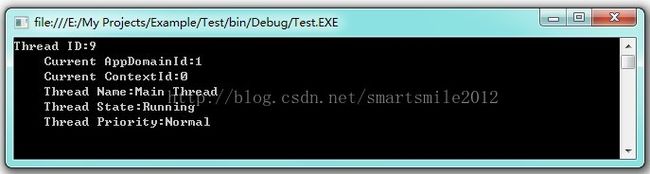
//以下这个例子,就是通过Thread显示当前线程信息
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread thread = Thread.CurrentThread;
thread.Name = "Main Thread";
string threadMessage = string.Format("Thread ID:{0}\n Current AppDomainId:{1}\n "+
"Current ContextId:{2}\n Thread Name:{3}\n "+
"Thread State:{4}\n Thread Priority:{5}\n",
thread.ManagedThreadId, Thread.GetDomainID(), Thread.CurrentContext.ContextID,
thread.Name, thread.ThreadState, thread.Priority);
Console.WriteLine(threadMessage);
Console.ReadKey();
}
/*
这里先以一个例子体现一下多线程带来的好处,首先在Message类中建立一个方法ShowMessage(),里面显示了当前运行线程的Id,并使用Thread.Sleep(int ) 方法模拟部分工作。在main()中通过ThreadStart委托绑定Message对象的ShowMessage()方法,然后通过Thread.Start()执行异步方法。请注意运行结果,在调用Thread.Start()方法后,系统以异步方式运行Message.ShowMessage(),而主线程的操作是继续执行的,在Message.ShowMessage()完成前,主线程已完成所有的操作。
*/
public class Message
{
public void ShowMessage()
{
string message = string.Format("Async threadId is :{0}",
Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine(message);
for (int n = 0; n < 10; n++)
{
Thread.Sleep(300);
Console.WriteLine("The number is:" + n.ToString());
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Main threadId is:"+
Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Message message=new Message();
Thread thread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(message.ShowMessage));
thread.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Do something ..........!");
Console.WriteLine("Main thread working is complete!");
}
}
/*
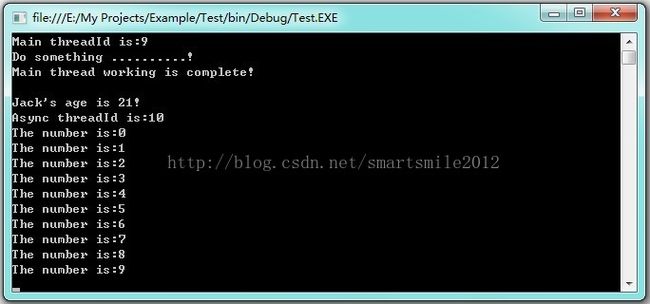
ParameterizedThreadStart委托与ThreadStart委托非常相似,但ParameterizedThreadStart委托是面向带参数方法的。注意ParameterizedThreadStart 对应方法的参数为object,此参数可以为一个值对象,也可以为一个自定义对象。
*/
public class Person
{
public string Name
{
get;
set;
}
public int Age
{
get;
set;
}
}
public class Message
{
public void ShowMessage(object person)
{
if (person != null)
{
Person _person = (Person)person;
string message = string.Format("\n{0}'s age is {1}!\nAsync threadId is:{2}",
_person.Name,_person.Age,Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
for (int n = 0; n < 10; n++)
{
Thread.Sleep(300);
Console.WriteLine("The number is:" + n.ToString());
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Main threadId is:"+Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Message message=new Message();
//绑定带参数的异步方法
Thread thread = new Thread(new ParameterizedThreadStart(message.ShowMessage));
Person person = new Person();
person.Name = "Jack";
person.Age = 21;
thread.Start(person); //启动异步线程
Console.WriteLine("Do something ..........!");
Console.WriteLine("Main thread working is complete!");
}
}
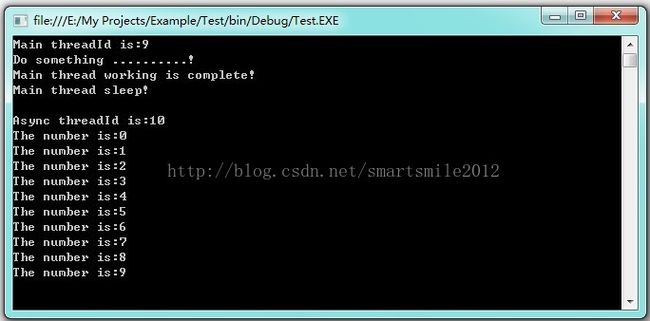
/*
为了等待其他后台线程完成后再结束主线程,就可以使用Thread.Sleep()方法。但系统无法预知异步线程需要运行的时间,所以用通过Thread.Sleep(int)阻塞主线程并不是一个好的解决方法。有见及此,.NET专门为等待异步线程完成开发了另一个方法thread.Join()。把上面例子中的最后一行Thread.Sleep(5000)修改为 thread.Join() 就能保证主线程在异步线程thread运行结束后才会终止。
