Spring Boot系列十六 WebSocket简介和spring boot集成简单消息代理
1. 概述
本文介绍webSocket相关的内容,主要有如下内容:
- WebSocket的诞生的背景、运行机制和抓包分析
- WebSocket 的应用场景、服务端和浏览器的版本要求
- Spring 内嵌的简单消息代理 和 消息流程图
- 在Spring boot中集成websocket,并介绍stomp、sockjs的用法
- 介绍拦截器HandshakeInterceptor和ChannelInterceptor,并演示拦截器的用法
- @SendTo和@SendToUser用法和区别
2. WebSocket的诞生的背景、运行机制和抓包分析
2.1. Websocket诞生的背景
对于需要实时响应、高并发的应用,传统的请求-响应模式的 Web的效率不是很好。在处理此类业务场景时,通常采用的方案有:
- 轮询,此方法容易浪费带宽,效率低下
- 基于 Flash,AdobeFlash 通过自己的 Socket 实现完成数据交换,再利用 Flash 暴露出相应的接口为 JavaScript 调用,从而达到实时传输目的。但是现在flash没落了,此方法不好用
- MQTT,Comet 开源框架,这些技术在大流量的情况,效果不是很好
在此背景下, HTML5规范中的(有 Web TCP 之称的) WebSocket ,就是一种高效节能的双向通信机制来保证数据的实时传输。
2.2. WebSocket 运行机制
WebSocket 是 HTML5 一种新的协议。它建立在 TCP 之上,实现了客户端和服务端全双工异步通信.
它和 HTTP 最大不同是:
- WebSocket 是一种双向通信协议,WebSocket 服务器和 Browser/Client Agent 都能主动的向对方发送或接收数据;
- WebSocket 需要类似 TCP 的客户端和服务器端通过握手连接,连接成功后才能相互通信。
传统 HTTP 请求响应客户端服务器交互图
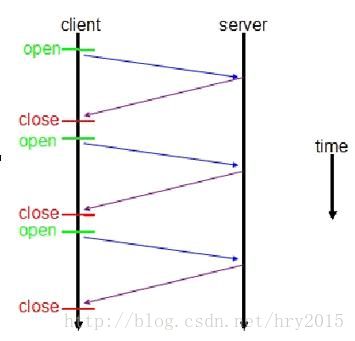
WebSocket 请求响应客户端服务器交互图
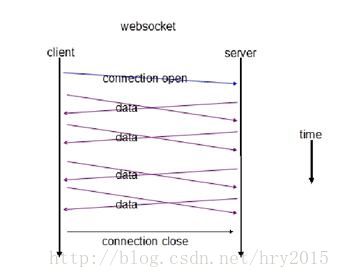
对比上面两图,相对于传统 HTTP 每次请求-应答都需要客户端与服务端建立连接的模式,WebSocket 一旦 WebSocket 连接建立后,后续数据都以帧序列的形式传输。在客户端断开 WebSocket 连接或 Server 端断掉连接前,不需要客户端和服务端重新发起连接请求,这样保证websocket的性能优势,实时性优势明显
2.3. WebSocket抓包分析
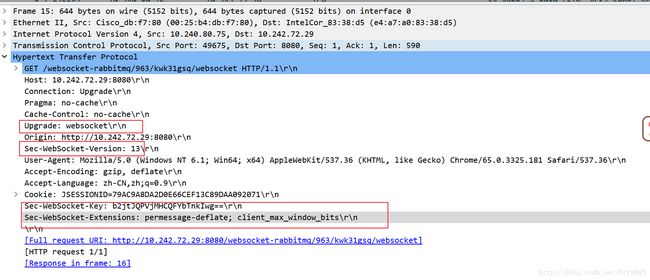
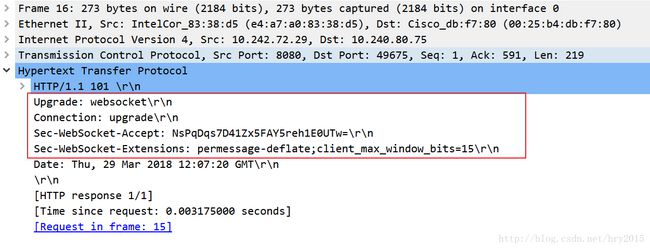
我们再通过客户端和服务端交互的报文看一下 WebSocket 通讯与传统 HTTP 的不同:
WebSocket 客户连接服务端端口,执行双方握手过程,客户端发送数据格式类似:
请求 :
- “Upgrade:websocket”参数值表明这是 WebSocket 类型请求
- “Sec-WebSocket-Key”是 WebSocket 客户端发送的一个 base64
编码的密文,要求服务端必须返回一个对应加密的“Sec-WebSocket-Accept”应答,否则客户端会抛出“Error during WebSocket handshake”错误,并关闭连接。
服务端收到报文后返回的数据格式类似:
- “Sec-WebSocket-Accept”的值是服务端采用与客户端一致的密钥计算出来后返回客户端的
- “HTTP/1.1 101” : Switching Protocols”表示服务端接受 WebSocket 协议的客户端连接,经过这样的请求-响应处理后,客户端服务端的 WebSocket 连接握手成功, 后续就可以进行 TCP 通讯了
3. WebSocket 的应用场景、服务端和浏览器的版本要求
3.1. 使用websocket的场景
客户端和服务器需要以高频率和低延迟交换事件。 对时间延迟都非常敏感,并且还需要以高频率交换各种各样的消息
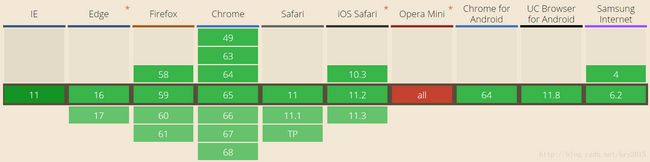
3.2. 服务端和浏览器的版本要求
WebSocket 服务端在各个主流应用服务器厂商中已基本获得符合 JEE JSR356 标准规范 API 的支持。当前支持websocket的版本:Tomcat 7.0.47+, Jetty 9.1+, GlassFish 4.1+, WebLogic 12.1.3+, and Undertow 1.0+ (and WildFly 8.0+).
浏览器的支持版本:
查看所有支持websocket浏览器的连接:
4. Spring 内嵌的简单消息代理 和 消息流程图
4.1. Simple Broker
Spring 内置简单消息代理。这个代理处理来自客户端的订阅请求,将它们存储在内存中,并将消息广播到具有匹配目标的连接客户端
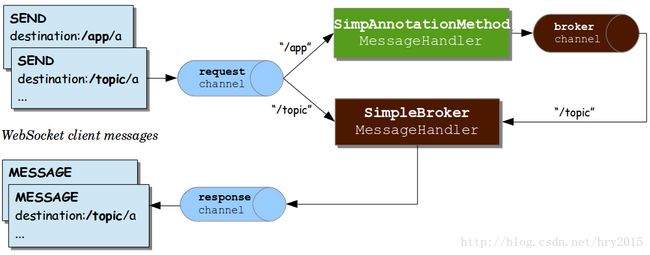
4.2. 消息流程图
上图3个消息通道说明如下:
- “clientInboundChannel” — 用于传输从webSocket客户端接收的消息
- “clientOutboundChannel” — 用于传输向webSocket客户端发送的消息
- “brokerChannel” — 用于传输从服务器端应用程序代码向消息代理发送消息
5. 在Spring boot中集成websocket,并介绍stomp、sockjs的用法
5.1. pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocketartifactId>
dependency>5.2. POJO类
RequestMessage: 浏览器向服务端请求的消息
