById(Window.ID_ANDROID_CONTENT)
.getTop();
int titleBarHeight = contentViewTop - statusBarHeight;
// 测试结果:ok之后 100多 ms 才运行了
Log.v("test", "=-init-= statusBarHeight=" + statusBarHeight
+ " contentViewTop=" + contentViewTop + " titleBarHeight="
+ titleBarHeight);
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/ImageView01"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>获取各种窗体高度
//取得窗口属性
getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(dm);
//窗口的宽度
int screenWidth = dm.widthPixels;
//窗口高度
int screenHeight = dm.heightPixels;
textView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView01);
textView.setText("屏幕宽度: " + screenWidth + "\n屏幕高度: " + screenHeight);
二、获取状态栏高度
decorView是window中的最顶层view,可以从window中获取到decorView,然后decorView有个getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame方法可以获取到程序显示的区域,包括标题栏,但不包括状态栏。
于是,我们就可以算出状态栏的高度了。
view plain
Rect frame = new Rect();
getWindow().getDecorView().getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(frame);
int statusBarHeight = frame.top;
三、获取标题栏高度
getWindow().findViewById(Window.ID_ANDROID_CONTENT)这个方法获取到的view就是程序不包括标题栏的部分,然后就可以知道标题栏的高度了。
view plain
int contentTop = getWindow().findViewById(Window.ID_ANDROID_CONTENT).getTop();
//statusBarHeight是上面所求的状态栏的高度
int titleBarHeight = contentTop - statusBarHeight获取内外置存储卡路径
/** 获取存储卡路径 */
File sdcardDir=Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory();
/** StatFs 看文件系统空间使用情况 */
StatFs statFs=new StatFs(sdcardDir.getPath());
/** Block 的 size*/
Long blockSize=statFs.getBlockSize();
/** 总 Block 数量 */
Long totalBlocks=statFs.getBlockCount();
/** 已使用的 Block 数量 */
Long availableBlocks=statFs.getAvailableBlocks();
private static String getStoragePath(Context mContext, boolean is_removale) {
StorageManager mStorageManager = (StorageManager) mContext.getSystemService(Context.STORAGE_SERVICE);
Class<?> storageVolumeClazz = null;
try {
storageVolumeClazz = Class.forName("android.os.storage.StorageVolume");
Method getVolumeList = mStorageManager.getClass().getMethod("getVolumeList");
Method getPath = storageVolumeClazz.getMethod("getPath");
Method isRemovable = storageVolumeClazz.getMethod("isRemovable");
Object result = getVolumeList.invoke(mStorageManager);
final int length = Array.getLength(result);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Object storageVolumeElement = Array.get(result, i);
String path = (String) getPath.invoke(storageVolumeElement);
boolean removable = (Boolean) isRemovable.invoke(storageVolumeElement);
if (is_removale == removable) {
return path;
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
通过反射的方式使用在sdk中被 隐藏 的类 StroageVolume 中的方法getVolumeList(),获取所有的存储空间(Stroage Volume),然后通过参数is_removable控制,来获取内部存储和外部存储(内外sd卡)的路径,参数 is_removable为false时得到的是内置sd卡路径,为true则为外置sd卡路径。
在API 23 Enviroment 类中的内部类 UserEnvironment 中有一方法getExternalDirs与此一样,代码如下:
public File[] getExternalDirs() {
final StorageVolume[] volumes = StorageManager.getVolumeList(mUserId,StorageManager.FLAG_FOR_WRITE);
final File[] files = new File[volumes.length];
for (int i = 0; i < volumes.length; i++) {