*/
public class Message
{
public void ShowMessage()
{
string message = string.Format("\nAsync threadId is:{0}",
Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine(message);
for (int n = 0; n < 10; n++)
{
Thread.Sleep(300);
Console.WriteLine("The number is:" + n.ToString());
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Main threadId is:"+
Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Message message=new Message();
Thread thread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(message.ShowMessage));
thread.IsBackground = true;
thread.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Do something ..........!");
Console.WriteLine("Main thread working is complete!");
Console.WriteLine("Main thread sleep!");
Thread.Sleep(5000);
}
}
/*
若想终止正在运行的线程,可以使用Abort()方法。在使用Abort()的时候,将引发一个特殊异常 ThreadAbortException 。
若想在线程终止前恢复线程的执行,可以在捕获异常后 ,在catch(ThreadAbortException ex){...} 中调用Thread.ResetAbort()取消终止。
而使用Thread.Join()可以保证应用程序域等待异步线程结束后才终止运行。
*/
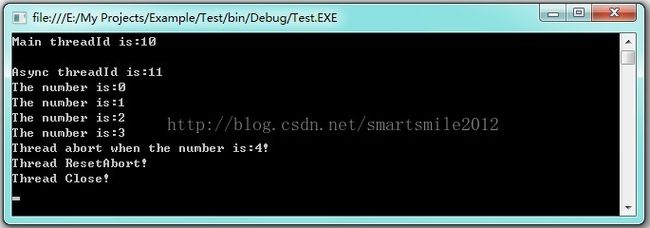
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Main threadId is:" +
Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Thread thread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(AsyncThread));
thread.IsBackground = true;
thread.Start();
thread.Join();
}
//以异步方式调用
static void AsyncThread()
{
try
{
string message = string.Format("\nAsync threadId is:{0}",
Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine(message);
for (int n = 0; n < 10; n++)
{
//当n等于4时,终止线程
if (n >= 4)
{
Thread.CurrentThread.Abort(n);
}
Thread.Sleep(300);
Console.WriteLine("The number is:" + n.ToString());
}
}
catch (ThreadAbortException ex)
{
//输出终止线程时n的值
if (ex.ExceptionState != null)
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Thread abort when the number is: {0}!",
ex.ExceptionState.ToString()));
//取消终止,继续执行线程
Thread.ResetAbort();
Console.WriteLine("Thread ResetAbort!");
}
//线程结束
Console.WriteLine("Thread Close!");
}
/*
四、CLR线程池的工作者线程
4.1 关于CLR线程池
使用ThreadStart与ParameterizedThreadStart建立新线程非常简单,但通过此方法建立的线程难于管理,若建立过多的线程反而会影响系统的性能。
有见及此,.NET引入CLR线程池这个概念。CLR线程池并不会在CLR初始化的时候立刻建立线程,而是在应用程序要创建线程来执行任务时,线程池才初始化一个线程。线程的初始化与其他的线程一样。在完成任务以后,该线程不会自行销毁,而是以挂起的状态返回到线程池。直到应用程序再次向线程池发出请求时,线程池里挂起的线程就会再度激活执行任务。这样既节省了建立线程所造成的性能损耗,也可以让多个任务反复重用同一线程,从而在应用程序生存期内节约大量开销。
注意:通过CLR线程池所建立的线程总是默认为后台线程,优先级数为ThreadPriority.Normal。
4.2 工作者线程与I/O线程
CLR线程池分为工作者线程(workerThreads)与I/O线程 (completionPortThreads) 两种,工作者线程是主要用作管理CLR内部对象的运作,I/O(Input/Output) 线程顾名思义是用于与外部系统交换信息,IO线程的细节将在下一节详细说明。
通过ThreadPool.GetMax(out int workerThreads,out int completionPortThreads )和 ThreadPool.SetMax( int workerThreads, int completionPortThreads)两个方法可以分别读取和设置CLR线程池中工作者线程与I/O线程的最大线程数。在Framework2.0中最大线程默认为25*CPU数,在Framewok3.0、4.0中最大线程数默认为250*CPU数,在近年 I3,I5,I7 CPU出现后,线程池的最大值一般默认为1000、2000。
若想测试线程池中有多少的线程正在投入使用,可以通过ThreadPool.GetAvailableThreads( out int workerThreads,out int completionPortThreads ) 方法。
