机器学习实战(八)——回归
线性回归拟合直线
平方误差与最小二乘
∑i=1m(yi−xTiw)2 ∑ i = 1 m ( y i − x i T w ) 2
其中, yi y i 为真实值, xTiw x i T w 为预测值。用矩阵表示:
(y−Xw)T(y−Xw) ( y − X w ) T ( y − X w )
为求得 w w ,将上式求导:
XT(Y−Xw) X T ( Y − X w )
令其等于0,解出 w w :
w^=(XTX)−1XTy w ^ = ( X T X ) − 1 X T y
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def loadDataSet(fileName):
numFeat = len(open(fileName).readline().split('\t')) - 1
xArr = []; yArr = []
fr = open(fileName)
for line in fr.readlines():
lineArr =[]
curLine = line.strip().split('\t')
for i in range(numFeat):
lineArr.append(float(curLine[i]))
xArr.append(lineArr)
yArr.append(float(curLine[-1]))
return xArr, yArr
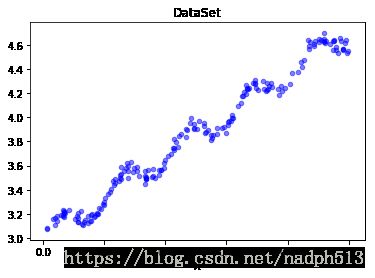
def show_data():
xArr, yArr = loadDataSet('ex0.txt')
n = len(xArr)
xcord = []; ycord = []
for i in range(n):
xcord.append(xArr[i][1]); ycord.append(yArr[i])
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.scatter(xcord, ycord, s = 20, c = 'blue',alpha = .5)
plt.title('DataSet')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.show()
show_data()def standRegres(xArr, yArr):
xMat = np.mat(xArr); yMat = np.mat(yArr).T
xTx = xMat.T * xMat
if np.linalg.det(xTx) == 0.0:
print("矩阵为奇异矩阵,不能求逆")
return
ws = xTx.I * (xMat.T*yMat)
return ws
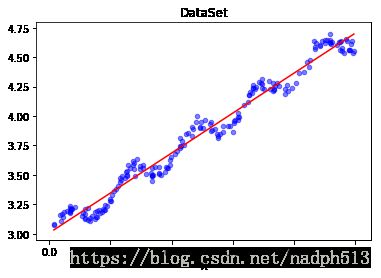
def plotRegression():
xArr, yArr = loadDataSet('ex0.txt')
ws = standRegres(xArr, yArr)
xMat = np.mat(xArr)
yMat = np.mat(yArr)
xCopy = xMat.copy()
xCopy.sort(0)
yHat = xCopy * ws
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.plot(xCopy[:, 1], yHat, c = 'red')
ax.scatter(xMat[:,1].flatten().A[0], yMat.flatten().A[0], s = 20, c = 'blue',alpha = .5) #绘制样本点
plt.title('DataSet')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.show()
plotRegression()局部加权线性回归
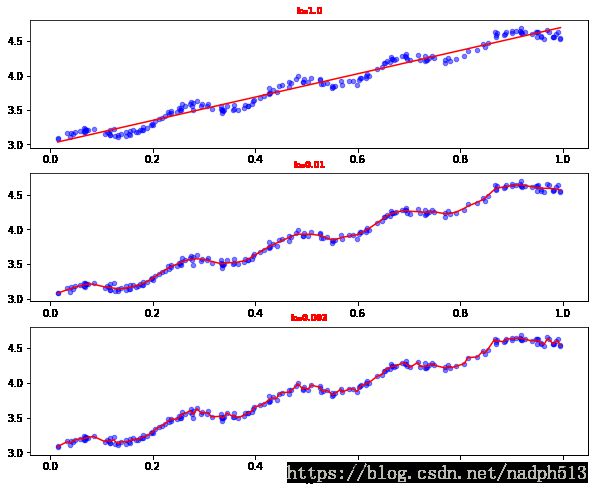
权线性回归(Locally Weighted Linear Regression,LWLR)。在该方法中,我们给待预测点附近的每个点赋予一定的权重。与kNN一样,这种算法每次预测均需要事先选取出对应的数据子集。该算法解出回归系数W的形式如下:
w^=(XTWX)−1XTWy w ^ = ( X T W X ) − 1 X T W y
其中 W W 是一个矩阵,这个公式跟我们上面推导的公式的区别就在于 W W ,它用来给每个点赋予权重。
LWLR使用”核”(与支持向量机中的核类似)来对附近的点赋予更高的权重。核的类型可以自由选择,最常用的核就是高斯核,高斯核对应的权重如下:
w(i,i)=exp(|x(i)−x|−2k2) w ( i , i ) = e x p ( | x ( i ) − x | − 2 k 2 )
def lwlr(testPoint, xArr, yArr, k = 1.0):
xMat = np.mat(xArr); yMat = np.mat(yArr).T
m = np.shape(xMat)[0]
weights = np.mat(np.eye((m)))
for j in range(m):
diffMat = testPoint - xMat[j, :]
weights[j, j] = np.exp(diffMat * diffMat.T/(-2.0 * k**2))
xTx = xMat.T * (weights * xMat)
if np.linalg.det(xTx) == 0.0:
print("矩阵为奇异矩阵,不能求逆")
return
ws = xTx.I * (xMat.T * (weights * yMat))
return testPoint * ws
def lwlrTest(testArr, xArr, yArr, k=1.0):
m = np.shape(testArr)[0]
yHat = np.zeros(m)
for i in range(m):
yHat[i] = lwlr(testArr[i],xArr,yArr,k)
return yHat
def plotlwlrRegression():
xArr, yArr = loadDataSet('ex0.txt')
yHat_1 = lwlrTest(xArr, xArr, yArr, 1.0)
yHat_2 = lwlrTest(xArr, xArr, yArr, 0.01)
