Spring Cloud使用zuul实现反向代理和负载均衡
首先,这篇文章参考的是http://blog.didispace.com/springcloud5/这位大牛的博客。本人是通过这篇博客来学习zuul的,现在写的博客只是个人在学习时个人的一些感受和理解。
谈到spring cloud,就要提及到其核心组件:zuul组件,这个组件其实功能很多,比如反向代理,负载均衡还有权限控制等功能,这篇博客主要写的是zuul的反向代理和负载均衡。
首先是进行eureka的实现,代码如下:
首先是pom.xml,添加依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka-serverartifactId>
<version>1.3.2.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
然后是application:
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@EnableEurekaServer
@SpringBootApplication
public class EurekaApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SpringApplicationBuilder(EurekaApplication.class).web(true).run(args);
}
}
接着是配置文件:
server.port=1111
#eureka.instance.hostname=localhost
eureka.client.register-with-eureka=false
eureka.client.fetch-registry=false
eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:${server.port}/eureka/
创建好eureka后,则是实现zuul:
首先是添加pom.xml文件的依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-zuulartifactId>
<version>1.3.4.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eurekaartifactId>
<version>1.3.2.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
然后是具体的实现,也非常简单:
@EnableZuulProxy
@SpringCloudApplication
public class ZuulApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SpringApplicationBuilder(ZuulApplication.class).web(true).run(args);
}
}
接下来是配置文件:
spring.application.name=api-gateway
server.port=5555
# routes to serviceId 这里边是通过serviceid来绑定地址,当在路径后添加/api-a/ 则是访问service-A对应的服务。
zuul.routes.api-a.path=/api-a/**
zuul.routes.api-a.serviceId=service-A
zuul.routes.api-b.path=/api-b/**
zuul.routes.api-b.serviceId=service-B
# routes to url 这里是绑定具体的ip地址
zuul.routes.api-a-url.path=/api-a-url/**
zuul.routes.api-a-url.url=http://localhost:2222/
eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:1111/eureka/
那么,其实在配置完这个配置文件后,其实zuul已经实现了反向代理和负载均衡的两个功能了,可能有人这时候就纳闷了,这里不是只是反向代理了吗?怎么实现负载均衡呢?其实zuul实现负载均衡很简单,使用serviceId进行绑定后,如果有多个相同的serviceid,则会进行轮询的方式进行访问。这个在下文会有具体的结果截图。
现在需要开启建立两个服务,具体的操作为实现a+b的操作,第一个为Service-A。
pom.xml中添加:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eurekaartifactId>
<version>1.3.2.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
然后是配置文件:
spring.application.name=service-A
server.port=2224
eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:1111/eureka/
然后是一个客户端和一个controller:
package com.example;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@SpringBootApplication
public class ControllerApplicationA {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SpringApplicationBuilder(ControllerApplicationA.class).web(true).run(args);
}
}
package com.example.web;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.DiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
public class ComputeController {
@Autowired
private DiscoveryClient client;
@RequestMapping(value = "/add/{a}/{b}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String add(@PathVariable Integer a,@PathVariable Integer b)
{
System.out.println("host:"+client.getLocalServiceInstance().getHost()+" -----port:"+client.getLocalServiceInstance().getPort());
return a+b+" ------ host:"+client.getLocalServiceInstance().getHost()+" -----port:"+client.getLocalServiceInstance().getPort();
}
}
这个客户端的代码是用来进行具体的操作的,在这中间我们在返回值中添加具体的服务器地址和端口号。
以同样的方式再建立一个服务Service-B。
然后先启动两个服务,截图如下:

这时候先不要急着访问Service-A和B,我们将service-A和B中的配置文件中的端口号修改后再启动:
结果如下:
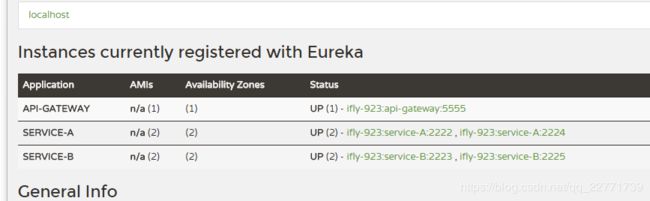
这时候我们看到了,serviceid为Service-A和B各有两个,那么接下来则是实验zuul负载均衡的时候了,我们在此只测试Service-A:
第一次访问http://localhost:5555/api-a/add/1/2:

第二次访问:

因此这就实现了负载均衡,但是这个负载均衡是属于客户端的负载均衡。在这我也就简要的说下客户端负载均衡。
客户端负载均衡:
基于客户端的负载均衡,简单的说就是在客户端程序里面,自己设定一个调度算法,在向服务器发起请求的时候,先执行调度算法计算出向哪台服务器发起请求,然后再发起请求给服务器。
特点:
- 由客户端内部程序实现,不需要额外的负载均衡器软硬件投入。
- 程序内部需要解决业务服务器不可用的问题,服务器故障对应用程序的透明度小。
- 程序内部需要解决业务服务器压力过载的问题。
使用场景:
- 可以选择为初期简单的负载均衡方案,和DNS负载均衡一样。
- 比较适合于客户端具有成熟的调度库函数,算法以及API等
- 毕竟适合对服务器入流量较大的业务,如HTTP POST文件上传,FTP文件上传,Memcache大流量写入。
- 可以结合其他负载均衡方案进行架构。