使用CLR线程池的工作者线程一般有两种方式,一是直接通过 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem() 方法,二是通过委托,下面将逐一细说。
4.3 通过QueueUserWorkItem启动工作者线程
ThreadPool线程池中包含有两个静态方法可以直接启动工作者线程:
一为 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(WaitCallback)
二为 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(WaitCallback,Object)
先把WaitCallback委托指向一个带有Object参数的无返回值方法,再使用 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(WaitCallback) 就可以异步启动此方法,此时异步方法的参数被视为null
*/
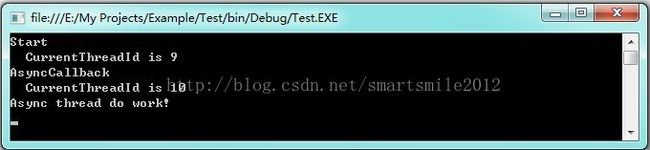
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//把CLR线程池的最大值设置为1000
ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(1000, 1000);
//显示主线程启动时线程池信息
ThreadMessage("Start");
//启动工作者线程
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(new WaitCallback(AsyncCallback));
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void AsyncCallback(object state)
{
Thread.Sleep(200);
ThreadMessage("AsyncCallback");
Console.WriteLine("Async thread do work!");
}
//显示线程现状
static void ThreadMessage(string data)
{
string message = string.Format("{0}\n CurrentThreadId is {1}",
data, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
}
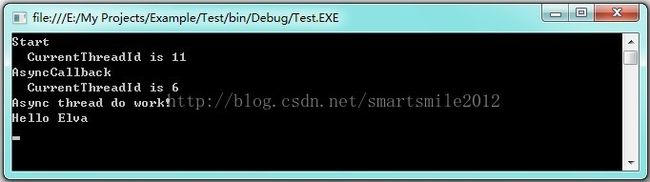
/*
使用 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(WaitCallback,Object) 方法可以把object对象作为参数传送到回调函数中。
下面例子中就是把一个string对象作为参数发送到回调函数当中。
*/
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//把线程池的最大值设置为1000
ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(1000, 1000);
ThreadMessage("Start");
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(new WaitCallback(AsyncCallback),"Hello Elva");
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void AsyncCallback(object state)
{
Thread.Sleep(200);
ThreadMessage("AsyncCallback");
string data = (string)state;
Console.WriteLine("Async thread do work!\n"+data);
}
//显示线程现状
static void ThreadMessage(string data)
{
string message = string.Format("{0}\n CurrentThreadId is {1}",
data, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
}
/*
通过ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem启动工作者线程虽然是方便,但WaitCallback委托指向的必须是一个带有Object参数的无返回值方法,这无疑是一种限制。若方法需要有返回值,或者带有多个参数,这将多费周折。有见及此,.NET提供了另一种方式去建立工作者线程,那就是委托。
*/
/*
当调用Invoke()方法时,对应此委托的所有方法都会被执行。而BeginInvoke与EndInvoke则支持委托方法的异步调用,由BeginInvoke启动的线程都属于CLR线程池中的工作者线程,在下面将详细说明。首先建立一个委托对象,通过IAsyncResult BeginInvoke(string name,AsyncCallback callback,object state) 异步调用委托方法,BeginInvoke 方法除最后的两个参数外,其它参数都是与方法参数相对应的。通过 BeginInvoke 方法将返回一个实现了 System.IAsyncResult 接口的对象,之后就可以利用EndInvoke(IAsyncResult ) 方法就可以结束异步操作,获取委托的运行结果。
*/
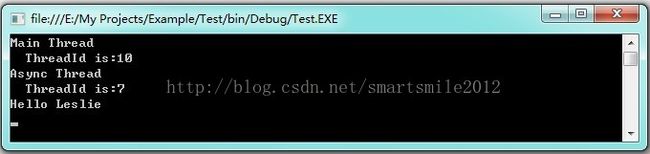
class Program
{
delegate string MyDelegate(string name);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ThreadMessage("Main Thread");
//建立委托
MyDelegate myDelegate = new MyDelegate(Hello);
//异步调用委托,获取计算结果
IAsyncResult result=myDelegate.BeginInvoke("Leslie", null, null);
//完成主线程其他工作
.............
