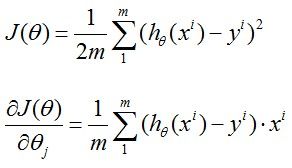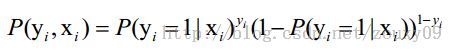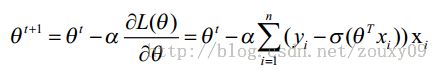机器学习--线性回归、逻辑回归
一、线性回归
线性回归无非就是训练得到线性函数的参数来回归出一个线性模型,学习《最优化方法》时中的最小二乘问题就是线性回归的问题。
关于线性回归,ng老师的视频里有讲,也可以看此博客单参数线性回归。简要说一下线性回归的原理。
假设拟合直线为h(x)=θ0+θ1*x, 记Cost Function为J(θ0,θ1)
这其实就是一个线性回归问题,上式也是一个最小二乘问题的模型。盗的图,我认为式中1/m完全没必要,还增加运算,完全可以删掉。线性回归就是要用数据训练出来参数θ,训练时要使目标函数最小,其中x(i)和y(i)中的i表示第i条样本数据,这就是一个无约束优化的问题,关于无约束优化问题的解决方法有很多,比如梯度下降,共轭梯度、牛顿法、步长加速法等等。关于无约束优化和最小二乘问题可以看《最优化方法》相关的书,都有很详细的讲解。这里用最简单的梯度下降。
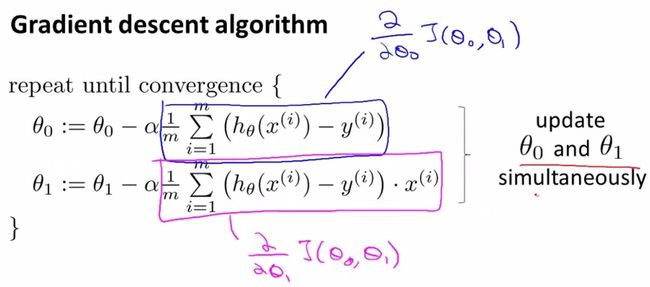
需要朝着目标函数J梯度下降的方向迭代更行参数θ,
由此
以上就是线性回归了。
二、逻辑回归
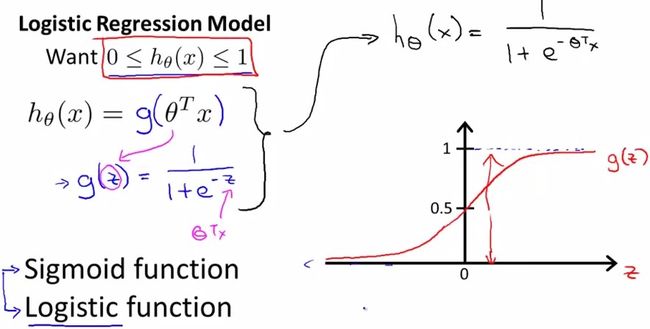
线性回归能到一个模型来进行预测,要想用来分类,就要用到逻辑回归。
要分类,就要把h(x)的结果限制在0~1范围内,引入sigmoid函数
假设我们的样本是{x, y},y是0或者1,表示正类或者负类,x是我们的m维的样本特征向量。那么这个样本x属于正类,也就是y=1的“概率”可以通过下面的逻辑函数来表示:
所以说,LogisticRegression 就是一个被logistic方程归一化后的线性回归,仅此而已。
怎么来构造代价函数,就用到最大似然,关于最大似然估计,本科概率论有相关知识。
假设我们有n个独立的训练样本{(x1, y1) ,(x2, y2),…, (xn, yn)},y={0, 1}。那每一个观察到的样本(xi, yi)出现的概率是:
那最大似然法就是求模型中使得似然函数最大的系数取值θ*。这个最大似然就是我们的代价函数(cost function)了。
这时候,用L(θ)对θ求导,得到:
下一步要做的就是优化求解了。所以以上都只是推导过程, 真正用到的就是这个式子 。三、优化
这一块可以看这篇博客逻辑回归,讲的很细。其实该篇博客主要内容来自《机器学习实战》
注意梯度下降和随机梯度下降的区别。梯度下降每一次迭代都要把整个数据来求导,随即梯度下降则是每一次迭代只用一个样本数据,梯度下降适合小数据,随即梯度下降适合大数据集。
四、总结
所以其实逻辑回归实现时真正用到的就是
每一次对上式迭代
关于matlab代码,上面博客作者的博客里有相关代码,但她是调用了无约束优化的相关函数,所以实现很简单,另外关于正则化的实现我认为她代码不对
上面的博客里有python的代码,《机器学习实战》也有。
- #################################################
- # logRegression: Logistic Regression
- # Author : zouxy
- # Date : 2014-03-02
- # HomePage : http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09
- # Email : [email protected]
- #################################################
- from numpy import *
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import time
- # calculate the sigmoid function
- def sigmoid(inX):
- return 1.0 / (1 + exp(-inX))
- # train a logistic regression model using some optional optimize algorithm
- # input: train_x is a mat datatype, each row stands for one sample
- # train_y is mat datatype too, each row is the corresponding label
- # opts is optimize option include step and maximum number of iterations
- def trainLogRegres(train_x, train_y, opts):
- # calculate training time
- startTime = time.time()
- numSamples, numFeatures = shape(train_x)
- alpha = opts['alpha']; maxIter = opts['maxIter']
- weights = ones((numFeatures, 1))
- # optimize through gradient descent algorilthm
- for k in range(maxIter):
- if opts['optimizeType'] == 'gradDescent': # gradient descent algorilthm
- output = sigmoid(train_x * weights)
- error = train_y - output
- weights = weights + alpha * train_x.transpose() * error
- elif opts['optimizeType'] == 'stocGradDescent': # stochastic gradient descent#对于大数据集就不要让随即梯度下降在k循环下循环了,
- for i in range(numSamples):
- output = sigmoid(train_x[i, :] * weights)
- error = train_y[i, 0] - output
- weights = weights + alpha * train_x[i, :].transpose() * error
