二叉查找树(二)
The search tree data structure supports many dynamic-set operations, including SEARCH, MINIMUM, MAXIMUM, PREDECESSOR, SUCCESSOR, INSERT, and DELETE. Thus, we can use a search tree both as a dictionary and as a priority queue.
设x是二叉搜索树中的一个结点。如果y是x的左子树中的一个结点,那么y.key<=x.key。如果y是x的右子树中的一个结点,那么y.key>=x.key。
1、查找
查找前驱
1)左子树存在,找到左子树中最大的节点;
2)左子树不存在,向上找到为右子树的节点的父节点;
查找后继
1)右子树存在,找到右子树中最小的节点;
2)右子树不存在,向上找到为左子树的节点的父节点;
2、插入
从根开始,根据key指,沿树下降,直到NULL,作为叶节点的孩子进行插入。
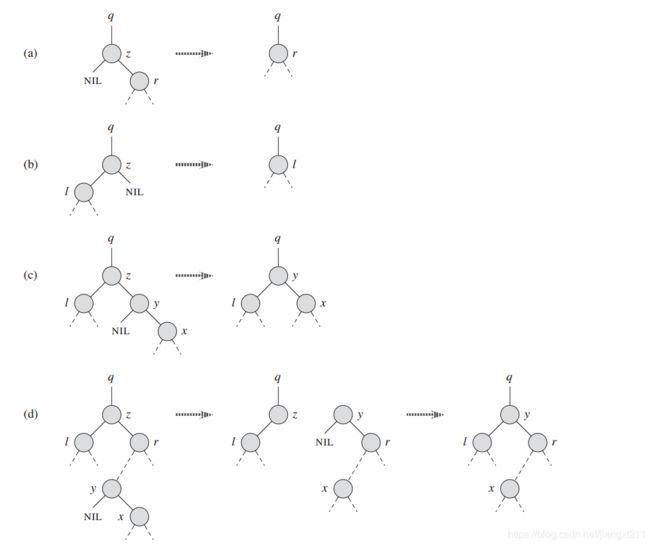
3、删除
1)如果z没有孩子,那么简单地删除z,并修改其父节点,用NULL作为孩子来代替z;
2)如果z只有一个孩子,那么将这个孩子提升到树中z的位置,并修改其父节点,用z的孩子来替换;
3)如果z有两个孩子,那么找z的后继y,并让y占据树中z的位置,z的原来的右子树部分成为y的新的右子树,并且z的左子树成为y的新的左子树。
#ifndef _BTREE_H
#define _BTREE_H
#define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER)
/**
* container_of - cast a member of a structure out to the containing structure
* @ptr: the pointer to the member.
* @type: the type of the container struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the member within the struct.
*
*/
#if 0
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \
const typeof(((type *)0)->member)*__mptr = (ptr); \
(type *)((char *)__mptr - offsetof(type, member)); })
#endif
#ifndef container_of
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) \
(type *)((char *)(ptr) - (char *) &((type *)0)->member)
#endif
#define list_entry(prt, type, member) container_of(ptr, type, member)
typedef int (BST_COMPARE)(const void *, const void *);
typedef struct bstnode
{
struct bstnode *parent;
struct bstnode *left;
struct bstnode *right;
} BST_NODE;
typedef struct bstree
{
BST_COMPARE *compare;
BST_NODE *root;
unsigned short key_offset;
unsigned short node_offset;
} BST_TREE;
/*
参数:BST_NODE *node
返回值:void
作用:初始化节点
*/
void bst_init_node(BST_NODE *node);
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree
BST_COMPARE *compare
unsigned short key_offset
unsigned short node_offset
返回值:void
作用:初始化二叉查找树
*/
void bst_init_tree(BST_TREE *tree, BST_COMPARE *compare,
unsigned short key_offset, unsigned short node_offset);
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree, void *key
返回值:void *
作用:通过key找到节点
*/
void *bst_find(BST_TREE *tree, void *key);
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree
返回值:void *
作用:找到树中最小节点
*/
void *bst_find_min(BST_TREE *tree);
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree
返回值:void *
作用:找到树中最大节点
*/
void *bst_find_max(BST_TREE *tree);
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node
返回值:void *
作用:找到指定节点的前驱(predecessor)
*/
void *bst_find_prev(BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node);
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node
返回值:void *
作用:找到指定节点的后继(successor)
*/
void *bst_find_next(BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node);
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node
返回值:void
作用:插入节点
*/
void bst_insert(BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node);
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node
返回值:void
作用:插入节点
*/
void bst_insert2(BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node);
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node
返回值:void *
作用:删除节点
*/
void bst_delete(BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node);
#endif
#include
#include
#include "btree.h"
#define BST_GET_KEY(tree, node) \
((void *)((unsigned char *)node - tree->node_offset + tree->key_offset))
#define BST_GET_OBJECT(tree, node) \
((node != NULL) ? (void *)((unsigned char *)node - tree->node_offset) : NULL)
/*
参数:BST_NODE *node
返回值:void
作用:初始化节点
*/
void bst_init_node(BST_NODE *node)
{
node->parent = NULL;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
}
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree
BST_COMPARE *compare
unsigned short key_offset
unsigned short node_offset
返回值:void
作用:初始化二叉查找树
*/
void bst_init_tree(BST_TREE *tree, BST_COMPARE *compare,
unsigned short key_offset, unsigned short node_offset)
{
tree->root = NULL;
tree->compare = compare;
tree->key_offset = key_offset;
tree->node_offset = node_offset;
}
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree, void *key