//等待异步方法完成,调用EndInvoke(IAsyncResult)获取运行结果
string data=myDelegate.EndInvoke(result);
Console.WriteLine(data);
Console.ReadKey();
}
static string Hello(string name)
{
ThreadMessage("Async Thread");
Thread.Sleep(2000); //虚拟异步工作
return "Hello " + name;
}
//显示当前线程
static void ThreadMessage(string data)
{
string message = string.Format("{0}\n ThreadId is:{1}",
data,Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
}
/*
善用IAsyncResult
在以上例子中可以看见,如果在使用myDelegate.BeginInvoke后立即调用myDelegate.EndInvoke,那在异步线程未完成工作以前主线程将处于阻塞状态,等到异步线程结束获取计算结果后,主线程才能继续工作,这明显无法展示出多线程的优势。此时可以好好利用IAsyncResult 提高主线程的工作性能,IAsyncResult有以下成员:
public interface IAsyncResult
{
object AsyncState {get;} //获取用户定义的对象,它限定或包含关于异步操作的信息。
WailHandle AsyncWaitHandle {get;} //获取用于等待异步操作完成的 WaitHandle。
bool CompletedSynchronously {get;} //获取异步操作是否同步完成的指示。
bool IsCompleted {get;} //获取异步操作是否已完成的指示。
}
通过轮询方式,使用IsCompleted属性判断异步操作是否完成,这样在异步操作未完成前就可以让主线程执行另外的工作。
*/
class Program
{
delegate string MyDelegate(string name);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ThreadMessage("Main Thread");
//建立委托
MyDelegate myDelegate = new MyDelegate(Hello);
//异步调用委托,获取计算结果
IAsyncResult result=myDelegate.BeginInvoke("Leslie", null, null);
//在异步线程未完成前执行其他工作
while (!result.IsCompleted)
{
Thread.Sleep(200); //虚拟操作
Console.WriteLine("Main thead do work!");
}
string data=myDelegate.EndInvoke(result);
Console.WriteLine(data);
Console.ReadKey();
}
static string Hello(string name)
{
ThreadMessage("Async Thread");
Thread.Sleep(2000);
return "Hello " + name;
}
static void ThreadMessage(string data)
{
string message = string.Format("{0}\n ThreadId is:{1}",
data,Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
}
/*
除此以外,也可以使用WailHandle完成同样的工作,WaitHandle里面包含有一个方法WaitOne(int timeout),它可以判断委托是否完成工作,在工作未完成前主线程可以继续其他工作。运行下面代码可得到与使用 IAsyncResult.IsCompleted 同样的结果,而且更简单方便 。
*/
namespace Test
{
class Program
{
delegate string MyDelegate(string name);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ThreadMessage("Main Thread");
//建立委托
MyDelegate myDelegate = new MyDelegate(Hello);
//异步调用委托,获取计算结果
IAsyncResult result=myDelegate.BeginInvoke("Leslie", null, null);
while (!result.AsyncWaitHandle.WaitOne(200))
{
Console.WriteLine("Main thead do work!");
}
string data=myDelegate.EndInvoke(result);
Console.WriteLine(data);
Console.ReadKey();
}
