SparkStreaming之基本数据源输入
输入DStreams表示从数据源获取的原始数据流。Spark Streaming拥有两类数据源
(1)基本源(Basic sources):这些源在StreamingContext API中直接可用。例如文件系统、套接字连接、
Akka的actor等。
(2)高级源(Advanced sources):这些源包括Kafka,Flume,Kinesis,Twitter等等。
1、基本数据源输入源码
SparkStream 对于外部的数据输入源,一共有下面几种:
(1)用户自定义的数据源:receiverStream
(2)根据TCP协议的数据源: socketTextStream、socketStream
(3)网络数据源:rawSocketStream
(4)hadoop文件系统输入源:fileStream、textFileStream、binaryRecordsStream
(5)其他输入源(队列形式的RDD):queueStream
<span style="font-size:18px;">/**
* Create an input stream with any arbitrary user implemented receiver.
* Find more details at http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/streaming-custom-receivers.html
* @param receiver Custom implementation of Receiver
*/
def receiverStream[T: ClassTag](receiver: Receiver[T]): ReceiverInputDStream[T] = {
withNamedScope("receiver stream") {
new PluggableInputDStream[T](this, receiver)
}
}
/**
* Creates an input stream from TCP source hostname:port. Data is received using
* a TCP socket and the receive bytes is interpreted as UTF8 encoded `\n` delimited
* lines.
* @param hostname Hostname to connect to for receiving data
* @param port Port to connect to for receiving data
* @param storageLevel Storage level to use for storing the received objects
* (default: StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER_2)
* @see [[socketStream]]
*/
def socketTextStream(
hostname: String,
port: Int,
storageLevel: StorageLevel = StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER_2
): ReceiverInputDStream[String] = withNamedScope("socket text stream") {
socketStream[String](hostname, port, SocketReceiver.bytesToLines, storageLevel)
}
/**
* Creates an input stream from TCP source hostname:port. Data is received using
* a TCP socket and the receive bytes it interpreted as object using the given
* converter.
* @param hostname Hostname to connect to for receiving data
* @param port Port to connect to for receiving data
* @param converter Function to convert the byte stream to objects
* @param storageLevel Storage level to use for storing the received objects
* @tparam T Type of the objects received (after converting bytes to objects)
*/
def socketStream[T: ClassTag](
hostname: String,
port: Int,
converter: (InputStream) => Iterator[T],
storageLevel: StorageLevel
)
: ReceiverInputDStream[T] = {
new SocketInputDStream[T](this, hostname, port, converter, storageLevel)
}
/**
* Create a input stream from network source hostname:port, where data is received
* as serialized blocks (serialized using the Spark's serializer) that can be directly
* pushed into the block manager without deserializing them. This is the most efficient
* way to receive data.
* @param hostname Hostname to connect to for receiving data
* @param port Port to connect to for receiving data
* @param storageLevel Storage level to use for storing the received objects
* (default: StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER_2)
* @tparam T Type of the objects in the received blocks
*/
def rawSocketStream[T: ClassTag](
hostname: String,
port: Int,
storageLevel: StorageLevel = StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER_2
)
: ReceiverInputDStream[T] = withNamedScope("raw socket stream") {
new RawInputDStream[T](this, hostname, port, storageLevel)
}
/**
* Create a input stream that monitors a Hadoop-compatible filesystem
* for new files and reads them using the given key-value types and input format.
* Files must be written to the monitored directory by "moving" them from another
* location within the same file system. File names starting with . are ignored.
* @param directory HDFS directory to monitor for new file
* @tparam K Key type for reading HDFS file
* @tparam V Value type for reading HDFS file
* @tparam F Input format for reading HDFS file
*/
def fileStream[
K: ClassTag,
V: ClassTag,
F <: NewInputFormat[K, V]: ClassTag
] (directory: String): InputDStream[(K, V)] = {
new FileInputDStream[K, V, F](this, directory)
}
/**
* Create a input stream that monitors a Hadoop-compatible filesystem
* for new files and reads them using the given key-value types and input format.