返回值:void *
作用:通过key找到节点
*/
void *bst_find(BST_TREE *tree, void *key)
{
BST_NODE *node = NULL;
int result = 0;
node = tree->root;
while (node != NULL) {
result = tree->compare(key, BST_GET_KEY(tree, node));
if (result > 0) {
node = node->right;
} else if (result < 0) {
node = node->left;
} else {
break;
}
}
return BST_GET_OBJECT(tree, node);
}
/*
参数:BST_NODE *node
返回值:BST_NODE *
作用:找到树中最小节点
*/
BST_NODE *_bst_find_min(BST_NODE *node)
{
if (node == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
while (node->left != NULL) {
node = node->left;
}
return node;
}
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree
返回值:void *
作用:找到树中最小节点
*/
void *bst_find_min(BST_TREE *tree)
{
BST_NODE *node = NULL;
node = tree->root;
if (node == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
while (node->left != NULL) {
node = node->left;
}
return BST_GET_OBJECT(tree, node);
}
/*
参数:BST_NODE *node
返回值:BST_NODE *
作用:找到树中最大节点
*/
BST_NODE *_bst_find_max(BST_NODE *node)
{
if (node == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
while (node->right != NULL) {
node = node->right;
}
return node;
}
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree
返回值:void *
作用:找到树中最大节点
*/
void *bst_find_max(BST_TREE *tree)
{
BST_NODE *node = NULL;
node = tree->root;
if (node == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
while (node->right != NULL) {
node = node->right;
}
return BST_GET_OBJECT(tree, node);
}
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node
返回值:void *
作用:找到指定节点的前驱(predecessor)
*/
void *bst_find_prev(BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node)
{
if (node == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
/* 1、左子树存在,找到左子树中最大的节点 */
if (node->left != NULL) {
node = node->left;
while (node->right != NULL) {
node = node->right;
}
} else {
/* 2、左子树不存在,向上找到为右子树的节点的父节点 */
while ((node->parent != NULL) && (node->parent->left == node)) {
node = node->parent;
}
node = node->parent;
}
return BST_GET_OBJECT(tree, node);
}
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node
返回值:void *
作用:找到指定节点的后继(successor)
*/
void *bst_find_next(BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node)
{
if (node == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
/* 1、右子树存在,找到右子树中最小的节点 */
if (node->right != NULL) {
node = node->right;
while (node->left != NULL) {
node = node->left;
}
} else {
/* 2、右子树不存在,向上找到为左子树的节点的父节点 */
while ((node->parent != NULL) && (node->parent->right == node)) {
node = node->parent;
}
node = node->parent;
}
return BST_GET_OBJECT(tree, node);
}
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node
返回值:void
作用:插入节点
*/
void bst_insert2(BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node)
{
BST_NODE *parent = NULL;
BST_NODE *iter = NULL;
int result = 0;
iter = tree->root;
while (iter != NULL) {
parent = iter;
result = tree->compare(BST_GET_KEY(tree, node), BST_GET_KEY(tree, iter));
if (result < 0) {
iter = iter->left;
} else {
iter = iter->right;
}
}
node->parent = parent;
if (parent == NULL) {
tree->root = node;
} else {
result = tree->compare(BST_GET_KEY(tree, node), BST_GET_KEY(tree, parent));
if (result < 0) {
parent->left = node;
} else {
parent->right = node;
}
}
}
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node
返回值:void
作用:插入节点
*/
void bst_insert2(BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node)
{
BST_NODE *parent = NULL;
int result = 0;
if (tree->root == NULL) {
tree->root = node;
return;
}
parent = tree->root;
while (parent != NULL) {
result = tree->compare(BST_GET_KEY(tree, node), BST_GET_KEY(tree, parent));
if (result > 0) {
if (parent->right == NULL) {
node->parent = parent;
parent->right = node;
break;
} else {
parent = parent->right;
}
} else if (result < 0) {
if (parent->left == NULL) {
node->parent = parent;
parent->left = node;
break;
} else {
parent = parent->left;
}
} else {
break; /* 已存在 */
}
}
}
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *unode, BST_NODE *vnode
返回值:void
作用:TRANSPLANT, which replaces one subtree as a child of its parent
with another subtree.
