ZygoteInit中启动的SystemServer分析
前面的文章分析记录了Android系统启动从最初的init内核加载到native方式的zygote即app_process的启动。之前深入理解Android一书说过“zygote本身是一个Native的应用程序,与驱动,内核等均无关系”,“zygote是在Android系统中创建了Java世界”。可以说zygote把东西从内核引渡到了framework层。zygote本身实现了appRuntime里面的几个函数,创建启动了Dalvik虚拟机,注册套接字响应请求,进行预装载类和资源,fork了一个SystemServer而后将线索引入到了Java地界。
下面就SystemServer流程进行整理记录。首先回到起始点,ZygoteInit中的主函数。
// 完成初始化.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeZygoteSnapshot();
// 初始化垃圾回收GC
gc();
//不再继续跟踪监测.
Trace.setTracingEnabled(false);
//调用startSystemServer函数
if (startSystemServer) {
startSystemServer(abiList, socketName);
}
//日志输出
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
/////////////////////////////////////
//函数如下
//其中参数abilist作用在fork的子进程上
private static boolean startSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName)
throws MethodAndArgsCaller, RuntimeException {
long capabilities = posixCapabilitiesAsBits(
OsConstants.CAP_BLOCK_SUSPEND,
OsConstants.CAP_KILL,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_ADMIN,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_BROADCAST,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_RAW,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_MODULE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_NICE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_RESOURCE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_TIME,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_TTY_CONFIG
);
/* 装载各种参数来启动system server,uid为1000,groups里面1001,1002。。。 */
String args[] = {
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1032,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007",
"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
"--runtime-init",
"--nice-name=system_server",
"com.android.server.SystemServer",
};
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null;
//进程的id,返回判断用
int pid;
try {
parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args);
ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
/* 调用Zygoted的函数fork system server */
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
} startSystemServer装填好各种参数后调用了Zygote类的forkSystemServer。在Zygote.java中看到如图:
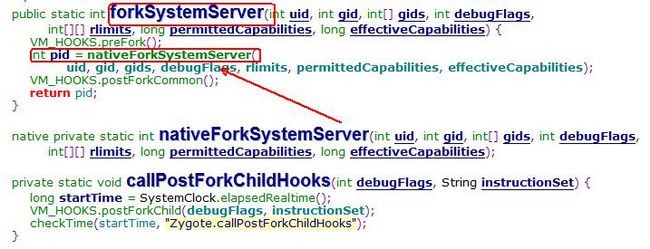
在native的函数的前后,存在着VM_HOOKS的两个函数。这两个函数主要是前面清理障碍,后面进行善后,去寻找代码。如下:
//停止各个daemon,等待所有线程停止,native层调用fork
public void preFork() {
Daemons.stop();
waitUntilAllThreadsStopped();
token = nativePreFork();
}
//启动,子进程启动daemons,即SystemServer
public void postForkCommon() {
Daemons.start();
}当fork后的进程pid为0时,即为子进程SystemServer时,对其要干个活进行分工。
/* For child process */
if (pid == 0) {
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
}
/*SystemServer进程开始准备干活*/
handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}干活前准备分为几部分。
1,关闭从zygote过来的套接字。
2,设置参数,配置好启动路径。
3,根据参数启动RuntimeInit。
RuntimeInit中都干了什么,如下代码所示:
public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
//重定向log流
redirectLogStreams();
//常规的初始化,主要是soket,http网络初始化
commonInit();
//native层初始化
nativeZygoteInit();
//应用层初始化,虚拟机堆的大小,目标SDK版本,以及...... applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
}对application的初始化最重要的就是最后要调用的invokeStaticMain(class,args)。因为通过它,就可以找到启动SystemServer的主函数。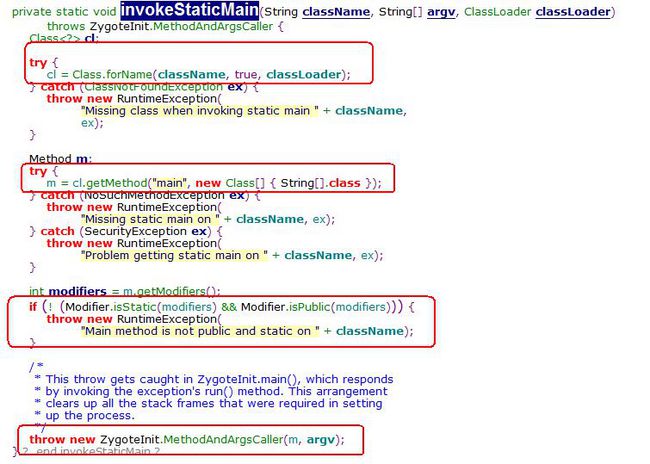
第一个框是利用java反射机制去寻找main函数,第二个框则是调用找到符合的那个main函数。第三个框是方法的一些条件判断。第四个框则为抛出异常,异常将会在ZygoteInit的main函数里被捕获。
书中说抛出这个异常将导致SystemServer类的main函数被调用,而不是直接在invokeStaticMian函数里调用,而采取抛异常方法。作者对这个问题的看法为:”调用发生在ZygoteInit的main函数中,即入口函数,位于栈的顶层。如果不采用抛异常的方式,而是在invokeStaticMain那里调用,则会浪费之前函数调用所占用的一些调用堆栈。“