files[i] = volumes[i].getPathFile();
}
return files;
}
再看Enviroment的getExternalStorageDirectory方法实现:
public static File getExternalStorageDirectory() {
throwIfUserRequired();
return sCurrentUser.getExternalDirs()[0];
}
可以看出,在API 23时,先是通过getExternalDirs()获取到所有存储空间的File[]数组,这个数组的第一个值:getExternalDirs()[0],即为内置sd卡所在路径。
而在API 23 之前的版本中,并没有类似getExternalDirs()的方法通过StorageVolume直接获得存储空间(Storage Volume),而时通过别的方式来实现的,看关键方法的源码:
public static File getExternalStorageDirectory() {
throwIfUserRequired();
return sCurrentUser.getExternalDirsForApp()[0];
}
这里的 getExternalDirsForApp() 和上面的 getExternalDirs() 的作用是一样的,都是得到所有存储空间的File[]数组。
public File[] getExternalDirsForApp() {
return mExternalDirsForApp;
}捕获Application全局异常
/** * UncaughtException处理类,当程序发生Uncaught异常的时候,有该类来接管程序,并记录发送错误报告. * * * */
public class CrashHandler implements UncaughtExceptionHandler {
public static final String TAG = "CrashHandler";
//系统默认的UncaughtException处理类
private Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler mDefaultHandler;
//CrashHandler实例
private static CrashHandler INSTANCE = new CrashHandler();
//程序的Context对象
private Context mContext;
//用来存储设备信息和异常信息
private Map<String, String> infos = new HashMap<String, String>();
//用于格式化日期,作为日志文件名的一部分
private DateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd-HH-mm-ss");
/** 保证只有一个CrashHandler实例 */
private CrashHandler() {
}
/** 获取CrashHandler实例 ,单例模式 */
public static CrashHandler getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
/** * 初始化 * * @param context */
public void init(Context context) {
mContext = context;
//获取系统默认的UncaughtException处理器
mDefaultHandler = Thread.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler();
//设置该CrashHandler为程序的默认处理器
Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(this);
}
/** * 当UncaughtException发生时会转入该函数来处理 */
@Override
public void uncaughtException(Thread thread, Throwable ex) {
if (!handleException(ex) && mDefaultHandler != null) {
//如果用户没有处理则让系统默认的异常处理器来处理
mDefaultHandler.uncaughtException(thread, ex);
} else {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error : ", e);
}
//退出程序
android.os.Process.killProcess(android.os.Process.myPid());
System.exit(1);
}
}
/** * 自定义错误处理,收集错误信息 发送错误报告等操作均在此完成. * * @param ex * @return true:如果处理了该异常信息;否则返回false. */
private boolean handleException(Throwable ex) {
if (ex == null) {
return false;
}
//使用Toast来显示异常信息
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
Looper.prepare();
Toast.makeText(mContext, "很抱歉,程序出现异常,即将退出.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
Looper.loop();
}
}.start();
//收集设备参数信息
collectDeviceInfo(mContext);
//保存日志文件
saveCrashInfo2File(ex);
return true;
}
/** * 收集设备参数信息 * @param ctx */
public void collectDeviceInfo(Context ctx) {
try {
PackageManager pm = ctx.getPackageManager();
PackageInfo pi = pm.getPackageInfo(ctx.getPackageName(), PackageManager.GET_ACTIVITIES);
if (pi != null) {
String versionName = pi.versionName == null ? "null" : pi.versionName;
String versionCode = pi.versionCode + "";
infos.put("versionName", versionName);
infos.put("versionCode", versionCode);
