Java核心技术笔记——数据结构(2)
上一篇中的提到集合具体实现类在后续章节中逐一分析,本篇来分析项目中经常用到的数组列表(ArrayList)
1 数组列表类关系
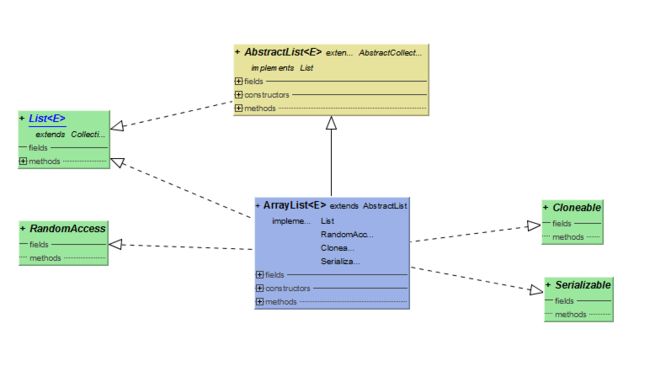
ArrayList主要实现了List、RandomAccess、Cloneable、Serializable接口,继承了AbstractList抽象类。
List接口定义了数组列表必须实现的方法
AbstractList实现了List中的通用的方法;
RandomAccess接口上一篇提到过,是为了监测列表查询效率,做个标记;
Cloneable接口可以实现对象的克隆;
Serializable接口标识序列号;
2 数组列表(ArrayList)源码分析
2.1 属性字段和构造函数
/**
* Integer.MAX_VALUE是int整形的最大取值2的31次方-1,这个常量用来控制集合的最大容量
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
/**
* 存放ArrayList对象的数组
*/
private transient Object[] elementData;
/**
* 数组列表大小
*/
private int size;
/**
* 根据传入的数字初始化elementData 数组
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
/**
* 默认elementData 的大小为10
*/
public ArrayList() {
this(10);
}
/**
* 根据传入的集合构造数组列表
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
//将传入的集合转换为数组,赋值给elementData
elementData = c.toArray();
size = elementData.length;
// 如果elementData 的元素类型不是Object,通过Arrays.copyOf转换为Object
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
}
2.2 添加元素
覆盖了AbstractList中的add()方法,这里有个问题,当超出列表的长度时,如何自动增加列表长度,添加元素,详细看下面你的源码分析:
/**
* 添加元素到列表
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
//确认列表容量方法
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
/**
* 当添加元素超过容器的容量时,自动扩增容器容量
*/
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// 注意这里实现了自动扩增容器容量
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
/**
* 自动扩增容器容量方法
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
/**
* 假设以空参数方法构造列表,则容器默认大小是10,当往列表中加载第11个元
* 素时,也就是说oldCapacity =11,11的二进制单位右移1位,是0000 0101,
* 十进制是5,即newCapacity =15,这里把容器的长度扩增了5位.
*/
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
//如果newCapacity <minCapacity,newCapacity 取最小值minCapacity
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
//如果newCapacity >MAX_ARRAY_SIZE ,newCapacity 取最大值
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
//调整elementData 的大小为新的容量
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
//Integer.MAX_VALUE是int整形的最大取值2的31次方-1
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
/**
* 添加元素的集合指定位置
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
//检查索引位置是否超出列表边界
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
//确定是否要扩增
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//将elementData数组中index的位置空留出来
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
//将新插入的element赋给elementData数组index位置的值
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
/**
* 检查索引位置是否超出列表边界
*/
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* 添加集合到列表
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
//转换引入的集合(c)为数组
Object[] a = c.toArray();
//获取引入集合的数组大小
int numNew = a.length;
//确定是否要扩增
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
//拷贝引入的数组到elementData的尾部
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);
//是列表的长度增加为size+numNew
size += numNew;
//引入的集合(c)大小不为空,则返回true
return numNew != 0;
}
/**
* 添加集合到列表指定位置
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
//同上
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
//根据传入的集合,确定是否需要扩增容量
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
int numMoved = size - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
//先将elementData数组中index到index + numNew 值后移,为引入c集合空出位置
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved);
//将c集合中元素复制到elementData数组中index到index + numNew的位置
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
//同上
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
2.3 移除元素
下面分析如何动态的移除数列表中的元素
/**
* 根据指定的索引移除元素
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
//注意modCount继承自AbstractList抽象类,是一个不包括在序列化中的值
modCount++;
// 访问elementData[index]值
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
//将elementData数组的元素从index+1位置后移到index
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
//将elementData数组最后一个位置元素设置为null
elementData[--size] = null; // Let gc do its work
//返回被移除的元素
return oldValue;
}
/**
* 判断移除元素的位置是否超出边界
*/
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
// 返回elementData[index]值
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
/**
* 根据传入的对象,去列表中循环查询,如果存在相同对象,调用fastRemove方法移除
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/*
* 根据位置index移除元素,和remove(int index) 方法的区别,是不用返回移除元素值
*/
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // Let gc do its work
}
2.3 访问元素
/**
* 随机访问数组列表中的元素
*/
public E get(int index) {
//判断index是否超出数组列表访问
rangeCheck(index);
//放回elementData[index]值,这里可以说明,ArrayList随机访问的效率高
return elementData(index);
}
2.4其他方法
2.4.1 包含运算
/**
* 暴露给外部的集合包含运算方法
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
/**
*实现集合包含运算
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
//如果o是null,循环elementData,查找是否有null值
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
//如果o不是是null,循环elementData,查找是否有相等的值,
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
//有相等的值返回索引i,否则返回-1;
return -1;
}
/**
* 顾名思义和上面的相反,反向查询是否相等的值
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
2.4.2 求交运算
/**
* 暴露给外部的集合求交集方法
*/
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
return batchRemove(c, true);
}
//实现交集运算,
private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) {
//将elementData数组转换为常量数组
final Object[] elementData = this.elementData;
int r = 0, w = 0;
boolean modified = false;
try {
for (; r < size; r++)
//循环访问列表,调用contains方法,判断引入的集合是否包含列表中的元素,如果有赋值给新的常量数组
if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement)
elementData[w++] = elementData[r];
} finally {
// Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection,
// even if c.contains() throws.
if (r != size) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, r,
elementData, w,
size - r);
w += size - r;
}
if (w != size) {
for (int i = w; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
modCount += size - w;
size = w;
modified = true;
}
}
return modified;
}
参考文章
1.《Java核心技术(卷一第9版)》
2. http://blog.csdn.net/jzhf2012/article/details/8540410