Android入门——Fragment详解之Fragment与Activity通信及数据交换(二)
引言
在Android入门——Fragment详解之基本概念与用法(一)中,总结了Fragment的基本操作与应用,也知道了Fragment与Activity之间联系紧密,这篇文章着重总结下Fragment与Activity通信及数据交换的知识点。
一、Fagment 与Activity的联系
Fragment必须被“嵌入”Activity中使用,虽然也拥有自己独立的生命周期,但在一定时期内也还是受到说依附的Activity的生命周期控制。
Fragment是作为Activity的UI组成的一部分,所以Fragment可以调用getActivity()方法获取所依附的Activity,同样地Activity也可以调用FragmentManager的findFragmentById()或者findFragmentByTag()获取对应的Fragment
在Activity运行的过程中可以通过FragmentTransaction的add、remove、replace、hide、show等方法动态管理Fragment。
某个Activity可以组合多个Fragment,反之,某个Fragment也可以被多个Activity复用。
二、Fragment之间的通信及数据交换
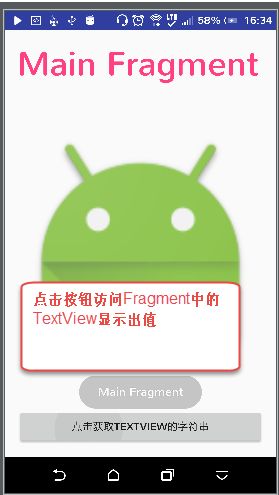
1、在Fragment获取自身的控件
我们知道在Fragment的onCreateView方法里返回的是Fragment自身对应的view,所以我们只需在此方法里通过view.findViewById获取即可。
MainActivity的布局文件activity_main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView android:text="Hello World!" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<FrameLayout android:id="@+id/id_content_layout" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
</RelativeLayout>MainFragment的布局文件fragment_main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView android:id="@+id/id_fragment_title_txt" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Main Fragment" android:textColor="@color/colorAccent" android:textSize="45sp" />
<ImageView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="0dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher" />
<Button android:id="@+id/id_tofragment_btn" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="点击获取TextView的字符串"/>
</LinearLayout>MainFragment的代码MainFragment.java:
/** * Created by cmo on 16-4-28. */
public class MainFragment extends Fragment {
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
final View view=inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_main,null);
Button button= (Button) view.findViewById(R.id.id_tofragment_btn);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
TextView textView=(TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.id_fragment_title_txt);
String txt=textView.getText().toString();
Toast.makeText(getActivity(),txt,Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
return view;
}
}MainActivity.java:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
MainFragment mainFragment=new MainFragment();
FragmentManager fragmentManager=getFragmentManager();
fragmentManager.beginTransaction().add(R.id.id_content_layout,mainFragment,"main").commit();
}
}1、同一个container中不同Fragment间的数据传递
例如在Fragment跳转时,从当前Fragment将参数传递给跳转到的目标Fragment(由于篇幅原因xml布局和MainActivity代码就不贴出来了)
1.1 借助Bundle对象通过fragment.setArguments(Bundle bundle)来传递参数
在创建目标Fragment时候,通过把参数封装为Bundle对象,再调用setArguments()传递Bundle对象。
再创建目标Fragment的UI时再通过getArguments()获取参数。
MainFragment.java:
*/
public class MainFragment extends Fragment {
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
final View view=inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_main,null);
Button button= (Button) view.findViewById(R.id.id_tofragment_btn);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Fragment fragment =getFragmentManager().findFragmentByTag("main");
ToFragment fragment2 = ToFragment.newInstance("从MianFragment传递至ToFragment的数据");
getFragmentManager().beginTransaction().hide(fragment)
.add(R.id.id_content_layout, fragment2)
.addToBackStack(null)
.commit();
}
});
return view;
}
}
ToFragment.java:
public class ToFragment extends Fragment {
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view=inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_to,null);
if (getArguments() != null) {
String mParam1 = getArguments().getString("param");