* Files must be written to the monitored directory by "moving" them from another
* location within the same file system.
* @param directory HDFS directory to monitor for new file
* @param filter Function to filter paths to process
* @param newFilesOnly Should process only new files and ignore existing files in the directory
* @tparam K Key type for reading HDFS file
* @tparam V Value type for reading HDFS file
* @tparam F Input format for reading HDFS file
*/
def fileStream[
K: ClassTag,
V: ClassTag,
F <: NewInputFormat[K, V]: ClassTag
] (directory: String, filter: Path => Boolean, newFilesOnly: Boolean): InputDStream[(K, V)] = {
new FileInputDStream[K, V, F](this, directory, filter, newFilesOnly)
}
/**
* Create a input stream that monitors a Hadoop-compatible filesystem
* for new files and reads them using the given key-value types and input format.
* Files must be written to the monitored directory by "moving" them from another
* location within the same file system. File names starting with . are ignored.
* @param directory HDFS directory to monitor for new file
* @param filter Function to filter paths to process
* @param newFilesOnly Should process only new files and ignore existing files in the directory
* @param conf Hadoop configuration
* @tparam K Key type for reading HDFS file
* @tparam V Value type for reading HDFS file
* @tparam F Input format for reading HDFS file
*/
def fileStream[
K: ClassTag,
V: ClassTag,
F <: NewInputFormat[K, V]: ClassTag
] (directory: String,
filter: Path => Boolean,
newFilesOnly: Boolean,
conf: Configuration): InputDStream[(K, V)] = {
new FileInputDStream[K, V, F](this, directory, filter, newFilesOnly, Option(conf))
}
/**
* Create a input stream that monitors a Hadoop-compatible filesystem
* for new files and reads them as text files (using key as LongWritable, value
* as Text and input format as TextInputFormat). Files must be written to the
* monitored directory by "moving" them from another location within the same
* file system. File names starting with . are ignored.
* @param directory HDFS directory to monitor for new file
*/
def textFileStream(directory: String): DStream[String] = withNamedScope("text file stream") {
fileStream[LongWritable, Text, TextInputFormat](directory).map(_._2.toString)
}
/**
* Create an input stream that monitors a Hadoop-compatible filesystem
* for new files and reads them as flat binary files, assuming a fixed length per record,
* generating one byte array per record. Files must be written to the monitored directory
* by "moving" them from another location within the same file system. File names
* starting with . are ignored.
*
* '''Note:''' We ensure that the byte array for each record in the
* resulting RDDs of the DStream has the provided record length.
*
* @param directory HDFS directory to monitor for new file
* @param recordLength length of each record in bytes
*/
def binaryRecordsStream(
directory: String,
recordLength: Int): DStream[Array[Byte]] = withNamedScope("binary records stream") {
val conf = _sc.hadoopConfiguration
conf.setInt(FixedLengthBinaryInputFormat.RECORD_LENGTH_PROPERTY, recordLength)
val br = fileStream[LongWritable, BytesWritable, FixedLengthBinaryInputFormat](
directory, FileInputDStream.defaultFilter: Path => Boolean, newFilesOnly = true, conf)
val data = br.map { case (k, v) =>
val bytes = v.getBytes
require(bytes.length == recordLength, "Byte array does not have correct length. " +
s"${bytes.length} did not equal recordLength: $recordLength")
bytes
}
data
}
/**
* Create an input stream from a queue of RDDs. In each batch,
* it will process either one or all of the RDDs returned by the queue.
*
* NOTE: Arbitrary RDDs can be added to `queueStream`, there is no way to recover data of
* those RDDs, so `queueStream` doesn't support checkpointing.
*
* @param queue Queue of RDDs. Modifications to this data structure must be synchronized.