- elif opts['optimizeType'] == 'smoothStocGradDescent': # smooth stochastic gradient descent
- # randomly select samples to optimize for reducing cycle fluctuations
- dataIndex = range(numSamples)
- for i in range(numSamples):
- alpha = 4.0 / (1.0 + k + i) + 0.01
- randIndex = int(random.uniform(0, len(dataIndex)))
- output = sigmoid(train_x[randIndex, :] * weights)
- error = train_y[randIndex, 0] - output
- weights = weights + alpha * train_x[randIndex, :].transpose() * error
- del(dataIndex[randIndex]) # during one interation, delete the optimized sample
- else:
- raise NameError('Not support optimize method type!')
- print 'Congratulations, training complete! Took %fs!' % (time.time() - startTime)
- return weights
- # test your trained Logistic Regression model given test set
- def testLogRegres(weights, test_x, test_y):
- numSamples, numFeatures = shape(test_x)
- matchCount = 0
- for i in xrange(numSamples):
- predict = sigmoid(test_x[i, :] * weights)[0, 0] > 0.5
- if predict == bool(test_y[i, 0]):
- matchCount += 1
- accuracy = float(matchCount) / numSamples
- return accuracy
- # show your trained logistic regression model only available with 2-D data
- def showLogRegres(weights, train_x, train_y):
- # notice: train_x and train_y is mat datatype
- numSamples, numFeatures = shape(train_x)
- if numFeatures != 3:
- print "Sorry! I can not draw because the dimension of your data is not 2!"
- return 1
- # draw all samples
- for i in xrange(numSamples):
- if int(train_y[i, 0]) == 0:
- plt.plot(train_x[i, 1], train_x[i, 2], 'or')
- elif int(train_y[i, 0]) == 1:
- plt.plot(train_x[i, 1], train_x[i, 2], 'ob')
- # draw the classify line
- min_x = min(train_x[:, 1])[0, 0]
- max_x = max(train_x[:, 1])[0, 0]
- weights = weights.getA() # convert mat to array
- y_min_x = float(-weights[0] - weights[1] * min_x) / weights[2]
- y_max_x = float(-weights[0] - weights[1] * max_x) / weights[2]
- plt.plot([min_x, max_x], [y_min_x, y_max_x], '-g')
- plt.xlabel('X1'); plt.ylabel('X2')
- plt.show()
- #################################################
- # logRegression: Logistic Regression
- # Author : zouxy
- # Date : 2014-03-02
- # HomePage : http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09
- # Email : [email protected]
- #################################################
- from numpy import *
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import time
- from logregression import trainLogRegres,testLogRegres,showLogRegres
- def loadData():
- train_x = []
- train_y = []
- fileIn = open('E:/Python/Machine Learning in Action/testSet.txt')
- for line in fileIn.readlines():
- lineArr = line.strip().split()
- train_x.append([1.0, float(lineArr[0]), float(lineArr[1])])#追加内容
- train_y.append(float(lineArr[2]))
- return mat(train_x), mat(train_y).transpose()
- ## step 1: load data
- print "step 1: load data..."
- train_x, train_y = loadData()
- test_x = train_x; test_y = train_y
- ## step 2: training...