TextView tv = (TextView)view.findViewById(R.id.id_tofragment_title_txt);
tv.setText(mParam1);
}
return view;
}
//Fragment间用SetArguments来传递,本例中值传递一个字符串,所以只把一个字符串封装至Bundle对象
public static ToFragment newInstance(String text) {
ToFragment fragment = new ToFragment();
Bundle args = new Bundle();
args.putString("param", text);
fragment.setArguments(args);
return fragment;
}
}1.2、利用回调接口函数传递
Fragment之间的通信尽管可以使用先得到对应的Fragment对象再去获取对应的元素这种方式,但是耦合度还是太高,所以不宜多个Fragment之间直接通信或者是调用(尽管可以这样做)。一般来说,Fragment之间的通信都应该通过他们说依附的Activity来完成,Fragment应该充当的是一个发起事件和传递数据的角色,他们所依附的Activity才应当真正是处理事件和数据的主角。一句话概括这种思想:通过回调接口,步骤有四:
- 在Fragment里定义一个回调接口
- 在Fragment里声明一个定义接口的应用变量,并在onAttach方法里强制所依附Activity必须实现该接口。
- 发送回调接口事件:再通过声明的接口在Fragment的相关事件中调用接口里的方法即完成发起事件的工作
- 在Activity处理回调:在所依附的Activity中实现Fragment的接口方法,即处理回调。
接下来我们还是实现1.1的效果,只不过使用的是回调的方式:
首先还是activity_main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal">
<fragment android:id="@+id/id_fragment_picindex" android:name="com.crazymo.fragmentcallback.MainFragment" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>
<fragment android:id="@+id/id_fragment_showpic" android:name="com.crazymo.fragmentcallback.TargetFragment" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="0dp" android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>MainActivity.java
package com.crazymo.fragmentcallback;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.FragmentManager;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.ImageView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements MainFragment.SelectPicIndexInterface {
private int[] imgs={R.mipmap.ic_blue_launcher,R.mipmap.ic_red_launcher,R.mipmap.ic_toy,R.mipmap.pool_balls_05};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Log.d("MainActivity","Activity完成创建!");
}
@Override
public void onSelectPicIndex(int index) {
FragmentManager manager = getFragmentManager();
TargetFragment targetFragment = (TargetFragment)manager.findFragmentById(R.id.id_fragment_showpic);
targetFragment.setImgBackGround(imgs[index]);
Log.d("MainActivity","MainActivity接收到MainFrament发送的事件并调用TargetFragment里的方法,即处理回调");
}
}然后fragment_main.xml(此例中充当发送回调事件的角色)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal">
<EditText android:id="@+id/id_pic_index_edt" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="0"/>
<!--用法模拟发送回调事件从而触发Activity里的对应方法-->
<Button android:id="@+id/id_choose_btn" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="确认选择" />
</LinearLayout>MainFragment.java
package com.crazymo.fragmentcallback;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
/** * Created by cmo on 16-5-4. */
public class MainFragment extends Fragment {
private SelectPicIndexInterface mSelectInterface;//声明一个回调接口变量,将用于把Activity强转
public interface SelectPicIndexInterface{
public void onSelectPicIndex(int index);
}
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view=inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_main,container,false);
Button button= (Button) view.findViewById(R.id.id_choose_btn);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
showPic();
}
});
Log.d("MainFragment","MainFragment 创建了自己的UI");
return view;
}
@Override
public void onAttach(Context context) {
super.onAttach(context);
try {
Log.d("MainFragment","MainFragment 完成与Activity的对接");
mSelectInterface = (SelectPicIndexInterface) context;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ClassCastException(context.toString() + "must implement SelectPicIndexInterface");
}
}
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
Log.d("MainFragment", "MainFragment 和依附的Activity对象创建完成");
}
public void showPic(){