* @param oneAtATime Whether only one RDD should be consumed from the queue in every interval
* @tparam T Type of objects in the RDD
*/
def queueStream[T: ClassTag](
queue: Queue[RDD[T]],
oneAtATime: Boolean = true
): InputDStream[T] = {
queueStream(queue, oneAtATime, sc.makeRDD(Seq[T](), 1))
}
/**
* Create an input stream from a queue of RDDs. In each batch,
* it will process either one or all of the RDDs returned by the queue.
*
* NOTE: Arbitrary RDDs can be added to `queueStream`, there is no way to recover data of
* those RDDs, so `queueStream` doesn't support checkpointing.
*
* @param queue Queue of RDDs. Modifications to this data structure must be synchronized.
* @param oneAtATime Whether only one RDD should be consumed from the queue in every interval
* @param defaultRDD Default RDD is returned by the DStream when the queue is empty.
* Set as null if no RDD should be returned when empty
* @tparam T Type of objects in the RDD
*/
def queueStream[T: ClassTag](
queue: Queue[RDD[T]],
oneAtATime: Boolean,
defaultRDD: RDD[T]
): InputDStream[T] = {
new QueueInputDStream(this, queue, oneAtATime, defaultRDD)
}
</span>
2、实验
2.1 用户自定义的数据输入源实验
第一步:创建外部scoket端,数据流模式器,程序如下:
<span style="font-size:18px;">import java.io.{PrintWriter}
import java.net.ServerSocket
import scala.io.Source
object streamingSimulation {
def index(n: Int) = scala.util.Random.nextInt(n)
def main(args: Array[String]) {
// 调用该模拟器需要三个参数,分为为文件路径、端口号和间隔时间(单位:毫秒)
if (args.length != 3) {
System.err.println("Usage: <filename> <port> <millisecond>")
System.exit(1)
}
// 获取指定文件总的行数
val filename = args(0)
val lines = Source.fromFile(filename).getLines.toList
val filerow = lines.length
// 指定监听某端口,当外部程序请求时建立连接
val listener = new ServerSocket(args(1).toInt)
while (true) {
val socket = listener.accept()
new Thread() {
override def run = {
println("Got client connected from: " + socket.getInetAddress)
val out = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(), true)
while (true) {
Thread.sleep(args(2).toLong)
// 当该端口接受请求时,随机获取某行数据发送给对方
val content = lines(index(filerow))
println("-------------------------------------------")
println(s"Time: ${System.currentTimeMillis()}")
println("-------------------------------------------")
println(content)
out.write(content + '\n')
out.flush()
}
socket.close()
}
}.start()
}
}
}
</span>
第二步:对上面文件进行 jar文件的打包,并放入到集群目录中
启动程序如下:
<span style="font-size:18px;">java -cp DataSimulation.jar streamingSimulation /root/application/upload/Information 9999 1000</span>
其中DataSimulation.jar是你打包的jar文件名字,streamingSimulation是你這个jar文件的main函数,
root/application/upload/Information 是数据文件 information 的位置,information内部数据如下:
9999是端口号
1000(ms)是发送数据间隔时间
第三步,编写自己的receiver函数和SparkStreaming程序,程序如下:
<span style="font-size:18px;">import java.io.{BufferedReader, InputStreamReader}
import java.net.Socket
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets
import org.apache.spark.{Logging, SparkConf}
import org.apache.spark.storage.StorageLevel
import org.apache.spark.streaming.{Seconds, StreamingContext}
import org.apache.spark.streaming.receiver.Receiver
/**
* Custom Receiver that receives data over a socket. Received bytes are interpreted as
* text and \n delimited lines are considered as records. They are then counted and printed.