public class RequestMessage {
private String name;
// set/get略
}ResponseMessage: 服务端返回给浏览器的消息
public class ResponseMessage {
private String responseMessage;
// set/get略
}5.3. BroadcastCtl
此类是@Controller类
- broadcastIndex()方法:使用 @RequestMapping转到的页面
- broadcast()方法上的注解说明
- @MessageMapping:指定要接收消息的地址,类似@RequestMapping
- @SendTo默认消息将被发送到与传入消息相同的目的地,但是目的地前面附加前缀(默认情况下为“/topic”}
@Controller
public class BroadcastCtl {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BroadcastCtl.class);
// 收到消息记数
private AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
/** * @MessageMapping 指定要接收消息的地址,类似@RequestMapping。除了注解到方法上,也可以注解到类上 * @SendTo默认 消息将被发送到与传入消息相同的目的地 * 消息的返回值是通过{@link org.springframework.messaging.converter.MessageConverter}进行转换 * @param requestMessage * @return */
@MessageMapping("/receive")
@SendTo("/topic/getResponse")
public ResponseMessage broadcast(RequestMessage requestMessage){
logger.info("receive message = {}" , JSONObject.toJSONString(requestMessage));
ResponseMessage responseMessage = new ResponseMessage();
responseMessage.setResponseMessage("BroadcastCtl receive [" + count.incrementAndGet() + "] records");
return responseMessage;
}
@RequestMapping(value="/broadcast/index")
public String broadcastIndex(HttpServletRequest req){
System.out.println(req.getRemoteHost());
return "websocket/simple/ws-broadcast";
}
}
5.4. WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer
配置消息代理,默认情况下使用内置的消息代理。
类上的注解@EnableWebSocketMessageBroker:此注解表示使用STOMP协议来传输基于消息代理的消息,此时可以在@Controller类中使用@MessageMapping
- 在方法registerStompEndpoints()里addEndpoint方法:添加STOMP协议的端点。这个HTTP URL是供WebSocket或SockJS客户端访问的地址;withSockJS:指定端点使用SockJS协议
- 在方法configureMessageBroker()里设置简单消息代理,并配置消息的发送的地址符合配置的前缀的消息才发送到这个broker
@Configuration
// 此注解表示使用STOMP协议来传输基于消息代理的消息,此时可以在@Controller类中使用@MessageMapping
@EnableWebSocketMessageBroker
public class WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer extends AbstractWebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer {
@Override
public void registerStompEndpoints(StompEndpointRegistry registry) {
/** * 注册 Stomp的端点 * addEndpoint:添加STOMP协议的端点。这个HTTP URL是供WebSocket或SockJS客户端访问的地址 * withSockJS:指定端点使用SockJS协议 */
registry.addEndpoint("/websocket-simple")
.setAllowedOrigins("*") // 添加允许跨域访问
.withSockJS();
}
@Override
public void configureMessageBroker(MessageBrokerRegistry registry) {
/** * 配置消息代理 * 启动简单Broker,消息的发送的地址符合配置的前缀来的消息才发送到这个broker */
registry.enableSimpleBroker("/topic","/queue");
}
@Override
public void configureClientInboundChannel(ChannelRegistration registration) {
super.configureClientInboundChannel(registration);