static string Hello(string name)
{
ThreadMessage("Async Thread");
Thread.Sleep(2000);
return "Hello " + name;
}
static void ThreadMessage(string data)
{
string message = string.Format("{0}\n ThreadId is:{1}",
data,Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
}
}
/*
当要监视多个运行对象的时候,使用IAsyncResult.WaitHandle.WaitOne可就派不上用场了。
幸好.NET为WaitHandle准备了另外两个静态方法:WaitAny(waitHandle[], int)与WaitAll (waitHandle[] , int)。
其中WaitAll在等待所有waitHandle完成后再返回一个bool值。
而WaitAny是等待其中一个waitHandle完成后就返回一个int,这个int是代表已完成waitHandle在waitHandle[]中的数组索引。
下面就是使用WaitAll的例子,运行结果与使用 IAsyncResult.IsCompleted 相同。
*/
class Program
{
delegate string MyDelegate(string name);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ThreadMessage("Main Thread");
//建立委托
MyDelegate myDelegate = new MyDelegate(Hello);
//异步调用委托,获取计算结果
IAsyncResult result=myDelegate.BeginInvoke("Leslie", null, null);
//此处可加入多个检测对象
WaitHandle[] waitHandleList = new WaitHandle[] { result.AsyncWaitHandle,........ };
while (!WaitHandle.WaitAll(waitHandleList,200))
{
Console.WriteLine("Main thead do work!");
}
string data=myDelegate.EndInvoke(result);
Console.WriteLine(data);
Console.ReadKey();
}
static string Hello(string name)
{
ThreadMessage("Async Thread");
Thread.Sleep(2000);
return "Hello " + name;
}
static void ThreadMessage(string data)
{
string message = string.Format("{0}\n ThreadId is:{1}",
data,Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
}
/*
回调函数
使用轮询方式来检测异步方法的状态非常麻烦,而且效率不高,有见及此,.NET为 IAsyncResult BeginInvoke(AsyncCallback , object)准备了一个回调函数。使用 AsyncCallback 就可以绑定一个方法作为回调函数,回调函数必须是带参数 IAsyncResult 且无返回值的方法: void AsycnCallbackMethod(IAsyncResult result) 。在BeginInvoke方法完成后,系统就会调用AsyncCallback所绑定的回调函数,最后回调函数中调用 XXX EndInvoke(IAsyncResult result) 就可以结束异步方法,它的返回值类型与委托的返回值一致。
*/
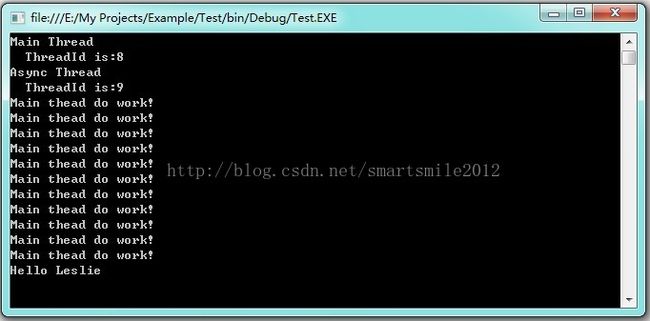
class Program
{
delegate string MyDelegate(string name);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ThreadMessage("Main Thread");
//建立委托
MyDelegate myDelegate = new MyDelegate(Hello);
//异步调用委托,获取计算结果
myDelegate.BeginInvoke("Leslie", new AsyncCallback(Completed), null);
//在启动异步线程后,主线程可以继续工作而不需要等待
for (int n = 0; n < 6; n++)
Console.WriteLine(" Main thread do work!");
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.ReadKey();
}
static string Hello(string name)
{
ThreadMessage("Async Thread");