*
* To run this on your local machine, you need to first run a Netcat server
* `$ nc -lk 9999`
* and then run the example
* `$ bin/run-example org.apache.spark.examples.streaming.CustomReceiver localhost 9999`
*/
object CustomReceiver {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
if (args.length < 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: CustomReceiver <hostname> <port>")
System.exit(1)
}
// Create the context with a 1 second batch size
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("CustomReceiver").setMaster("local[4]")
val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(1))
// Create an input stream with the custom receiver on target ip:port and count the
// words in input stream of \n delimited text (eg. generated by 'nc')
val lines = ssc.receiverStream(new CustomReceiver(args(0), args(1).toInt))
val words = lines.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val wordCounts = words.map(x => (x, 1)).reduceByKey(_ + _)
wordCounts.print()
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()
}
}
class CustomReceiver(host: String, port: Int)
extends Receiver[String](StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_2) with Logging {
def onStart() {
// Start the thread that receives data over a connection
new Thread("Socket Receiver") {
override def run() { receive() }
}.start()
}
def onStop() {
// There is nothing much to do as the thread calling receive()
// is designed to stop by itself isStopped() returns false
}
/** Create a socket connection and receive data until receiver is stopped */
private def receive() {
var socket: Socket = null
var userInput: String = null
try {
logInfo("Connecting to " + host + ":" + port)
socket = new Socket(host, port)
logInfo("Connected to " + host + ":" + port)
val reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))
userInput = reader.readLine()
while(!isStopped && userInput != null) {
store(userInput)
userInput = reader.readLine()
}
reader.close()
socket.close()
logInfo("Stopped receiving")
restart("Trying to connect again")
} catch {
case e: java.net.ConnectException =>
restart("Error connecting to " + host + ":" + port, e)
case t: Throwable =>
restart("Error receiving data", t)
}
}
}</span>
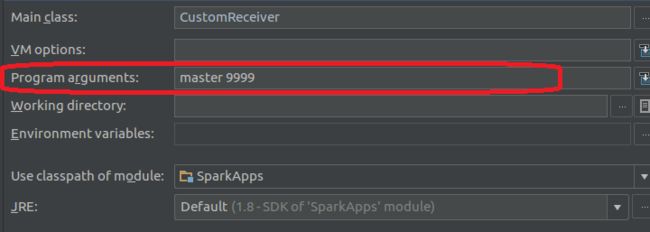
第四步、配置完运行CustomReceiver的函数
第五步、运行程序
2.2 根据TCP协议的数据源实验
(1)socketTextStream函数
第一步:数据模拟,参考前面
第二步:编写SparkStreaming程序,程序如下:
<span style="font-size:18px;">import org.apache.log4j.{Level, Logger}
import org.apache.spark.streaming.{Seconds, StreamingContext}
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
/**
* Created by legotime on 6/1/16.
*/