}
} catch (NameNotFoundException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "an error occured when collect package info", e);
}
Field[] fields = Build.class.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
try {
field.setAccessible(true);
infos.put(field.getName(), field.get(null).toString());
Log.d(TAG, field.getName() + " : " + field.get(null));
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "an error occured when collect crash info", e);
}
}
}
/** * 保存错误信息到文件中 * * @param ex * @return 返回文件名称,便于将文件传送到服务器 */
private String saveCrashInfo2File(Throwable ex) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : infos.entrySet()) {
String key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
sb.append(key + "=" + value + "\n");
}
Writer writer = new StringWriter();
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(writer);
ex.printStackTrace(printWriter);
Throwable cause = ex.getCause();
while (cause != null) {
cause.printStackTrace(printWriter);
cause = cause.getCause();
}
printWriter.close();
String result = writer.toString();
sb.append(result);
try {
long timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
String time = formatter.format(new Date());
String fileName = "crash-" + time + "-" + timestamp + ".log";
if (Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)) {
String path = "/sdcard/crash/";
File dir = new File(path);
if (!dir.exists()) {
dir.mkdirs();
}
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(path + fileName);
fos.write(sb.toString().getBytes());
fos.close();
}
return fileName;
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "an error occured while writing file...", e);
}
return null;
}
}
在收集异常信息时,朋友们也可以使用Properties,因为Properties有一个很便捷的方法properties.store(OutputStream out, String comments),用来将Properties实例中的键值对外输到输出流中,但是在使用的过程中发现生成的文件中异常信息打印在同一行,看起来极为费劲,所以换成Map来存放这些信息,然后生成文件时稍加了些操作。
完成这个CrashHandler后,我们需要在一个Application环境中让其运行,为此,我们继承android.app.Application,添加自己的代码,CrashApplication.java代码如下:
public class CrashApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
CrashHandler crashHandler = CrashHandler.getInstance();
crashHandler.init(getApplicationContext());
}
}
/** * 网络是否可用 * * @param context * @return */
public static boolean isNetworkAvailable(Context context) {
ConnectivityManager mgr = (ConnectivityManager) context.getSystemService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE);
NetworkInfo[] info = mgr.getAllNetworkInfo();
if (info != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < info.length; i++) {
if (info[i].getState() == NetworkInfo.State.CONNECTED) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
} 禁止Home键
问题的提出
Android Home键系统负责监听,捕获后系统自动处理。有时候,系统的处理往往不随我们意,想自己处理点击Home后的事件,那怎么办?
问题的解决
先禁止Home键,再在onKeyDown里处理按键值,点击Home键的时候就把程序关闭,或者随你XXOO。
@Override
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event)
{ // TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(KeyEvent.KEYCODE_HOME==keyCode)
android.os.Process.killProcess(android.os.Process.myPid());
return super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event);