yHat_3 = lwlrTest(xArr, xArr, yArr, 0.003)
xMat = np.mat(xArr)
yMat = np.mat(yArr)
srtInd = xMat[:, 1].argsort(0)
xSort = xMat[srtInd][:,0,:]
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=3, ncols=1,sharex=False, sharey=False, figsize=(10,8))
axs[0].plot(xSort[:, 1], yHat_1[srtInd], c = 'red')
axs[1].plot(xSort[:, 1], yHat_2[srtInd], c = 'red')
axs[2].plot(xSort[:, 1], yHat_3[srtInd], c = 'red')
axs[0].scatter(xMat[:,1].flatten().A[0], yMat.flatten().A[0], s = 20, c = 'blue', alpha = .5)
axs[1].scatter(xMat[:,1].flatten().A[0], yMat.flatten().A[0], s = 20, c = 'blue', alpha = .5)
axs[2].scatter(xMat[:,1].flatten().A[0], yMat.flatten().A[0], s = 20, c = 'blue', alpha = .5)
axs0_title_text = axs[0].set_title('k=1.0')
axs1_title_text = axs[1].set_title('k=0.01')
axs2_title_text = axs[2].set_title(u'k=0.003')
plt.setp(axs0_title_text, size=8, weight='bold', color='red')
plt.setp(axs1_title_text, size=8, weight='bold', color='red')
plt.setp(axs2_title_text, size=8, weight='bold', color='red')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.show()
plotlwlrRegression()缩减系数
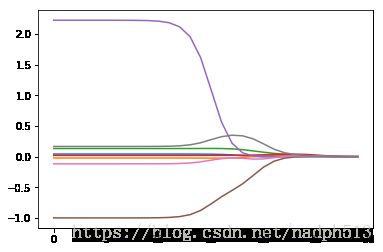
如果数据的特征比样本点多, X X 为 m×n m × n 的矩阵,此时 m>n m > n , X X 为非满秩矩阵。因此,在求逆时会出错。因此,使用岭回归和lasso法缩减系数。
岭回归
岭回归就是在矩阵 XTX X T X 上加一个 λI λ I 从而使得矩阵非奇异,进而能对 XTX+λI X T X + λ I 求逆。其中 I I 是一个 m×m m × m 的单位阵。 λ λ 是自定的数值。在这种情况下,回归系数计算公式将变为:
w^=(XTX+λI)−1XTy w ^ = ( X T X + λ I ) − 1 X T y
def ridgeRegres(xMat, yMat, lam=0.2):
xTx = xMat.T * xMat
denom = xTx + np.eye(np.shape(xMat)[1]) * lam
if np.linalg.det(denom) == 0.0:
print("This mat is singular")
return
ws = denom.I * (xMat.T * yMat)
return ws
def ridgeTest(xArr, yArr):
xMat = np.mat(xArr);
yMat = np.mat(yArr).T;
yMean = np.mean(yMat, 0)
yMat = yMat - yMean
xMeans = np.mean(xMat, 0)
xVar = np.var(xMat, 0)
xMat = (xMat - xMeans) / xVar
numTestPts = 30
wMat = np.zeros((numTestPts, np.shape(xMat)[1]))
for i in range(numTestPts):
ws = ridgeRegres(xMat, yMat, np.exp(i - 10))
wMat[i, :] = ws.T
return wMat
abX, abY = loadDataSet('abalone.txt')
ridgeWeights = ridgeTest(abX, abY)fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.plot(ridgeWeights)
plt.show()lasso
lasso对回归系数做了限定,对应的约束条件如下:
∑k=1n|wk|≤λ ∑ k = 1 n | w k | ≤ λ
逐步向前回归
def stageWise(xArr,yArr,eps=0.01,numIt=100):
xMat = np.mat(xArr); yMat=np.mat(yArr).T
yMean = np.mean(yMat,0)
yMat = yMat - yMean
xMat = np.regularize(xMat)
m,n=np.shape(xMat)
returnMat = np.zeros((numIt,n)) #testing code remove
ws = np.zeros((n,1)); wsTest = ws.copy(); wsMax = ws.copy()
for i in range(numIt):
print(ws.T)
lowestError = inf;
for j in range(n):
for sign in [-1,1]:
wsTest = ws.copy()
wsTest[j] += eps*sign
yTest = xMat*wsTest
rssE = rssError(yMat.A,yTest.A)
if rssE < lowestError:
lowestError = rssE
wsMax = wsTest
ws = wsMax.copy()
returnMat[i,:]=ws.T
return returnMat
stageWise(xArr, yArr, 0.01, 200)