object TCPOnStreaming {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
Logger.getLogger("org.apache.spark").setLevel(Level.ERROR)
Logger.getLogger("org.eclipse.jetty.Server").setLevel(Level.OFF)
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("TCPOnStreaming example").setMaster("local[4]")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val ssc = new StreamingContext(sc,Seconds(2))
//set the Checkpoint directory
ssc.checkpoint("/Res")
//get the socket Streaming data
val socketStreaming = ssc.socketTextStream("master",9999)
val data = socketStreaming.map(x =>(x,1))
data.print()
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()
}
}</span>
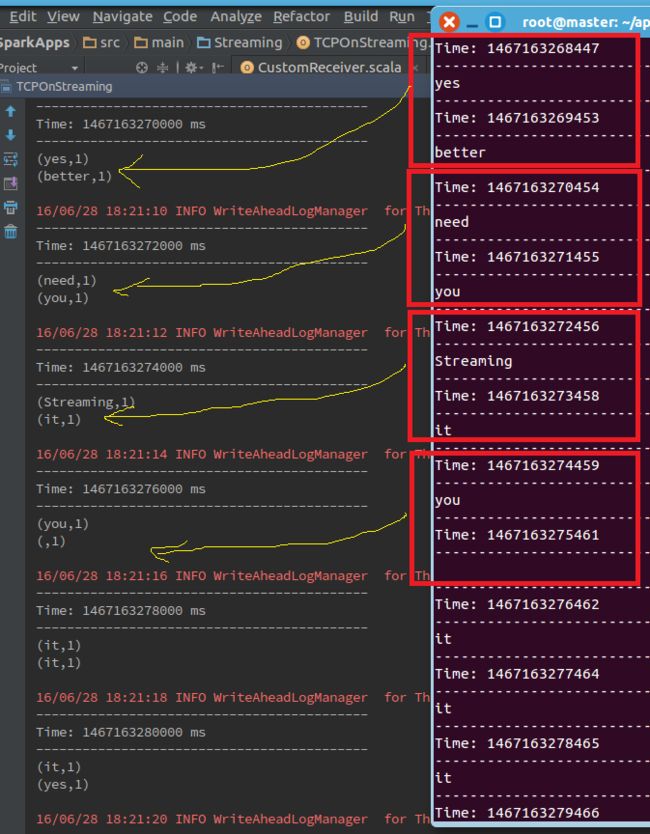
第三步,运行程序,结果如下:
(2)socketStream函数
第一步:数据模拟,参考前面
第二步:编写SparkStreaming程序,程序如下:
<span style="font-size:18px;">import java.io.{InputStream}
import org.apache.log4j.{Level, Logger}
import org.apache.spark.storage.StorageLevel
import org.apache.spark.streaming.{Seconds, StreamingContext}
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
/**
* Created by legotime on 6/1/16.
*/
object socketStreamData {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
Logger.getLogger("org.apache.spark").setLevel(Level.ERROR)
Logger.getLogger("org.eclipse.jetty.Server").setLevel(Level.OFF)
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("<span style="font-family: 宋体;">socketStreamData</span>").setMaster("local[4]")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val ssc = new StreamingContext(sc,Seconds(2))
//set the Checkpoint directory
ssc.checkpoint("/Res")
val SocketData = ssc.socketStream[String]("master",9999,myDeserialize,StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER )
//val data = SocketData.map(x =>(x,1))
//data.print()
SocketData.print()
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()
}
def myDeserialize(data:InputStream): Iterator[String]={
data.read().toString.map( x => x.hashCode().toString).iterator
}
}
</span>
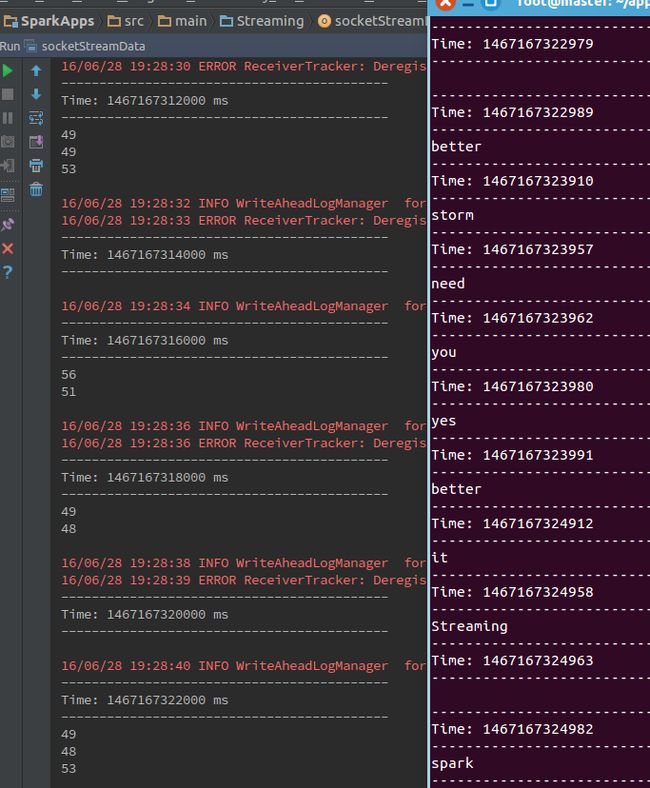
第三步,运行程序,结果如下:
2.3 网络数据源:rawSocketStream
<span style="font-size:18px;">import org.apache.spark.SparkConf
import org.apache.spark.storage.StorageLevel
import org.apache.spark.streaming._
import org.apache.spark.util.IntParam
/**
* Receives text from multiple rawNetworkStreams and counts how many '\n' delimited
* lines have the word 'the' in them. This is useful for benchmarking purposes. This
* will only work with spark.streaming.util.RawTextSender running on all worker nodes
* and with Spark using Kryo serialization (set Java property "spark.serializer" to
* "org.apache.spark.serializer.KryoSerializer").