EditText editText= (EditText) getView().findViewById(R.id.id_pic_index_edt);//获取MainFragment里的EditText的值将回掉给Activity
int index=Integer.valueOf(editText.getText().toString())==null?0:Integer.valueOf(editText.getText().toString());
if(index>3){
index=3;
}
mSelectInterface.onSelectPicIndex(index);//发送事件
Log.d("MainFragment","点击MainFragment里的Button 发送回调事件");
}
}
fragment_target.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent">
<ImageView android:id="@+id/id_pic_imgv" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>TargetFragment.java(此例中充当与间接处理回调事件的角色,因为Activity实际的处理就是TargetFragment的业务逻辑)
/** * Created by cmo on 16-5-4. */
public class TargetFragment extends Fragment {
private ImageView mImageView;
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view=inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_target,container,false);
mImageView= (ImageView) view.findViewById(R.id.id_pic_imgv);
Log.d("TargetFragment","TargetFragment创建了自己的UI");
return view;
}
//这里的imgIndex即是Fragment1传递过来的index
public void setImgBackGround(int imgIndex){
Log.d("TargetFragment","Activty处理对调的时候真正调用的函数");
mImageView.setBackgroundResource(imgIndex);
}
@Override
public void onAttach(Context context) {
super.onAttach(context);
Log.d("TargetFragment", "TargetFragment 完成与Activity的对接");
}
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
Log.d("TargetFragment", "TargetFragment 和依附的Activity对象创建完成");
}
}
运行结果分析(效果与上例相同就不重复贴图了),主要梳理下逻辑,如日志所示:
- 首先是Fragment及Activity的建立这里的逻辑很简单,值得注意的是Activity的onCreate方法是在Fragment的onActivityCreated之前执行的。
- 接着在此例中我们是把MainFragment作为通讯的发起者(即事件的发送者),所以我们会在代码里定义一个自己的回调接口, 而接口是给Activity用的,任何对象使用前都需要赋值,所以还需要在Activity中赋值(可以有很多方法,如果你愿意你可以选择setter的方式,但如果用户忘记了则会发生不可预知的异常,所以通常采取在fragment与activity相关联时,进行强转赋值)
- 再接着Fragment作为发送事件的角色,不可能会自动地发送回调事件去触发Activity的回调,所以我们还得去触发(可以在Fragment的生命周期里或者其他事件去触发),本例中选择的是通过点击Button的方式,每点击一次,就会触发Activity去处理一次回调,发送事件其实很简单就是使用自己声明的回调接口变量去调用自己的接口里的回调方法并传入相关数据即可。
- 通过上面三步,我们发送事件的角色搭建完毕,接着去真正的处理回调,本例中我们是想实现在MainFragment输入一个索引值,在TargerFragment中显示对应的图片,那么TargetFragment显示图片则是我处理回调的时候真正要做的事,那么要做的就是实现对应的业务方法。
- 最后再到Activity,在Fragment之间通信承担着一个桥梁的作用,因为在发送者角色中强制了必须实现指定接口,所以第一步implement是相关回调接口,然后在从MainFragment发送的回调事件里接收到传递的参数,然后获取TargetFragment对象并调用暴露出来的业务方法,从而完成一次回调。
2、同一个Activity,不同container间的数据传递
2.1、在Activity里直接findViewById获取Fragment里的控件
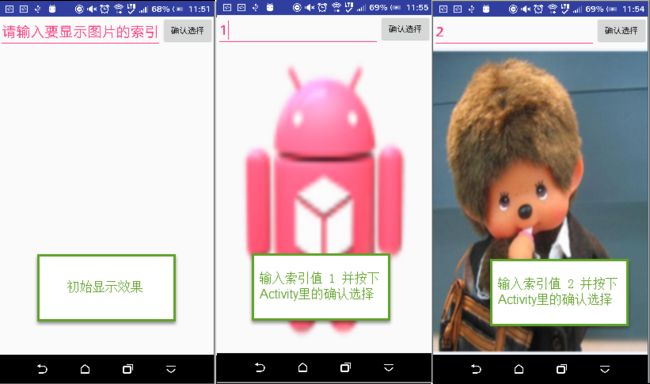
例:在PicIndexFragment里输入要显示图片的索引值,然后在Activity里的按钮显示出对应图片于ShowPicFragment。
activity_showpic.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal">
<fragment android:id="@+id/id_fragment_picindex" android:name="com.crazymo.fragmentsdemo.PicIndexFragment" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" />
<Button android:id="@+id/id_choose_btn" android:onClick="showPic" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="确认选择" />
</LinearLayout>
<fragment android:id="@+id/id_fragment_showpic" android:name="com.crazymo.fragmentsdemo.ShowPicFragment" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="0dp" android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>ShowPicActivity.java:
/** * Created by cmo on 16-4-29. */
public class ShowPicActivity extends Activity {
private int[] imgs={R.mipmap.ic_blue_launcher,R.mipmap.ic_red_launcher,R.mipmap.ic_toy,R.mipmap.pool_balls_05};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_showpic);
}
public void showPic(View view){
EditText editText= (EditText) findViewById(R.id.id_index_edt);//直接把Fragment里的EditText当成Activity上的普通控件一样通过findViewById
int index=Integer.valueOf(editText.getText().toString())==null?0:Integer.valueOf(editText.getText().toString());
if(index>3){
index=3;
}