}
@Override
public void onAttachedToWindow()
{ // TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.getWindow().setType(WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_KEYGUARD);
super.onAttachedToWindow();
}
加权限禁止Home键
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.DISABLE_KEYGUARD"></uses-permission>开机启动
public class StartupReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Intent startupintent = new Intent(context,StrongTracks.class);
startupintent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
context.startActivity(startupintent);
}
}
2)<receiver
android:name=".StartupReceiver">
<intent-filter>
<!-- 系统启动完成后会调用 -->
<action
android:name="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED">
</action>
</intent-filter>
</receiver> 控制对话框位置
window =dialog.getWindow();// 得到对话框的窗口.
WindowManager.LayoutParams wl = window.getAttributes();
wl.x = x;//这两句设置了对话框的位置.0为中间
wl.y =y;
wl.width =w;
wl.height =h;
wl.alpha =0.6f;// 这句设置了对话框的透明度 模拟器错误
1、找到android模拟器安装目录:C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\.android\avd\AVD23.avd
2、编辑config.ini文件,就是这块配置错误导致错误产生。
3、如果硬盘空间比较紧张,可以把模拟器文件放到其它盘符上:你可以在命令行下用mkcard创建一个SDCARD文件,如: mksdcard 50M D:\sdcard.img
4、下面代码可以整个覆盖原来的config文件 hw.sdCard=yes hw.lcd.density=240 skin.path=800×480 skin.name=800×480 vm.heapSize=24 sdcard.path=D:\sdcard.img hw.ramSize=512 image.sysdir.1=platforms\android-8\images\
5、OK,模拟器正常运行挪动dialog的位置
Window mWindow = dialog.getWindow();
WindowManager.LayoutParams lp = mWindow.getAttributes();
lp.x = 10; //新位置X坐标
lp.y = -100; //新位置Y坐标
dialog.onWindowAttributesChanged(lp);屏幕适配
常见手机屏幕像素及对应分别率级别:
ldpi 320*240
mdpi 480*320
hdpi 800*480
xhdpi 1280*720
xxhdpi 1920*1080
dp和px之间的简单换算关系:
ldpi的手机 1dp=0.75px
mdpi的手机 1dp=1.0px
hdpi的手机 1dp=1.5px
xhdpi的手机 1dp=2.0px
xxhdpi的手机 1dp=3.0px
名词解释:
分辨率:eg:480*800,1280*720。表示物理屏幕区域内像素点的总和。(切记:跟屏幕适配没有任何关系)
因为我们既可以把1280*720的分辨率做到4.0的手机上面。我也可以把1280*720的分辨率做到5.0英寸的手机上面,如果分辨率相同,手机屏幕越小清晰。
px(pix):像素,就是屏幕中最小的一个显示单元
dpi(像素密度):即每英寸屏幕所拥有的像素数,像素密度越大,显示画面细节就越丰富。
计算公式:像素密度=√{(长度像素数^2+宽度像素数^2)}/ 屏幕尺寸
注:屏幕尺寸单位为英寸 例:分辨率为1280*720 屏幕宽度为6英寸 计算所得像素密度约等于245,屏幕尺寸指屏幕对角线的长度。
1、屏幕适配方式都有哪些
1.1 适配方式之dp
1.2 适配方式之dimens
在values-1280x720中,中间的是大写字母X的小写形式x,而不是加减乘除的乘号。如果我们在values-1280x720中放置了dimens常量,一定记得也将该常量的对应值在values目录下的dimens.xml中放一份,因为该文件是默认配置,当用户的手机不是1280*720的情况下系统应用使用的是默认values目录中的dimens.xml。
1.3 适配方式之layout
跟values一样,在Android工程目录中layout目录也支持类似values目录一样的适配,在layout中我们可以针对不同手机的分辨率制定不同的布局
1.4 适配方式之java代码适配
为了演示用java代码控制适配的效果,因此假设有这样的需求,让一个TextView控件的宽和高分别为屏幕的宽和高的一半。
//获取TextView控件
TextView tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv);
//找到当前控件的夫控件(父控件上给当前的子控件去设定一个规则)
DisplayMetrics metrics = new DisplayMetrics();
//给当前metrics去设置当前屏幕信息(宽(像素)高(像素))
getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(metrics);
//获取屏幕的高度和宽度
Constant.srceenHeight = metrics.heightPixels;
Constant.srceenWidth = metrics.widthPixels;
//日志输出屏幕的高度和宽度
Log.i(tag, "Constant.srceenHeight = "+Constant.srceenHeight);
Log.i(tag, "Constant.srceenWidth = "+Constant.srceenWidth);
//宽高各 50%