* Usage: RawNetworkGrep <numStreams> <host> <port> <batchMillis>
* <numStream> is the number rawNetworkStreams, which should be same as number
* of work nodes in the cluster
* <host> is "localhost".
* <port> is the port on which RawTextSender is running in the worker nodes.
* <batchMillise> is the Spark Streaming batch duration in milliseconds.
*/
object RawNetworkGrep {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
if (args.length != 4) {
System.err.println("Usage: RawNetworkGrep <numStreams> <host> <port> <batchMillis>")
System.exit(1)
}
StreamingExamples.setStreamingLogLevels()
val Array(IntParam(numStreams), host, IntParam(port), IntParam(batchMillis)) = args
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("RawNetworkGrep")
// Create the context
val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Duration(batchMillis))
val rawStreams = (1 to numStreams).map(_ =>
ssc.rawSocketStream[String](host, port, StorageLevel.MEMORY_ONLY_SER_2)).toArray
val union = ssc.union(rawStreams)
union.filter(_.contains("the")).count().foreachRDD(r =>
println("Grep count: " + r.collect().mkString))
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()
}
}</span>
2.4 hadoop文件系统输入源:fileStream、textFileStream、binaryRecordsStream(1)fileStream函数
(2)textFileStream函数
第一步、写好SparkStreaming程序,并启动
<span style="font-size:18px;">import org.apache.log4j.{Level, Logger}
import org.apache.spark.streaming.{Seconds, StreamingContext}
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
object fileStreamData {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
Logger.getLogger("org.apache.spark").setLevel(Level.ERROR)
Logger.getLogger("org.eclipse.jetty.Server").setLevel(Level.OFF)
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("fileStreamData").setMaster("local[2]")
val sc =new SparkContext(conf)
val ssc = new StreamingContext(sc, Seconds(2))
//fileStream 用法
//val lines = ssc.fileStream[LongWritable, Text, TextInputFormat]("hdfs:///examples/").map{ case (x, y) => (x.toString, y.toString) }
//val lines = ssc.fileStream[LongWritable, Text, TextInputFormat]("/root/application/dataDir/").map{ case (x, y) => (x.toString, y.toString) }
//lines.print()
val lines = ssc.textFileStream("/root/application/dataDir/")
val wordCount = lines.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map(x => (x,1)).reduceByKey(_+_)
wordCount.print()
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()
}
}</span>
第二步,在textFileStream指定目录输入文件
第三步、查看结果
2.5 其他输入源(队列形式的RDD):queueStream
直接运行下面程序
<span style="font-size:18px;">import scala.collection.mutable.Queue
import org.apache.spark.SparkConf
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.streaming.{Seconds, StreamingContext}
object QueueStream {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("QueueStream").setMaster("local[4]")
// Create the context
val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(1))
// Create the queue through which RDDs can be pushed to
// a QueueInputDStream
val rddQueue = new Queue[RDD[Int]]()
// Create the QueueInputDStream and use it do some processing
val inputStream = ssc.queueStream(rddQueue)
val mappedStream = inputStream.map(x => (x % 10, 1))
val reducedStream = mappedStream.reduceByKey(_ + _)
reducedStream.print()
ssc.start()
// Create and push some RDDs into rddQueue
for (i <- 1 to 30) {
rddQueue.synchronized {
rddQueue += ssc.sparkContext.makeRDD(1 to 1000, 10)
}
Thread.sleep(1000)
}
ssc.stop()
}
}
</span>
结果