}
}
5.5. 前端stomp、sockjs的配置
Stomp
websocket使用socket实现双工异步通信能力。但是如果直接使用websocket协议开发程序比较繁琐,我们可以使用它的子协议Stomp
SockJS
sockjs是websocket协议的实现,增加了对浏览器不支持websocket的时候的兼容支持
SockJS的支持的传输的协议有3类: WebSocket, HTTP Streaming, and HTTP Long Polling。默认使用websocket,如果浏览器不支持websocket,则使用后两种的方式。
SockJS使用”Get /info”从服务端获取基本信息。然后客户端会决定使用哪种传输方式。如果浏览器使用websocket,则使用websocket。如果不能,则使用Http Streaming,如果还不行,则最后使用 HTTP Long Polling
ws-broadcast.jsp
前端页面
引入相关的stomp.js、sockjs.js、jquery.js
<script src="/websocket/jquery.js">script>
<script src="/websocket/stomp.js">script>
<script src="/websocket/sockjs.js">script>前端访问websocket,重要代码说明如下:
- var socket = new SockJS(‘/websocket-simple’):websocket的连接地址,此值等于WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer中registry.addEndpoint(“/websocket-simple”).withSockJS()配置的地址
- stompClient.subscribe(‘/topic/getResponse’, function(respnose){ … }): 客户端订阅消息的目的地址:此值和BroadcastCtl中的@SendTo(“/topic/getResponse”)注解的配置的值相同
- stompClient.send(“/receive”, {}, JSON.stringify({ ‘name’: name })): 客户端消息发送的目的地址:服务端使用BroadcastCtl中@MessageMapping(“/receive”)注解的方法来处理发送过来的消息
<body onload="disconnect()">
<div>
<div>
<button id="connect" onclick="connect();">连接button>
<button id="disconnect" disabled="disabled" onclick="disconnect();">断开连接button>
div>
<div id="conversationDiv">
<label>输入你的名字label><input type="text" id="name" />
<button id="sendName" onclick="sendName();">发送button>
<p id="response">p>
div>
div>
<script type="text/javascript"> var stompClient = null; function setConnected(connected) { document.getElementById('connect').disabled = connected; document.getElementById('disconnect').disabled = !connected; document.getElementById('conversationDiv').style.visibility = connected ? 'visible' : 'hidden'; $('#response').html(); } function connect() { // websocket的连接地址,此值等于WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer中registry.addEndpoint("/websocket-simple").withSockJS()配置的地址 var socket = new SockJS('/websocket-simple'); stompClient = Stomp.over(socket); stompClient.connect({}, function(frame) { setConnected(true); console.log('Connected: ' + frame); // 客户端订阅消息的目的地址:此值BroadcastCtl中被@SendTo("/topic/getResponse")注解的里配置的值 stompClient.subscribe('/topic/getResponse', function(respnose){ showResponse(JSON.parse(respnose.body).responseMessage); }); }); } function disconnect() { if (stompClient != null) { stompClient.disconnect(); } setConnected(false); console.log("Disconnected"); } function sendName() { var name = $('#name').val(); // 客户端消息发送的目的:服务端使用BroadcastCtl中@MessageMapping("/receive")注解的方法来处理发送过来的消息 stompClient.send("/receive", {}, JSON.stringify({ 'name': name })); } function showResponse(message) { var response = $("#response"); response.html(message + "\r\n" + response.html()); } script>
