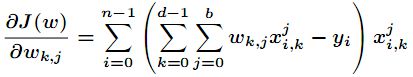多项式回归模型(Office Prices)
题目:https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/predicting-office-space-price
分析:还是上次的房价预测题目,指明要用多项式回归拟合。在多元多项式拟合时候,目标函数表示如下
对其目标函数求偏导得到
很容易写出代码。
代码:
#coding:utf-8
import math
class Data:
def __init__(self):
self.x = []
self.y = 0.0
def makeMatrix(row, col, fill = 0.0):
mat = []
for i in range(row):
mat.append([fill] * col)
return mat
def WX(d, w, b):
res = 0.0
for k in range(len(d.x)):
for j in range(b + 1):
res += w[k][j] * math.pow(d.x[k], j)
return res
def Gradient(d, w, f, b, alpha):
for k in range(f):
for j in range(b + 1):
t1, t2 = 0.0, 0.0
for i in range(len(d)):
t1 += (WX(d[i], w, b) - d[i].y) * math.pow(d[i].x[k], j)
w[k][j] -= alpha * t1
def getValues(d, w, b):
res = 0.0
for i in range(len(d)):
tmp = WX(d[i], w, b)
res += 0.5 * (d[i].y - tmp) * (d[i].y - tmp)
return res
def Iterator(d, w, f, b):
alpha = 0.003
delta = 0.5
oldVal = getValues(d, w, b)
Gradient(d, w, f, b, alpha)
newVal = getValues(d, w, b)
while abs(oldVal - newVal) > delta:
oldVal = newVal
Gradient(d, w, f, b, alpha)
newVal = getValues(d, w, b)
def main():
while True:
try:
F, N = map(int, raw_input().split())
d = []
b = 5
w = makeMatrix(F, b + 1)
for i in range(0, N):
t = Data()
t.x = map(float, raw_input().split())
t.y = t.x.pop()
d.append(t)
Iterator(d, w, F, b)
N = int(raw_input())
for i in range(0, N):
t = Data()
t.x = map(float, raw_input().split())
print '%.2f'% WX(t, w, b)
except EOFError:
break
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
不过,上述代码得到的结果偏差比较大,需要重新考虑。除了上述方式外,还有一种特征组合方法效果不错。
代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define Vector vector
using namespace std;
struct Data
{
Vector x;
double y;
};
double WX(const Data& d, const Vector& w)
{
double ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < w.size(); i++)
ans += w[i] * d.x[i];
return ans;
}
void Gradient(const Vector& d, Vector &w, double alpha)
{
for(int i = 0; i < w.size(); i++)
{
double tmp = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < d.size(); j++)
tmp += alpha * d[j].x[i] * (WX(d[j], w) - d[j].y);
w[i] -= tmp;
}
}
double getValues(const Vector& d, Vector w)
{
double res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < d.size(); i++)
{
double tmp = WX(d[i], w);
res += fabs(d[i].y - tmp);
}
return res;
}
void Iterator(const Vector& d, Vector &w)
{
double alpha = 0.3 / d.size();
double delta = 0.5;
double oldVal = getValues(d, w);
Gradient(d, w, alpha);
double newVal = getValues(d, w);
while(fabs(oldVal - newVal) > delta)
{
oldVal = newVal;
Gradient(d, w, alpha);
newVal = getValues(d, w);
}
}
Vector getFeatures(Vector x)
{
Vector res;
int n = x.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = i; j < n; j++)
for(int k = j; k < n; k++)
res.push_back(x[i] * x[j] * x[k]);
return res;
}
int main()
{
int F, N;
Vector w;
Vector d;
while(scanf("%d %d", &F, &N) != EOF)
{
d.clear();
w.clear();
int features = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
Data t;
double _x, _y;
t.x.push_back(1);
for(int j = 1; j <= F; j++)
{
scanf("%lf", &_x);
t.x.push_back(_x);
}
t.x = getFeatures(t.x);
features = t.x.size();
scanf("%lf", &_y);
t.y = _y;
d.push_back(t);
}
for(int i = 0; i < features; i++)
w.push_back(0);
Iterator(d, w);
d.clear();
scanf("%d", &N);
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
Data t;
double _x;
t.x.push_back(1);
for(int j = 1; j <= F; j++)
{
scanf("%lf", &_x);
t.x.push_back(_x);
}
t.x = getFeatures(t.x);
printf("%.2lf\n", WX(t, w));
}
}
return 0;
}
另外利用Python的机器学习开源库sklearn很方便处理。具体可以参考如下链接。
题解:http://blog.guozengxin.cn/2015/01/08/hackerrank-predicting-office-space-price/
sklearn官网:http://scikit-learn.org/stable/
sklearn源代码:https://github.com/scikit-learn/scikit-learn/