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams layoutParams = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(
//数学角度上 四舍五入
(int)(Constant.srceenWidth*0.5+0.5),
(int)(Constant.srceenHeight*0.5+0.5));
//给tv控件设置布局参数
tv.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
1.5适配方式之weight权重适配
在控件中使用属性android:layout_weight="1"可以起到适配效果,但是该属性的使用有如下规则:
1、只能用在线性控件中,比如LinearLayout。
2、竖直方向上使用权重的控件高度必须为0dp(Google官方的推荐用法)
3、水平方向上使用权重的控件宽度必须为0dp(Google官方的推荐用法)
2、屏幕适配的处理技巧都有哪些
手机自适应主要分为两种情况:横屏和竖屏的切换,以及分辨率大小的不同。
2.1横屏和竖屏的切换
1、Android应用程序支持横竖屏幕的切换,Android中每次屏幕的切换动会重启Activity,所以应该在Activity销毁(执行onPause()方法和onDestroy()方法)前保存当前活动的状态;在Activity再次创建的时候载入配置,那样,进行中的游戏就不会自动重启了!有的程序适合从竖屏切换到横屏,或者反过来,这个时候怎么办呢?可以在配置Activity的地方进行如下的配置android:screenOrientation="portrait"(landscape是横向,portrait是纵向)。这样就可以保证是竖屏总是竖屏了。
2、而有的程序是适合横竖屏切换的。如何处理呢?首先要在配置Activity的时候进行如下的配置:
android:configChanges="keyboardHidden|orientation",另外需要重写Activity的onConfigurationChanged方法。实现方式如下:
@Override
public void onConfigurationChanged(Configuration newConfig){
super.onConfigurationChanged(newConfig);
if(this.getResources().getConfiguration().orientation==Configuration.ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE){
//TODO
}else if(
this.getResources().getConfiguration().orientation==Configuration.ORIENTATION_PORTRAIT){
//TODO
}
}
2.2 分辨率大小不同
对于分辨率问题,官方给的解决办法是创建不同的layout文件夹,这就需要对每种分辨率的手机都要写一个布局文件,虽然看似解决了分辨率的问题,但是如果其中一处或多处有修改了,就要每个布局文件都要做出修改,这样就造成很大的麻烦。那么可以通过以下几种方式解决:
一)使用layout_weight
目前最为推荐的Android多屏幕自适应解决方案。
该属性的作用是决定控件在其父布局中的显示权重,一般用于线性布局中。其值越小,则对应的layout_width或layout_height的优先级就越高(一般到100作用就不太明显了);一般横向布局中,决定的是layout_width的优先级;纵向布局中,决定的是layout_height的优先级。
传统的layout_weight使用方法是将当前控件的layout_width和layout_height都设置成fill_parent,这样就可以把控件的显示比例完全交给layout_weight;这样使用的话,就出现了layout_weight越小,显示比例越大的情况(即权重越大,显示所占的效果越小)。不过对于2个控件还好,如果控件过多,且显示比例也不相同的时候,控制起来就比较麻烦了,毕竟反比不是那么好确定的。于是就有了现在最为流行的0px设值法。看似让人难以理解的layout_height=0px的写法,结合layout_weight,却可以使控件成正比例显示,轻松解决了当前Android开发最为头疼的碎片化问题之一。
二)清单文件配置:【不建议使用这种方式,需要对不同的界面写不同的布局】
需要在AndroidManifest.xml文件的<manifest>元素如下添加子元素
<supports-screensandroid:largeScreens="true"
android:normalScreens="true"
android:anyDensity="true"
android:smallScreens="true"
android:xlargeScreens="true">
</supports-screens>
以上是为我们的屏幕设置多分辨率支持(更准确的说是适配大、中、小三种密度)。
Android:anyDensity="true",这一句对整个的屏幕都起着十分重要的作用,值为true,我们的应用程序当安装在不同密度的手机上时,程序会分别加载hdpi,mdpi,ldpi文件夹中的资源。相反,如果值设置为false,即使我们在hdpi,mdpi,ldpi,xdpi文件夹下拥有同一种资源,那么应用也不会自动地去相应文件夹下寻找资源。而是会在大密度和小密度手机上加载中密度mdpi文件中的资源。
有时候会根据需要在代码中动态地设置某个值,可以在代码中为这几种密度分别设置偏移量,但是这种方法最好不要使用,最好的方式是在xml文件中不同密度的手机进行分别设置。这里地图的偏移量可以在values-xpdi,values-hpdi,values-mdpi,values-ldpi四种文件夹中的dimens.xml文件进行设置。
三)、其他:
说明:
在不同分辨率的手机模拟器下,控件显示的位置会稍有不同
通过在layout中定义的布局设置的参数,使用dp(dip),会根据不同的屏幕分辨率进行适配
但是在代码中的各个参数值,都是使用的像素(px)为单位的
技巧:
1、尽量使用线性布局,相对布局,如果屏幕放不下了,可以使用ScrollView(可以上下拖动)
ScrowView使用的注意:
在不同的屏幕上显示内容不同的情况,其实这个问题我们往往是用滚动视图来解决的,也就是ScrowView;需要注意的是ScrowView中使用layout_weight是无效的,既然使用ScrowView了,就把它里面的控件的大小都设成固定的吧。
2、指定宽高的时候,采用dip的单位,dp单位动态匹配
3、由于android代码中写的单位都是像素,所有需要通过工具类进行转化
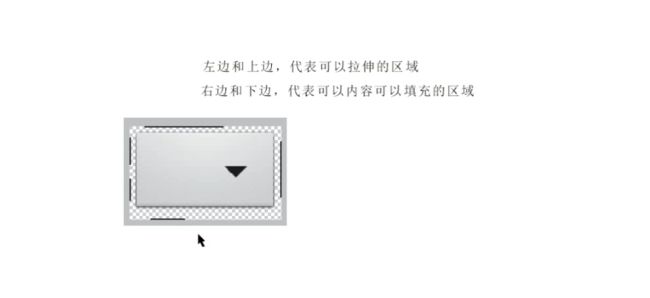
4、尽量使用9-patch图,可以自动的依据图片上面显示的内容被拉伸和收缩。其中在编辑的时候,灰色区域是被拉伸的,上下两个点控制水平方向的拉伸,左右两点控制垂直方向的拉伸