相比较Android5.0的源码,SystemServer的启动则简化了没有以前那么曲折了,main函数如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}其余操作都封装在构造函数以及调用的run函数上。run函数里面要写入一些虚拟机的设置,binder通信有没有建立的监测,准备main looper 线程、初始化native服务(即导入native的lib库),初始化系统环境,创建SystemServiceManager,开启各项服务,进行消息循环并处理消息。
代码如下:
/** * The main entry point from zygote. * 主入口 */
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}
private void run() {
//检测系统时间
// If a device's clock is before 1970 (before 0), a lot of
// APIs crash dealing with negative numbers, notably
// java.io.File#setLastModified, so instead we fake it and
// hope that time from cell towers or NTP fixes it shortly.
if (System.currentTimeMillis() < EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME) {
Slog.w(TAG, "System clock is before 1970; setting to 1970.");
SystemClock.setCurrentTimeMillis(EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME);
}
Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!");
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_SYSTEM_RUN, SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.dalvik.vm.lib.2", VMRuntime.getRuntime().vmLibrary());
//启动分析设备
// Enable the sampling profiler.
if (SamplingProfilerIntegration.isEnabled()) {
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
mProfilerSnapshotTimer = new Timer();
mProfilerSnapshotTimer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeSnapshot("system_server", null);
}
}, SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL, SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL);
}
//获取更多内存
// Mmmmmm... more memory!
VMRuntime.getRuntime().clearGrowthLimit();
// The system server has to run all of the time, so it needs to be
// as efficient as possible with its memory usage.
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.8f);
//系统的属性配置Fingerprint
// Some devices rely on runtime fingerprint generation, so make sure
// we've defined it before booting further.
Build.ensureFingerprintProperty();
//设置用户环境需求
// Within the system server, it is an error to access Environment paths without
// explicitly specifying a user.
Environment.setUserRequired(true);
//保证binder具有高优先级
// Ensure binder calls into the system always run at foreground priority.
BinderInternal.disableBackgroundScheduling(true);
//开启looper的主线程
// Prepare the main looper thread (this thread).
android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(
android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND);
android.os.Process.setCanSelfBackground(false);
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
//加载libandroid_servers.so库
// Initialize native services.
System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
//native层初始化
nativeInit();
// Check whether we failed to shut down last time we tried.
// This call may not return.
performPendingShutdown();
//初始化系统上下文环境
// Initialize the system context.
createSystemContext();
//创建系统服务管理者
// Create the system service manager.
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
//启动各项服务
// Start services.
try {
//开启activity 服务,power服务等
startBootstrapServices();
//开启屏幕服务,电池服务,application状态服务
startCoreServices();
//开启电话注册服务,输入管理者,窗口管理者
startOtherServices();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
throw ex;
}
//日志信息供分析使用
// For debug builds, log event loop stalls to dropbox for analysis.
if (StrictMode.conditionallyEnableDebugLogging()) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Enabled StrictMode for system server main thread.");
}
// Loop forever.
//进行消息循环,处理消息。
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
System Service Manager的成功创建将会引领系统走向成功。即home activity。整个系统流程也就完成了。