body>
5.6. 测试
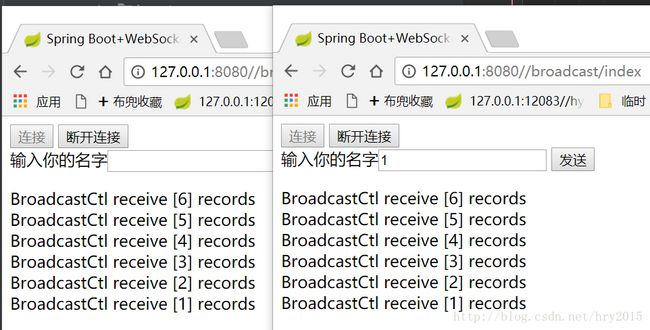
启动服务WebSocketApplication
在打开多个标签,执行请求: http://127.0.0.1:8080//broadcast/index
点击”连接”,然后”发送”多次,结果如下:
可知websocket执行成功,并且将所有的返回值发送给所有的订阅者
6. 介绍拦截器HandshakeInterceptor和ChannelInterceptor,并演示拦截器的用法
我们可以为websocket配置拦截器,默认有两种:
- HandshakeInterceptor:拦截websocket的握手请求。在服务端和客户端在进行握手时会被执行
- ChannelInterceptor:拦截Message。可以在Message对被在发送到MessageChannel前后查看修改此值,也可以在MessageChannel接收MessageChannel对象前后修改此值
6.1. HandShkeInceptor
拦截websocket的握手请求。实现 接口 HandshakeInterceptor或继承类DefaultHandshakeHandler
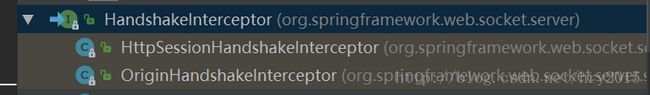
HttpSessionHandshakeInterceptor:关于httpSession的操作,这个拦截器用来管理握手和握手后的事情,我们可以通过请求信息,比如token、或者session判用户是否可以连接,这样就能够防范非法用户
OriginHandshakeInterceptor:检查Origin头字段的合法性
自定义HandshakeInterceptor :
@Component
public class MyHandShakeInterceptor implements HandshakeInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean beforeHandshake(ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response, WebSocketHandler wsHandler, Map attributes) throws Exception {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getCanonicalName() + "http协议转换websoket协议进行前, 握手前"+request.getURI());
// http协议转换websoket协议进行前,可以在这里通过session信息判断用户登录是否合法
return true;
}
@Override
public void afterHandshake(ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response, WebSocketHandler wsHandler, Exception ex) {
//握手成功后,
System.out.println(this.getClass().getCanonicalName() + "握手成功后...");
}
}
6.2. ChannelInterceptor
ChannelInterceptor:可以在Message对象在发送到MessageChannel前后查看修改此值,也可以在MessageChannel接收MessageChannel对象前后修改此值
在此拦截器中使用StompHeaderAccessor 或 SimpMessageHeaderAccessor访问消息
自定义ChannelInterceptorAdapter
@Component
public class MyChannelInterceptorAdapter extends ChannelInterceptorAdapter {
@Autowired
private SimpMessagingTemplate simpMessagingTemplate;
@Override
public boolean preReceive(MessageChannel channel) {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getCanonicalName() + " preReceive");
return super.preReceive(channel);
}
@Override
public Message preSend(Message message, MessageChannel channel) {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getCanonicalName() + " preSend");
StompHeaderAccessor accessor = StompHeaderAccessor.wrap(message);
StompCommand command = accessor.getCommand();
//检测用户订阅内容(防止用户订阅不合法频道)
if (StompCommand.SUBSCRIBE.equals(command)) {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getCanonicalName() + " 用户订阅目的地=" + accessor.getDestination());
