Android中的布局 Layout
布局Layout管理
布局即是指Activity中组件的呈现方式,即组件大小、间距和对齐方式等。
Android提供了两种创建布局的方式:
1.在XML配置文件中声明(推荐)。
2.在程序中通过代码直接实例化布局及其组件。
在Android中常见的布局方式:
线性布局(LinearLayout):按照垂直或者水平方向布局组件。
帧布局(FrameLayout):组件从屏幕的左上角坐标布局组件。
表格布局(TableLayout):按照行列方式布局组件。
相对布局(RelativeLayout):相对其他组件的布局方式。
绝对布局(AbsoluteLayout):按照绝对坐标来布局组件。(已废)。
各种布局方式之间可以互相嵌套,只需要将布局理解成为一个容器控件即可,官方的说法叫View Group,见http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/overview.html。
线性布局LinearLayout
线性布局是将子组件按照垂直或者水平方向来布局。
线性布局的方向由
android:orientation="vertical"或者"horizontal"来控制。
一般情况下都是在LinearLayout的开头就设定方向和宽高,至于里面摆放的控件,就具体设定其控件的属性。
帮助文档:
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/LinearLayout.html
里面有很多的属性介绍。
比较常用的是:
android:gravity属性,指定控件的基本位置,如设置TextView中的文字的位置。
android:background指定控件使用的背景色
android:padding指定控件的内边距,设定一个值之后四个边的内边距都是这个值。
android:layout_weight属性用来控制各个控件所占空间的权重。
例子:
自己新建一个布局文件,放在res\layout文件夹里(貌似文件名必须都是小写字母。)
布局文件如下:
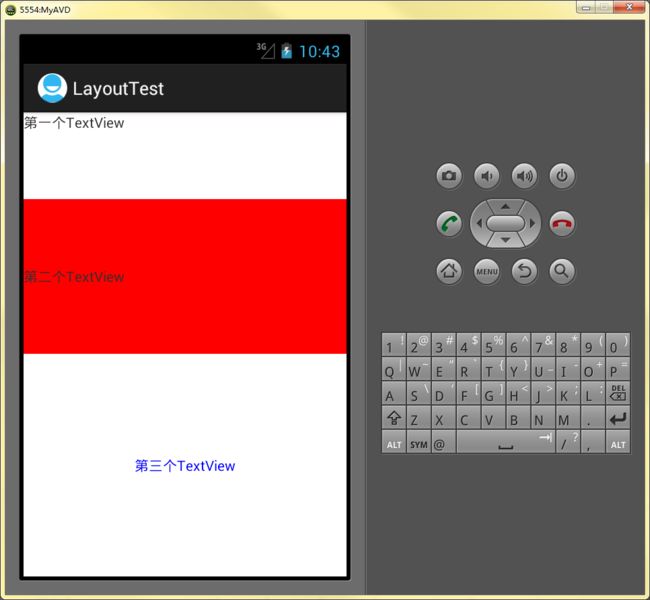
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <TextView android:id = "@+id/firstText" android:text="@string/TextOne" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" > </TextView> <TextView android:id = "@+id/secondText" android:text="@string/TextTwo" android:gravity="center_vertical" android:background="@color/red" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="2" > </TextView> <TextView android:id = "@+id/thirdText" android:text="@string/TextThree" android:gravity="center" android:textColor="@color/blue" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="3" > </TextView> </LinearLayout>
运行结果如下:
帧布局FrameLayout
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/FrameLayout.html
帧布局是从屏幕的左上角坐标(0,0)开始布局,多个组件层叠排序,后面的组件覆盖前面的组件。
帧布局中没有权重这一说。
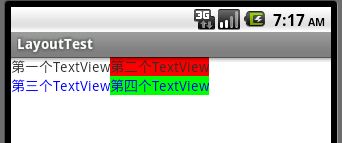
把上文中的LinearLayout改为FrameLayout,
程序运行结果如下:
其中红色是第二个TextView的背景色,而第三个TextView没有背景色,直接覆盖在上面了。
表格布局TableLayout
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/TableLayout.html
表格布局以行、列表格的方式布局子组件。
TableLayout中使用TableRow来定义多行。
TableLayout中如果不用TableRow,则所有控件从上到下排列。
用了TableRow,每个TableRow中的控件构成多列。
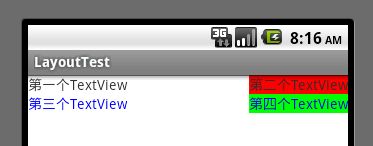
如下图,每一个TableRow中放两个TextView:
属性android:stretchColumns表示拉伸列,表示如果填充不满时,拉伸该序号(序号从0开始)的列,填满空间。
比如设置
android:stretchColumns="0"后,拉伸第一列。
如下图:
android:collapseColumns表示隐藏指定的列。
表格布局的代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:stretchColumns="0" > <TableRow> <TextView android:id = "@+id/firstText" android:text="@string/TextOne" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" > </TextView> <TextView android:id = "@+id/secondText" android:text="@string/TextTwo" android:gravity="center_vertical" android:background="@color/red" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" > </TextView> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView android:id = "@+id/thirdText" android:text="@string/TextThree" android:gravity="center_vertical" android:textColor="@color/blue" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" > </TextView> <TextView android:id = "@+id/fourthText" android:text="@string/TextFour" android:gravity="center_vertical" android:background="@color/green" android:textColor="@color/blue" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" > </TextView> </TableRow> </TableLayout>
相对布局RelativeLayout
相对布局按照组件之间的相对位置来布局,如在某个组件的左右上下等。
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/RelativeLayout.html
通过设置控件的属性来设置控件的相对位置。
属性可以分为四大类:
第一类:上下左右四个相对位置。
第二类:边缘对齐的五个属性(加上一个基线对齐)。
第三类:是否和父控件在上下左右边缘对齐的四个属性。
第四类:居中方式的三个属性。
前两类设置时设置指定控件的id,后两类的值为true或者false。
绝对布局AbsoluteLayout
绝对布局通过指定子组件的确切XY坐标位置,该类已经过期,可以使用其他布局代替之。
资源
布局教程汇总:http://www.apkbus.com/android-50865-1-1.html
官方文档教程:http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/declaring-layout.html