*/
void _bst_transplant(BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *unode, BST_NODE *vnode)
{
if (unode->parent == NULL) {
tree->root = vnode;
} else if (unode == unode->parent->left) {
unode->parent->left = vnode;
} else {
unode->parent->right = vnode;
}
if (vnode != NULL) {
vnode->parent = unode->parent;
}
}
/*
参数:BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node
返回值:void *
作用:删除节点
*/
void bst_delete(BST_TREE *tree, BST_NODE *node)
{
BST_NODE *next = NULL;
if (node == NULL) {
return;
}
if (node->left == NULL) {
_bst_transplant(tree, node, node->right);
} else if (node->right == NULL) {
_bst_transplant(tree, node, node->left);
} else { /* node has two children */
next = _bst_find_min(node->right);
if (next->parent != node) {
_bst_transplant(tree, next, next->right);
next->right = node->right;
next->right->parent = next;
}
/* 使用后继next替换node节点 */
_bst_transplant(tree, node, next);
next->left = node->left;
next->left->parent = next;
}
}
#include
#include
#include
#include "btree.h"
typedef struct life {
BST_NODE node;
int work;
int study;
int play;
} LIFE;
typedef struct all_life {
BST_TREE tree;
} ALL_LIFE;
void bst_print(BST_NODE *node)
{
LIFE *plife = NULL;
if (node == NULL) {
return;
}
/* 中序遍历 */
bst_print(node->left);
plife = (LIFE *)node;
printf("work: %d, study: %d, play: %d\n",
plife->work, plife->study, plife->play);
bst_print(node->right);
}
void bst_print2(ALL_LIFE *all_life)
{
LIFE *plife = NULL;
int index = 0;
plife = bst_find_min(&(all_life->tree));
for (; plife != NULL;
plife = bst_find_next(&(all_life->tree), &(plife->node))) {
printf("%2d: work: %d, study: %d, play: %d\n",
++index, plife->work, plife->study, plife->play);
}
printf("\n");
}
int bstcmp(const void *key1, const void *key2)
{
int *pkey1 = (int *)key1;
int *pkey2 = (int *)key2;
return (*pkey1 - *pkey2 > 0 ? 1 : (*pkey1 - *pkey2 < 0 ? -1 : 0));
}
int main()
{
int i = 0;
int arr[] = { 17, 11, 3, 34, 35, 7, 8, 9, 15, 4, 22, 1 };
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
struct all_life real_life = { 0 };
struct life *my_life = NULL;
bst_init_tree(&real_life.tree, bstcmp, offsetof(LIFE, work), offsetof(LIFE, node));
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
my_life = (struct life *)malloc(sizeof(struct life));
if (my_life == NULL) {
printf("malloc error!\n");
return 1;
}
bst_init_node(&(my_life->node));
my_life->work = arr[i];
my_life->study = arr[i] + 1;
my_life->play = arr[i] + 2;
bst_insert(&(real_life.tree), &(my_life->node));
}
bst_print2(&real_life);
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
printf("Delete key: %d\n", arr[i]);
my_life = bst_find(&(real_life.tree), (void *)&(arr[i]));
bst_delete(&(real_life.tree), &(my_life->node));
free(my_life);
my_life = NULL;
bst_print2(&real_life);
}
getchar();
return 0;
}
内容参考《算法导论》第三版