// 如果该用户订阅的频道不合法直接返回null前端用户就接受不到该频道信息
return super.preSend(message, channel);
} else {
return super.preSend(message, channel);
}
}
@Override
public void afterSendCompletion(Message message, MessageChannel channel, boolean sent, Exception ex) {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getCanonicalName() +" afterSendCompletion");
StompHeaderAccessor accessor = StompHeaderAccessor.wrap(message);
StompCommand command = accessor.getCommand();
if (StompCommand.SUBSCRIBE.equals(command)){
System.out.println(this.getClass().getCanonicalName() + " 订阅消息发送成功");
this.simpMessagingTemplate.convertAndSend("/topic/getResponse","消息发送成功");
}
//如果用户断开连接
if (StompCommand.DISCONNECT.equals(command)){
System.out.println(this.getClass().getCanonicalName() + "用户断开连接成功");
simpMessagingTemplate.convertAndSend("/topic/getResponse","{'msg':'用户断开连接成功'}");
}
super.afterSendCompletion(message, channel, sent, ex);
}
}6.3. 在WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer中配置拦截器
- 在registerStompEndpoints()方法中通过registry.addInterceptors(myHandShakeInterceptor)添加自定义HandShkeInceptor 拦截
- 在configureClientInboundChannel()方法中registration.setInterceptors(myChannelInterceptorAdapter)添加ChannelInterceptor拦截器
@Configuration
// 此注解表示使用STOMP协议来传输基于消息代理的消息,此时可以在@Controller类中使用@MessageMapping
@EnableWebSocketMessageBroker
public class WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer extends AbstractWebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer {
@Autowired
private MyHandShakeInterceptor myHandShakeInterceptor;
@Autowired
private MyChannelInterceptorAdapter myChannelInterceptorAdapter;
@Override
public void registerStompEndpoints(StompEndpointRegistry registry) {
/** * 注册 Stomp的端点 * * addEndpoint:添加STOMP协议的端点。这个HTTP URL是供WebSocket或SockJS客户端访问的地址 * withSockJS:指定端点使用SockJS协议 */
registry.addEndpoint("/websocket-simple")
.setAllowedOrigins("*") // 添加允许跨域访问
//. setAllowedOrigins("http://mydomain.com");
.addInterceptors(myHandShakeInterceptor) // 添加自定义拦截
.withSockJS();
}
@Override
public void configureClientInboundChannel(ChannelRegistration registration) {
ChannelRegistration channelRegistration = registration.setInterceptors(myChannelInterceptorAdapter);
super.configureClientInboundChannel(registration);
}
}
6.4. 测试:
和上个例子相同的方式进行测试,这里略
7. @SendTo和@SendToUser用法和区别
上文@SendTo会将消息推送到所有订阅此消息的连接,即订阅/发布模式。@SendToUser只将消息推送到特定的一个订阅者,即点对点模式
@SendTo:会将接收到的消息发送到指定的路由目的地,所有订阅该消息的用户都能收到,属于广播。
@SendToUser:消息目的地有UserDestinationMessageHandler来处理,会将消息路由到发送者对应的目的地, 此外该注解还有个broadcast属性,表明是否广播。就是当有同一个用户登录多个session时,是否都能收到。取值true/false.