Thread.Sleep(2000); \\模拟异步操作
return "\nHello " + name;
}
static void Completed(IAsyncResult result)
{
ThreadMessage("Async Completed");
//获取委托对象,调用EndInvoke方法获取运行结果
AsyncResult _result = (AsyncResult)result;
MyDelegate myDelegate = (MyDelegate)_result.AsyncDelegate;
string data = myDelegate.EndInvoke(_result);
Console.WriteLine(data);
}
static void ThreadMessage(string data)
{
string message = string.Format("{0}\n ThreadId is:{1}",
data, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
}
/*
可以看到,主线在调用BeginInvoke方法可以继续执行其他命令,而无需再等待了,这无疑比使用轮询方式判断异步方法是否完成更有优势。
在异步方法执行完成后将会调用AsyncCallback所绑定的回调函数,注意一点,回调函数依然是在异步线程中执行,这样就不会影响主线程的运行,这也使用回调函数最值得青昧的地方。
在回调函数中有一个既定的参数IAsyncResult,把IAsyncResult强制转换为AsyncResult后,就可以通过 AsyncResult.AsyncDelegate 获取原委托,再使用EndInvoke方法获取计算结果。
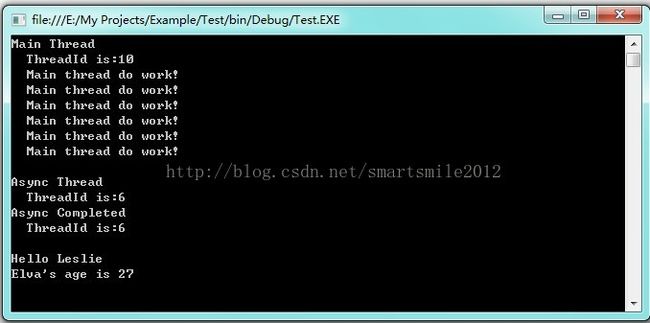
运行结果如下:
*/
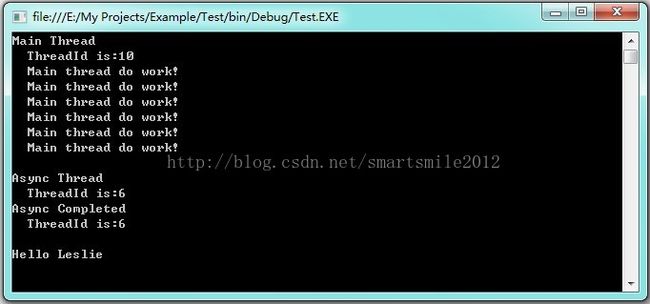
/*
如果想为回调函数传送一些外部信息,就可以利用BeginInvoke(AsyncCallback,object)的最后一个参数object,它允许外部向回调函数输入任何类型的参数。只需要在回调函数中利用 AsyncResult.AsyncState 就可以获取object对象。
*/
class Program
{
public class Person
{
public string Name;
public int Age;
}
delegate string MyDelegate(string name);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ThreadMessage("Main Thread");
//建立委托
MyDelegate myDelegate = new MyDelegate(Hello);
//建立Person对象
Person person = new Person();
person.Name = "Elva";
person.Age = 27;
//异步调用委托,输入参数对象person, 获取计算结果
myDelegate.BeginInvoke("Leslie", new AsyncCallback(Completed), person);
//在启动异步线程后,主线程可以继续工作而不需要等待
for (int n = 0; n < 6; n++)
Console.WriteLine(" Main thread do work!");
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.ReadKey();
}
static string Hello(string name)
{
ThreadMessage("Async Thread");
Thread.Sleep(2000);
return "\nHello " + name;
}
static void Completed(IAsyncResult result)
{
ThreadMessage("Async Completed");
//获取委托对象,调用EndInvoke方法获取运行结果
AsyncResult _result = (AsyncResult)result;
MyDelegate myDelegate = (MyDelegate)_result.AsyncDelegate;
string data = myDelegate.EndInvoke(_result);
//获取Person对象
Person person = (Person)result.AsyncState;
string message = person.Name + "'s age is " + person.Age.ToString();
Console.WriteLine(data+"\n"+message);
}
static void ThreadMessage(string data)
{
string message = string.Format("{0}\n ThreadId is:{1}",
data, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
}