个人机器学习笔记之SVM
吴恩达机器学习笔记(4)——SVM
机器学习个人笔记,学习中水平有限,内容如有缺漏还请多多包涵。
序言
本来打算接着按视频顺序学习神经网络的,但是考虑到神经网络是一个很大块的知识点,于是打算先学完监督学习部分中小块的知识再来攻坚,可没想到SVM这章并没有给出实现的公式,因此只好调用现成的库(主要是sklearn)来完成SVM的探究。
调用sklearn实现的SVM的python代码
import numpy as np
from sklearn import svm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
def plot_decision_boundary(model, axis):#绘制分类区间的函数
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(#生产网格数据
np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], int((axis[1]-axis[0])*100)).reshape(-1, 1),
np.linspace(axis[2], axis[3], int((axis[3]-axis[2])*100)).reshape(-1, 1),
)
X_new = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()]
#np.c_是按行连接两个矩阵,就是把两矩阵左右相加,要求行数相等。
y_predict = model.predict(X_new)
zz = y_predict.reshape(x0.shape)
custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A','#FFF59D','#90CAF9'])
plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap)#绘制等高线图
iris = datasets.load_iris()#引入iris数据集
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
# 只取前两个特征
X = X[y<2,:2]
y = y[y<2]
standardScaler = StandardScaler()
standardScaler.fit(X)
X_standard = standardScaler.transform(X)#对数据进行归一化
clf = svm.SVC(kernel='linear',C=0.00000001)#使用线性分类
clf.fit(X_standard,y)
plot_decision_boundary(clf, axis=[-3, 3, -3,3])
plt.scatter(X_standard[y==0,0], X_standard[y==0,1], color='red')
plt.scatter(X_standard[y==1,0], X_standard[y==1,1], color='blue')
plt.show()
当C=0.4时的分类情况

当C=0.00000001时的分类情况
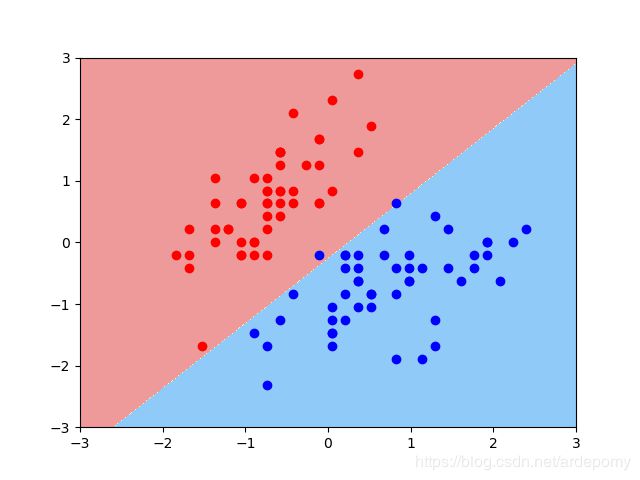
实现过程记录
发现对sklearn还不熟悉,只好在学习吴恩达课程的同时摸摸sklearn的各种功能
sklearn中实现SVM的函数的参数说明:
sklearn.svm.SVC(C=1.0, kernel='rbf', degree=3, gamma='auto', coef0=0.0, shrinking=True, probability=False,
tol=0.001, cache_size=200, class_weight=None, verbose=False, max_iter=-1, decision_function_shape=None,random_state=None)
参数:
C:C-SVC的惩罚参数C?默认值是1.0
''' C越大,相当于惩罚松弛变量,希望松弛变量接近0,即对误分类的惩罚增大,趋向于对训练集全分对的情况,这样对训练集测试时准确率很高,但泛化能力弱。C值小,对误分类的惩罚减小,允许容错,将他们当成噪声点,泛化能力较强。 '''
kernel :核函数,默认是rbf,可以是‘linear’, ‘poly’, ‘rbf’, ‘sigmoid’, ‘precomputed’
''' 0 – 线性:u'v 1 – 多项式:(gamma*u'*v + coef0)^degree 2 – RBF函数:exp(-gamma|u-v|^2) 3 –sigmoid:tanh(gamma*u'*v + coef0) '''
degree :多项式poly函数的维度,默认是3,选择其他核函数时会被忽略。
gamma : ‘rbf’,‘poly’ 和‘sigmoid’的核函数参数。默认是’auto’,则会选择1/n_features
coef0 :核函数的常数项。对于‘poly’和 ‘sigmoid’有用。
probability :是否采用概率估计?.默认为False
shrinking :是否采用shrinking heuristic方法,默认为true
tol :停止训练的误差值大小,默认为1e-3
cache_size :核函数cache缓存大小,默认为200
class_weight :类别的权重,字典形式传递。设置第几类的参数C为weight*C(C-SVC中的C)
verbose :允许冗余输出?
max_iter :最大迭代次数。-1为无限制。
decision_function_shape :‘ovo’, ‘ovr’ or None, default=None3
random_state :数据洗牌时的种子值,int值
主要调节的参数有:C、kernel、degree、gamma、coef0。
sklearn是个极其方便的库,本来要写一大段才能实现的算法,现在只需要fit一下就好了。
公式部分
SVM原本的损失函数公式:
1 m [ ∑ i = 1 m ( y ( i ) c o s t 1 ( θ T x ( i ) ) + ( 1 − y ( i ) ) c o s t 0 ( θ T x ( i ) ) ) + λ 2 ∑ j = 0 m θ j 2 ] \frac{1}{m}[\sum_{i=1}^m (y^{(i)}cost_{1}(\theta^{T} x^{(i)})+(1-y^{(i)})cost_{0}(\theta^{T} x^{(i)}))+\frac{\lambda}{2}\sum_{j=0}^m\theta_{j}^2] m1[i=1∑m(y(i)cost1(θTx(i))+(1−y(i))cost0(θTx(i)))+2λj=0∑mθj2]
式中cost1()和cost0()分别等于
− l o g h θ ( x ( i ) ) . − l o g ( 1 − h θ ( x ( i ) ) ) . -logh_{\theta}(x^{(i)}). -log(1-h_{\theta}(x^{(i)})). −loghθ(x(i)).−log(1−hθ(x(i))).
将式中第一个求和部分看做A,第二个求和部分看做B,则最小化目标可以变为A+λB,也可写作CA+B,其中C等于1/λ
最终的损失函数公式:
C [ ∑ i = 1 m ( y ( i ) c o s t 1 ( θ T x ( i ) ) + ( 1 − y ( i ) ) c o s t 0 ( θ T x ( i ) ) ) ] + 1 2 ∑ i = 0 m θ i 2 C[\sum_{i=1}^m (y^{(i)}cost_{1}(\theta^{T} x^{(i)})+(1-y^{(i)})cost_{0}(\theta^{T} x^{(i)}))]+\frac{1}{2}\sum_{i=0}^m\theta_{i}^2 C[i=1∑m(y(i)cost1(θTx(i))+(1−y(i))cost0(θTx(i)))]+21i=0∑mθi2
引用
sklearn系列之 sklearn.svm.SVC详解
svm代码实现
学习视频
SVM
其他笔记
- 机器学习入门
- 目录