3、dp和px之间的关系
dp:是dip的简写,指密度无关的像素。
指一个抽象意义上的像素,程序用它来定义界面元素。一个与密度无关的,在逻辑尺寸上,与一个位于像素密度为160dpi的屏幕上的像素是一致的。要把密度无关像素转换为屏幕像素,可以用这样一个简单的公式:pixels=dips*(density/160)。举个例子,在DPI为240的屏幕上,1个DIP等于1.5个物理像素。
布局时最好使用dp来定义我们程序的界面,因为这样可以保证我们的UI在各种分辨率的屏幕上都可以正常显示。
/** * 根据手机的分辨率从 px(像素) 的单位 转成为 dp */
public static int px2dip(Context context, float pxValue) {
final float scale = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;
return (int) (pxValue / scale + 0.5f);
}
/** * 根据手机的分辨率从 dip 的单位 转成为 px(像素) */
public static int dip2px(Context context, float dpValue) {
final float scale = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;
return (int) (dpValue * scale + 0.5f);
} 设置APN
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put(NAME, "CMCC cmwap");
values.put(APN, "cmwap");
values.put(PROXY, "10.0.0.172");
values.put(PORT, "80");
values.put(MMSPROXY, "");
values.put(MMSPORT, "");
values.put(USER, "");
values.put(SERVER, "");
values.put(PASSWORD, "");
values.put(MMSC, "");
values.put(TYPE, "");
values.put(MCC, "460");
values.put(MNC, "00");
values.put(NUMERIC, "46000");
reURI = getContentResolver().insert(Uri.parse("content://telephony/carriers"), values);
//首选接入点"content://telephony/carriers/preferapn"调节屏幕亮度
public void setBrightness(int level) {
ContentResolver cr = getContentResolver();
Settings.System.putInt(cr, "screen_brightness", level);
Window window = getWindow();
LayoutParams attributes = window.getAttributes();
float flevel = level;
attributes.screenBrightness = flevel / 255;
getWindow().setAttributes(attributes);
} 重启
第一,root权限,这是必须的
第二,Runtime.getRuntime().exec("su -c reboot");
第三,模拟器上运行不出来,必须真机
第四,运行时会提示你是否加入列表 , 同意就好拍照、录音、录像
package com.cons.dcg.collect;
import java.io.File;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.*;
import android.app.*;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.provider.MediaStore;
import android.view.*;
import android.widget.*;
public class RecordActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private static final int RESULT_CAPTURE_IMAGE = 1;// 照相的requestCode
private static final int REQUEST_CODE_TAKE_VIDEO = 2;// 摄像的照相的requestCode
private static final int RESULT_CAPTURE_RECORDER_SOUND = 3;// 录音的requestCode
private String strImgPath = "";// 照片文件绝对路径
private String strVideoPath = "";// 视频文件的绝对路径
private String strRecorderPath = "";// 录音文件的绝对路径
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
this.setContentView(R.layout.problem_report);
}
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
switch (requestCode) {
case RESULT_CAPTURE_IMAGE://拍照
if (resultCode == RESULT_OK) {
Toast.makeText(this, strImgPath, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
break;
case REQUEST_CODE_TAKE_VIDEO://拍摄视频
if (resultCode == RESULT_OK) {
Uri uriVideo = data.getData();
Cursor cursor=this.getContentResolver().query(uriVideo, null, null, null, null);
if (cursor.moveToNext()) {
/** _data:文件的绝对路径 ,_display_name:文件名 */
strVideoPath = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("_data"));