- print "step 2: training..."
- opts = {'alpha': 0.01, 'maxIter': 20, 'optimizeType': 'smoothStocGradDescent'}#字典
- optimalWeights = trainLogRegres(train_x, train_y, opts)
- ## step 3: testing
- print "step 3: testing..."#新版本要加括号
- accuracy = testLogRegres(optimalWeights, test_x, test_y)
- ## step 4: show the result
- print "step 4: show the result..."
- print 'The classify accuracy is: %.3f%%' % (accuracy * 100)
- showLogRegres(optimalWeights, train_x, train_y)
数据集
- -0.017612 14.053064 0
- -1.395634 4.662541 1
- -0.752157 6.538620 0
- -1.322371 7.152853 0
- 0.423363 11.054677 0
- 0.406704 7.067335 1
- 0.667394 12.741452 0
- -2.460150 6.866805 1
- 0.569411 9.548755 0
- -0.026632 10.427743 0
- 0.850433 6.920334 1
- 1.347183 13.175500 0
- 1.176813 3.167020 1
- -1.781871 9.097953 0
- -0.566606 5.749003 1
- 0.931635 1.589505 1
- -0.024205 6.151823 1
- -0.036453 2.690988 1
- -0.196949 0.444165 1
- 1.014459 5.754399 1
- 1.985298 3.230619 1
- -1.693453 -0.557540 1
- -0.576525 11.778922 0
- -0.346811 -1.678730 1
- -2.124484 2.672471 1
- 1.217916 9.597015 0
- -0.733928 9.098687 0
- -3.642001 -1.618087 1
- 0.315985 3.523953 1
- 1.416614 9.619232 0
- -0.386323 3.989286 1
- 0.556921 8.294984 1
- 1.224863 11.587360 0
- -1.347803 -2.406051 1
- 1.196604 4.951851 1
- 0.275221 9.543647 0
- 0.470575 9.332488 0
- -1.889567 9.542662 0
- -1.527893 12.150579 0
- -1.185247 11.309318 0
- -0.445678 3.297303 1
- 1.042222 6.105155 1
- -0.618787 10.320986 0
- 1.152083 0.548467 1
- 0.828534 2.676045 1
- -1.237728 10.549033 0
- -0.683565 -2.166125 1
- 0.229456 5.921938 1
- -0.959885 11.555336 0
- 0.492911 10.993324 0
- 0.184992 8.721488 0
- -0.355715 10.325976 0
- -0.397822 8.058397 0
- 0.824839 13.730343 0
- 1.507278 5.027866 1
- 0.099671 6.835839 1
- -0.344008 10.717485 0
- 1.785928 7.718645 1
- -0.918801 11.560217 0
- -0.364009 4.747300 1
- -0.841722 4.119083 1
- 0.490426 1.960539 1
- -0.007194 9.075792 0
- 0.356107 12.447863 0
- 0.342578 12.281162 0
- -0.810823 -1.466018 1
- 2.530777 6.476801 1
- 1.296683 11.607559 0
- 0.475487 12.040035 0
- -0.783277 11.009725 0
- 0.074798 11.023650 0
- -1.337472 0.468339 1
- -0.102781 13.763651 0
- -0.147324 2.874846 1
- 0.518389 9.887035 0
- 1.015399 7.571882 0
- -1.658086 -0.027255 1
- 1.319944 2.171228 1
- 2.056216 5.019981 1
- -0.851633 4.375691 1
- -1.510047 6.061992 0
- -1.076637 -3.181888 1
- 1.821096 10.283990 0
- 3.010150 8.401766 1
- -1.099458 1.688274 1
- -0.834872 -1.733869 1
- -0.846637 3.849075 1
- 1.400102 12.628781 0
- 1.752842 5.468166 1
- 0.078557 0.059736 1
- 0.089392 -0.715300 1
- 1.825662 12.693808 0
- 0.197445 9.744638 0
- 0.126117 0.922311 1
- -0.679797 1.220530 1
- 0.677983 2.556666 1
- 0.761349 10.693862 0
- -2.168791 0.143632 1
- 1.388610 9.341997 0
- 0.317029 14.739025 0
五、在分布式系统中实现
关于lr在maprudece中的实现,logistic regression不支持并行,也就是mahout实现的也是单机的,运行在hadoop上面也没有意义(个人观点)。
看mahout中的源码分析:mahout源码分析之logistic regression(2)--RunLogistic
参考文献:
[1]. Ng机器学习视频
[2]. 机器学习实战
[3]. Stanford机器学习---第三讲. 逻辑回归和过拟合问题的解决 logistic Regression & Regularization
[4]. 机器学习算法与Python实践之(七)逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)