ImageView imageView= (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.id_pic_imgv);
imageView.setBackgroundResource(imgs[index]);
}
}fragment_picindex.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent">
<EditText android:id="@+id/id_index_edt" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textSize="24sp" android:textColor="@color/colorAccent" android:textColorHint="@color/colorAccent" android:hint="请输入要显示图片的索引"/>
</LinearLayout>PicIndexFragment.java:
public class PicIndexFragment extends Fragment {
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view=inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_picindex,container,false);
return view;
}
}fragment_showpic.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent">
<ImageView android:id="@+id/id_pic_imgv" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>ShowPicFragment.java:
public class ShowPicFragment extends Fragment {
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view=inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_showpic,container,false);
return view;
}
}三、Fragment与Activity之间的通信
1、在Fragment中获取Activity中的控件
由于Fragment是依附于Activity的,属于Activity的一部分,并且拥有自己独立的view对象。所以我们可以通过getActivity()先得到依附的Activity对应的view,再通过view.findViewById()即可。
MainActivity的布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity" android:orientation="vertical">
<EditText android:id="@+id/id_content_edt" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textSize="25sp" android:textColor="@color/colorAccent" android:hint="即将在Fragment中访问的目标"/>
<FrameLayout android:id="@+id/id_content_layout" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="0dp" android:layout_weight="1"/>
</LinearLayout>MainActivity.java:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity" android:orientation="vertical">
<EditText android:id="@+id/id_content_edt" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textSize="25sp" android:textColor="@color/colorAccent" android:hint="即将在Fragment中访问的目标"/>
<FrameLayout android:id="@+id/id_content_layout" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="0dp" android:layout_weight="1"/>
</LinearLayout>
MainFragment的布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView android:id="@+id/id_fragment_title_txt" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Main Fragment" android:textColor="@color/colorAccent" android:textSize="45sp" />
<ImageView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="0dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher" />
<Button android:id="@+id/id_tofragment_btn" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="点击访问所依附的Activity的EditText"/>
</LinearLayout>MainFragment.java:
public class MainFragment extends Fragment {
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
final View view=inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_main,null);
Button button= (Button) view.findViewById(R.id.id_tofragment_btn);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
TextView textView=(TextView) getActivity().findViewById(R.id.id_content_edt);
String txt=textView.getText().toString();
Toast.makeText(getActivity(),txt,Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
return view;
}
}2、在Activity中访问Fragement里的控件、成员变量
2.1、使用fragment标签直接构建的Fragment
我们在所依附的Activity里可以通过getFragmentManager()先获取FragmentManager对象
再通过调用FragmentManager对象的findFragmentByTag()和findFragmentById()得到Fragment对象
再调用Fragment对象的getView()获取Fragment对应的View对象view
最后再调用View的view.findViewById方法获取或者直接通过Fragment对象调用相关访问属性的方法。
2.2、动态Java代码构建的Fragment
由于我们add时候会先用代码声明一个Fragment对象,所以我们可以跳过前面的2步,直接使用Fragment对象的getProperty()方法获取成员,其他的与静态构建Fragment相同