Toast.makeText(this, strVideoPath, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
break;
case RESULT_CAPTURE_RECORDER_SOUND://录音
if (resultCode == RESULT_OK) {
Uri uriRecorder = data.getData();
Cursor cursor=this.getContentResolver().query(uriRecorder, null, null, null, null);
if (cursor.moveToNext()) {
/** _data:文件的绝对路径 ,_display_name:文件名 */
strRecorderPath = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("_data"));
Toast.makeText(this, strRecorderPath, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
break;
}
}
/** * 照相功能 */
private void cameraMethod() {
Intent imageCaptureIntent = new Intent(MediaStore.ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURE);
strImgPath = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().toString() + "/CONSDCGMPIC/";//存放照片的文件夹
String fileName = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmss").format(new Date()) + ".jpg";//照片命名
File out = new File(strImgPath);
if (!out.exists()) {
out.mkdirs();
}
out = new File(strImgPath, fileName);
strImgPath = strImgPath + fileName;//该照片的绝对路径
Uri uri = Uri.fromFile(out);
imageCaptureIntent.putExtra(MediaStore.EXTRA_OUTPUT, uri);
imageCaptureIntent.putExtra(MediaStore.EXTRA_VIDEO_QUALITY, 1);
startActivityForResult(imageCaptureIntent, RESULT_CAPTURE_IMAGE);
}
/** * 拍摄视频 */
private void videoMethod() {
Intent intent = new Intent(MediaStore.ACTION_VIDEO_CAPTURE);
intent.putExtra(MediaStore.EXTRA_VIDEO_QUALITY, 0);
startActivityForResult(intent, REQUEST_CODE_TAKE_VIDEO);
}
/** * 录音功能 */
private void soundRecorderMethod() {
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_GET_CONTENT);
intent.setType("audio/amr");
startActivityForResult(intent, RESULT_CAPTURE_RECORDER_SOUND);
}
/** * 提示信息 * @param text * @param duration */
private void showToast(String text, int duration) {
Toast.makeText(ProblemReport.this, text, duration).show();
}
}隐藏软键盘
getWindow().setSoftInputMode(WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_ADJUST_RESIZE | WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_STATE_HIDDEN);隐藏以及显示软键盘以及不自动弹出键盘的方法
1、//隐藏软键盘
((InputMethodManager)getSystemService(INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE)).hideSoftInputFromWindow(WidgetSearchActivity.this.getCurrentFocus().getWindowToken(), InputMethodManager.HIDE_NOT_ALWAYS);
2、//显示软键盘,控件ID可以是EditText,TextView
((InputMethodManager)getSystemService(INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE)).showSoftInput(控件ID, 0); BitMap、Drawable、inputStream及byte[] 互转
(1) BitMap to inputStream:
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
bm.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.PNG, 100, baos);
InputStream isBm = new ByteArrayInputStream(baos .toByteArray());
(2)BitMap to byte[]:
Bitmap defaultIcon = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(in);
ByteArrayOutputStream stream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
defaultIcon.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.JPEG, 100, stream);
byte[] bitmapdata = stream.toByteArray();
(3)Drawable to byte[]:
Drawable d; // the drawable (Captain Obvious, to the rescue!!!)
