【读书笔记】Android 应用程序进程的启动过程
这是罗升阳《Android 系统源代码》一书中第12章,Android 应用程序进程的启动过程,的摘要;
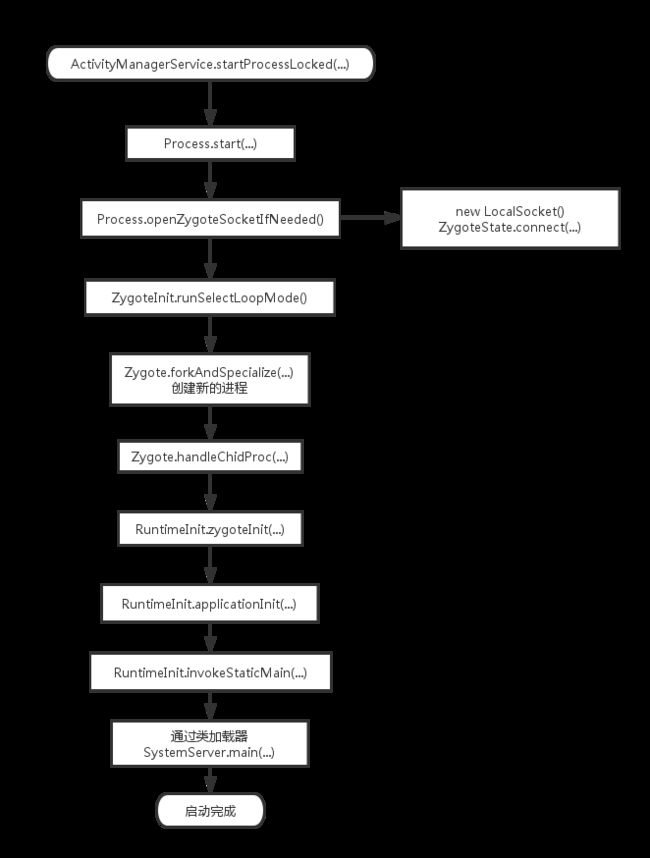
当 ActivityMangerService 启动一个应用程序组件时,如果发现这个组件所需要的进程没有启动,就会请求 Zygote 启动新的进程。Zygote 通过复制自身的方式创建一个新的进程,同时也会获取一个虚拟机实例;
应用程序进程启动过程中,除了获得一个虚拟机实例外,还获得一个 Binder 线程池和一个消息循环。
一、应用程序进程创建的过程
当 ActivityManagerService 创建一个新的进程是,会调用 ActivityManagerService.startProcessLocked 方法向 Zygote 发送一个创建进程请求;
Zygote.forkAndSpecialize(...) 通过调用native 方法 nativeForkAndSpecialize(...) ,fork 一个新的进程;
ZygoteConnection.handleChildProc(...) 启动新的进程;
二、消息循环的创建过程
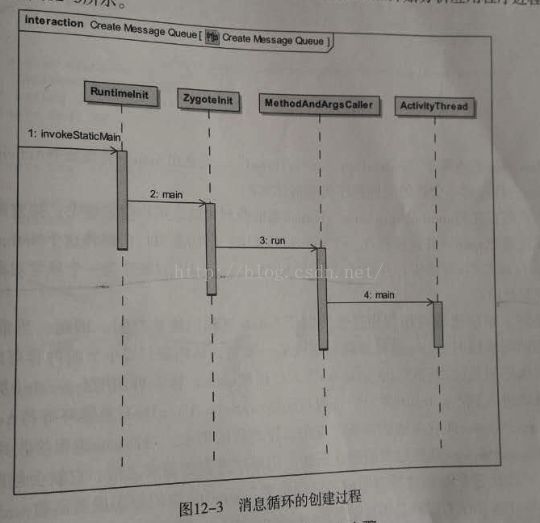
一个新的应用进程创建完成之后,就会调用 RuntimeInit 类的静态成员函数 invokeStaticMain 将 ActivityThread 类的静态成员函数 main 设置为新创建的应用程序进程入口。 ActivityThread 类的静态成员函数 main 在调用的过程中,就会在当前应用程序进程中创建一个消息循环。
Z
ygoteInit.invokeStaticMain 方法
static void invokeStaticMain(ClassLoader loader, String className, String[] argv)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
Class<?> cl;
try {
cl = loader.loadClass(className);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Missing class when invoking static main " + className, ex);
}
Method m;
try {
// 通过反射进入获取ActivityThread 类的 main 方法
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Missing static main on " + className, ex);
} catch (SecurityException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Problem getting static main on " + className, ex);
}
int modifiers = m.getModifiers();
if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) {
throw new RuntimeException("Main method is not public and static on " + className);
}
/*
* This throw gets caught in ZygoteInit.main(), which responds
* by invoking the exception's run() method. This arrangement
* clears up all the stack frames that were required in setting
* up the process.
*/
// 抛出 caller 异常,在 ZygoteInit 的 main 方法里捕获
throw new ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
}
在 ZygoteInit.main 方法中捕获 caller 异常
public static void main(String argv[]) {
·····
} catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
caller.run();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
···
}
}
调用 MethodAndArgsCaller.run 方法
public static class MethodAndArgsCaller extends Exception implements Runnable {
/** method to call */
private final Method mMethod;
/** argument array */
private final String[] mArgs;
public MethodAndArgsCaller(Method method, String[] args) {
mMethod = method;
mArgs = args;
}
public void run() {
try {
// 调用 ActivityThread 类的 main 方法
mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { mArgs });
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
···
}
}
}
ActivityThread.main 方法里面开启消息循环
public static void main(String[] args) {
···
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
··
Looper.loop();
···
}
使用抛出异常的方式进入 ActivityThread 的 main 方法的原因:
ActivityMangerService 请求 Zygote 进程创建的应用程序的入口函数为 ActivityThread 类的 main 函数。但是由于新创建的应用程序
进程一开始就需要在内部初始化运行时库,以及启动 Binder 线程池,因此,当 ActivityThread 类的静态成员函数 main 被调用时,新
创建的应用程序进程实际上已经执行了相当多的代码。为了使得新创建的应用程序进程觉得它的入口函数就是 ActivityThread 类的 main
,系统就不可以在 ZygoteInit.invokeStaticMain 中直接调用。而是先抛出一个异常回到 ZygoteInit 类的 main 中,然后间接调用它,这样
巧妙利用 Java 语言的异常处理机制清理它前面的调用栈。