数据结构之大小堆&&优先级队列
大小堆>
一.什仫是堆?
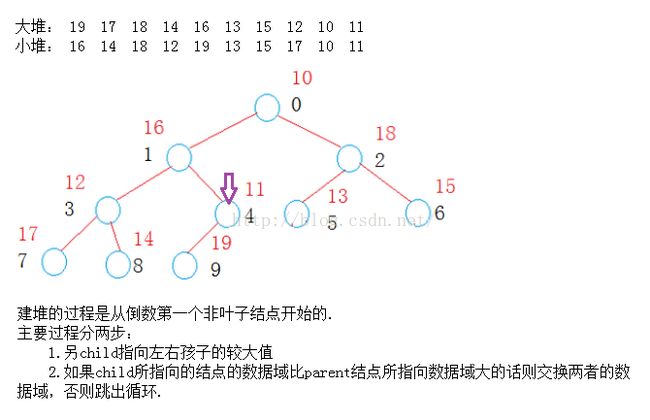
堆这种数据结构说白了就是一颗完全二叉树,堆的含义说明这颗完全二叉树中的所有非终端结点的值均不大于(或不小于)其左,右孩子结点的值.若一维数组{k1,k2,k3,k4...kn}是堆,则堆顶元素必为序列中n个元素的最小值(或最大值)
最大堆:每个父结点的值都大于其孩子结点.
最小堆:每个父结点的值都小于其孩子结点.
二.如何利用一维数组构建大小堆?
下面都以建大堆为例.在建堆的过程中我们是从倒数第一个非叶子结点开始向下调整的,因为叶子结点是没有左子树也没有右子树的当然不需要调整了.在这种思路下,假设起初有n个结点,建堆的时间复杂度为O(n*lgn).
三.在建好堆之后如何插入和删除一个结点?
Push>
其实在一个堆中是可以在任意位置插入和删除结点的,为了高效起见我们在插入一个结点时我们将该结点尾插到存储堆结构的顺序表中,如果我们插入的结点比原来的大堆中的所有数据都大的话我们就破坏了原来的大顶堆的结构了,此时我们就需要调整新堆的,在这里用的是向上调整的算法.
插入数据的时间复杂度为O(lgn).
Pop>
1).将最后一个结点的数据域与堆顶的元素交换.
2).删除最后一个结点,此时删除的就是原来的堆顶元素
3).向下调整删除之后的堆,使其继续满足大顶堆的定义.
删除数据的时间复杂度为O(lgn).
优先级队列>
我们知道队列的特性是先进先出,那仫什仫是优先级队列呢?在某一情况下队列的先进先出并不能满足我们的需求,我们需要优先级高的先出队列,这就类似VIP之类的.
下面给出实现优先级队列的两种思路:
想法一:
Push:在需求的优先级的位置插入数据,时间复杂度为O(n).
Pop:直接从队头删除数据,时间复杂度为O(1).
想法二:
Push:直接插在队尾,时间复杂度为O(1).
Pop:找到优先级最高的元素删除,时间复杂度为O(n).
在实际应用中第一种想法是优于第二种想法的,但是其实还有一种更加高效的方法,那就是用堆实现优先级队列
四.代码实现>
Heap.h
#pragma once
//利用仿函数的特性实现代码的复用性
template<class T>
struct Small
{
bool operator()(const T& l,const T& r)
{
return l < r;
}
};
template<class T>
struct Large
{
bool operator()(const T& l,const T& r)
{
return l > r;
}
};
template<class T,class Compare=Large<T>> //缺省是建大堆
class Heap
{
public:
Heap(const T *a,int size)
{
assert(a);
_a.reserve(size);
for (int i=0;i<size;++i)
{
_a.push_back(a[i]);
}
//建堆的时候从倒数第一个非叶子结点开始.
for (int j=(size-2)/2;j>=0;--j)
{
_AdjustDown(j);
}
}
void Push(const T& x)
{
_a.push_back(x);
_AdjustUp(_a.size()-1);
}
void Pop()
{
assert(!_a.empty());
swap(_a[0],_a[_a.size()-1]);
_a.pop_back();
_AdjustDown(0);
}
size_t Size()
{
return _a.size();
}
bool Empty()
{
return _a.empty();
}
const T& Top()const
{
assert(!_a.empty());
return _a[0];
}
void Display()
{
for (size_t i=0;i<_a.size();++i)
{
cout<<_a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
protected:
void _AdjustDown(int root)
{
int parent=root;
size_t child=2*root+1;
while (child < _a.size())
{
Compare com;
//child指向左右孩子中较大的那个数
//if (child+1 < _a.size()
// && _a[child+1] > _a[child])
if(child+1 < _a.size()
&& com(_a[child+1],_a[child]))
{
child++;
}
//if (_a[child] > _a[parent])
if(com(_a[child],_a[parent]))
{
swap(_a[child],_a[parent]);
parent=child;
//初始的child默认指向左孩子
child=2*parent+1;
}
else
break;
}
}
void _AdjustUp(int child)
{
while (child > 0)
{
int parent=(child-1)/2;
Compare com;
//if (_a[child] > _a[parent])
if(com(_a[child],_a[parent]))
{
swap(_a[child],_a[parent]);
child=parent;
}
else
//插入的数据比父节点的数据域小
break;
}
}
protected:
vector<T> _a;
};
//利用堆解决优先级队列的问题
template<class T,class Compare=Large<T>>
class PriorityQueue
{
public:
PriorityQueue(int *a,int size)
:_pq(a,size)
{}
void Push(const T& x)
{
_pq.Push(x);
}
void Pop()
{
_pq.Pop();
}
const T& Top()const
{
return _pq.Top();
}
void Display()
{
_pq.Display();
}
protected:
Heap<T,Compare> _pq;
};
void testHeap()
{
int a[]={10,16,18,12,11,13,15,17,14,19};
int size=sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]);
Heap<int,Large<int>> hp1(a,size); //建大堆
hp1.Display();
hp1.Push(20);
cout<<"Top?"<<hp1.Top()<<endl; //20
hp1.Pop();
cout<<"Top?"<<hp1.Top()<<endl; //19
cout<<"Size?"<<hp1.Size()<<endl; //10
cout<<"Empty?"<<hp1.Empty()<<endl; //0
hp1.Push(2);
hp1.Pop();
Heap<int,Small<int>> hp2(a,size); //建小堆
hp2.Display();
}
void testPriQueue()
{
int a[]={10,16,18,12,11,13,15,17,14,19};
int size=sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]);
PriorityQueue<int> pq1(a,size);
pq1.Display(); //19 17 18 14 16 13 15 12 10
cout<<"Top?"<<pq1.Top()<<endl; //19
pq1.Push(20);
pq1.Display(); //20 19 18 14 17 13 15 12 10 11 16
pq1.Pop();
pq1.Display();
PriorityQueue<int,Small<int>> pq2(a,size);
pq2.Display(); //10 11 13 12 16 18 15 17 14 19
}