Bitmap bitmap = ((BitmapDrawable)d).getBitmap();
ByteArrayOutputStream stream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
defaultIcon.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.JPEG, 100, bitmap);
byte[] bitmapdata = stream.toByteArray();
(4)byte[] to Bitmap :
Bitmap bitmap =BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(byte[], 0,byte[].length);drawable转bitmap
/** * drawableתbitmap * * @param drawable * @return */
private Bitmap drawableToBitamp(Drawable drawable)
{
if (drawable instanceof BitmapDrawable)
{
BitmapDrawable bd = (BitmapDrawable) drawable;
return bd.getBitmap();
}
int w = drawable.getIntrinsicWidth();
int h = drawable.getIntrinsicHeight();
Bitmap bitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(w, h, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(bitmap);
drawable.setBounds(0, 0, w, h);
drawable.draw(canvas);
return bitmap;
}Android目录结构
data
- app:用户安装的应用
- data:应用的专属文件夹
- system:系统的配置信息,注册表文件
- anr:anr异常的记录信息
dev:devices的缩写
- 存放设备所对应的文件
mnt:mount的缩写
- 挂载在系统上的设备:sdcard,u盘
proc:硬件配置,状态信息
- cpuinfo、meminfo
sbin:system bin
- 系统重要的二进制执行文件
- adbd:服务器的adb进程
system:
- app:存放系统应用,默认不能删除
- bin:Android中可执行的linux指令文件
- etc:host:主机名和ip地址的映射
- fonts:Android中自带的字体
- framework:存放谷歌提供的java api
- lib:核心功能的类库,C/C++文件
- media/audio:存放Android的音效文件
- tts:语音发声引擎,默认不支持中文
- usr:用户设备的配置信息,键盘编码和按键编码的映射
- xbin:是专为开发人员准备的二进制指令
Android下的Linux指令
- su:superuser
- 切换到超级用户
- rm:remove,删除文件
- rm 文件名
- ls:列出目录下的所有文件和文件夹
- ls -l:查看文件的详细信息
- ls -a:查看隐藏文件
- cd:切换到某个目录
- cat:查看文件内容
- cat 文件名
- 不要cat二进制可执行文件
- mv:move 修改文件名
- mv 原文件名 新文件名
- mkdir:创建文件夹
- mkdir 文件夹名字
- rmdir:删除文件夹
- rmdir 文件夹名字
- touch:创建新文件
- touch 文件名
- chmod:change mode,切换文件访问权限
- chmod 777 文件名
- echo:回显数据;重定向数据
- echo 数据 > 文件名
- sleep:睡眠几秒
- df:显示指定目录的容量
- id:打印当前用户的id
- uid=0:root
- uid=1000:system
- uid=2000:shell
- uid=10000+:一般应用程序的id
- ps:列出系统中运行的所有进程
- kill:杀死指定pid的进程
- kill pid
- chown:change owner,修改拥有者
- chown 0.0 文件名
- mount:挂载文件系统
- mount -o remount rw /:挂载当前目录为可读可写权限
- mount -o remount rw /system:重新挂载指定目录
Android中特有的指令
am:ActivityManager,可以进行跟activity相关的操作
- am start -n com.test.createfile/com.test.createfile.MainActivity:开启指定Activity
- am kill com.test.createfile:结束非前台进程
- am force-stop com.test.createfile:结束进程
pm:PackageManager
- pm disable 包名:冻结指定应用
- pm enable 包名:解冻指定应用
monkey -p com.test.createfile 1000:自动点击指定应用1000次
刷模拟器,rom写文件(su)
- 如果想让真实手机运行这些指令,手机必须要有root权限
- 刷root原理:把su二进制文件拷贝到/system/bin或者/system/xbin
- Android刷root软件,工作的原理全部都是利用系统的漏洞实现
- rom:可以理解为android系统的安装文件
- 把su文件和superuser.apk写入img文件
- 执行su指令
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(“su”);
修改字体
- 把ttf文件刷进img中
- Android系统默认的中文字体为DroidSansFallBack.ttf
- 用你想使用的字体ttf文件替换掉这个文件即可
修改开机动画
- 从真机中得到bootanimation.zip
- 把bootanimation.zip放入system/media目录下
删除锁屏密码
- 删除data/system下的key文件
- 文本密码为password.key
- 手势密码为gesture.key
关于9path
上传代码到github
1、github创建库
2、进入创建好的Android项目目录
3、配置邮箱和用户名,这样就可以表示是谁提交的了
git config --global user.name "Lemoner"
git config --flobal user.email "[email protected]"
4、开始拷贝下来的GitHub仓库地址了,把它拷贝过来
git clone https://github.com/Lemoner/demo.git
5、看到一个跟GitHub仓库同名的目录,把里面的文件都拷贝到上一级目录,GitHub的同名目录就可以删掉了。
下面输入命令将文件添加进版本控制:
git add .
注意add后面的空格是一定要加的,不然会报错。
添加进来之后,执行提交命令
git commit -m "My First Commit"
这样就将修改提交到了本地仓库
接下来将本地仓库内容上传到GitHub上
git push origin master
最后一步如果没有登录可能需要你的GitHub密码,直接按照提示输入就好了