7.1. BroadcastSingleCtl
此类上面的BroadcastCtl 大部分相似,下面只列出不同的地方
broadcast()方法:这里使用 @SendToUser注解
@Controller
public class BroadcastSingleCtl {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BroadcastSingleCtl.class);
// 收到消息记数
private AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
// @MessageMapping 指定要接收消息的地址,类似@RequestMapping。除了注解到方法上,也可以注解到类上
@MessageMapping("/receive-single")
/** * 也可以使用SendToUser,可以将将消息定向到特定用户 * 这里使用 @SendToUser,而不是使用 @SendTo */
@SendToUser("/topic/getResponse")
public ResponseMessage broadcast(RequestMessage requestMessage){
….
}
@RequestMapping(value="/broadcast-single/index")
public String broadcastIndex(){
return "websocket/simple/ws-broadcast-single";
}
7.2. 在WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer中配置
@Configuration
@MessageMapping
@EnableWebSocketMessageBroker
public class WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer extends AbstractWebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer {
@Override
public void registerStompEndpoints(StompEndpointRegistry registry) {
….
registry.addEndpoint("/websocket-simple-single").withSockJS();
}
….
}7.3. ws-broadcast-single.jsp页面
ws-broadcast-single.jsp页面:和ws-broadcast.jsp相似,这里只列出不同的地方
最大的不同是 stompClient.subscribe的订阅的目的地的前缀是/user,后面再上@SendToUser(“/topic/getResponse”)注解的里配置的值
<script type="text/javascript"> var stompClient = null; … function connect() { // websocket的连接地址,此值等于WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer中registry.addEndpoint("/websocket-simple-single").withSockJS()配置的地址 var socket = new SockJS('/websocket-simple-single'); //1 stompClient = Stomp.over(socket); stompClient.connect({}, function(frame) { setConnected(true); console.log('Connected: ' + frame); // 客户端订阅消息的目的地址:此值等于BroadcastCtl中@SendToUser("/topic/getResponse")注解的里配置的值。这是请求的地址必须使用/user前缀 stompClient.subscribe('/user/topic/getResponse', function(respnose){ //2 showResponse(JSON.parse(respnose.body).responseMessage); }); }); } function disconnect() { if (stompClient != null) { stompClient.disconnect(); } setConnected(false); console.log("Disconnected"); } function sendName() { var name = $('#name').val(); //// 客户端消息发送的目的:服务端使用BroadcastCtl中@MessageMapping("/receive-single")注解的方法来处理发送过来的消息 stompClient.send("/receive-single", {}, JSON.stringify({ 'name': name })); } … script>
7.4. 测试
启动服务WebSocketApplication
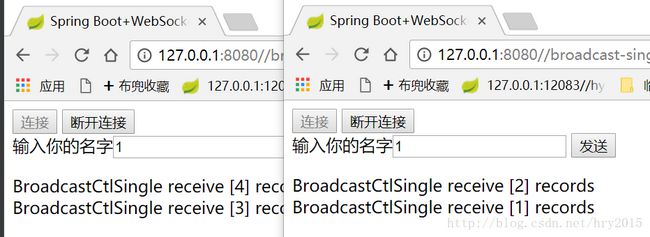
执行请求: http://127.0.0.1:8080//broadcast-single/index
点击”连接”,在两个页面各发送两次消息,结果如下:
可知websocket执行成功,并且所有的返回值只返回发送者,而不是所有的订阅者
8. 代码
所有的详细代码见github代码,请尽量使用tag v0.19,不要使用master,因为master一直在变,不能保证文章中代码和github上的代码一直相同