基于BP神经网络的DNN和python实现
神经网络可以用来处理回归和分类的问题,典型的神经网络算法即为BP(Back Propagation)算法,我们这里对BP神经网络的构建进行详细讲解,基于BP算法延伸出多层神经网络,并对一些问题提出解决方法。
BP神经网络的原理
1. 单个神经元的构成
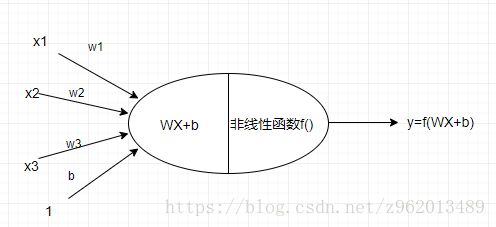
如上图所示为一个典型的神经元结构,输入端为n个输入 xn x n ,对应n个权重 wn w n ,以及一个阈值b,将这些值进行线性组合 WX+b W X + b 就可以得到神经元的输入值,我们姑且称作 α α ,然后再将这个输入值 α α 传入神经元后半部分进行非线性处理(激活处理),神经网络之所以可以非线性的拟合原因就在其每个神经元都会经过一个非线性的步骤,这里使用的激活函数有很多种
1.1 阶跃函数
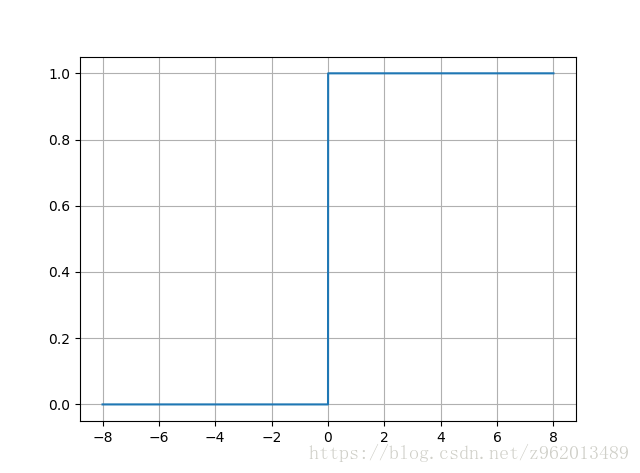
阶跃函数是很理想的激活函数,他将输入值映射为0或1,o表示神经元被抑制,1表示神经元被激活,但是该函数不连续不光滑,因此不常用
1.2 Sigmoid函数
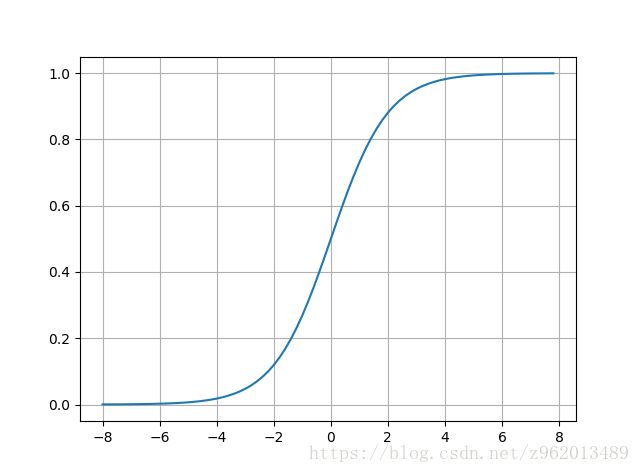
该函数将一个实数集映射到(0,1)的空间,可以对应于概率,并且相对于阶跃函数而言,他是连续且光滑的,并且该函数的导数有个很好的性质: f′(x)=f(x)(1−f(x)) f ′ ( x ) = f ( x ) ( 1 − f ( x ) )
但是当输入非常大或非常小时我们可以发现其导数非常小,即梯度非常小,这在bp算法的训练中非常不利
1.3 ReLU函数
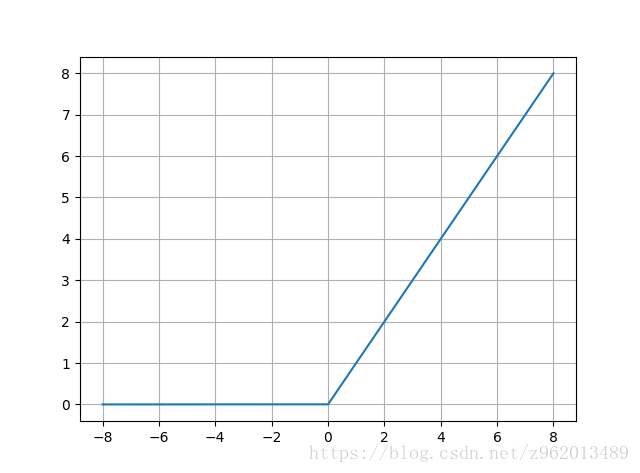
这个函数相比于sigmoid函数的变化有三点:
1.单侧抑制
2. 相对宽阔的兴奋边界
3. 稀疏激活性,0以前的状态完全未激活
sigmoid函数一定程度上会造成梯度消失现象,而ReLU函数因为是线性的,梯度不会饱和,收敛速度会比sigmoid函数快,但是该函数在训练时很脆弱,会导致神经元坏死,可以适当减小学习率来防止
1.4 Softmax函数
该函数是用于多分类神经网络的输出,其中 z1,2,3,...K z 1 , 2 , 3 , . . . K 为K个输入,对应于K个输出神经元,公式计算的是第j个神经元的输出,可以看做概率输出,下图便于理解。
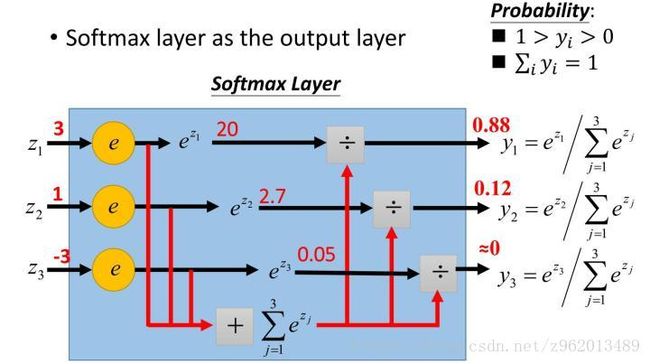
图来自《一天搞懂深度学习》
2. 神经网络结构
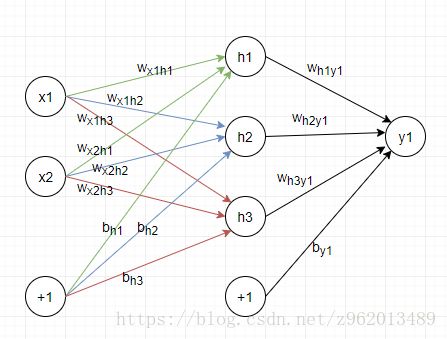
这里我们画了一个简易的神经网络,其中包含2个输入神经元,3个隐含神经元,1个输出神经元,权重和阈值都写在了图中,神经网络的训练过程是首先将样本x输入,经过层层计算后获得输出 yˆ1 y ^ 1 ,然后我们通过一个损失函数(loss function)计算loss,然后使用bp算法更新所有权重和阈值,直到使得损失函数的值收敛到目标值。
2.1 损失函数
损失函数也有很多种,这里列出来几个:
2.1.1 最小平方误差
该损失函数非常常用,既可用于分类问题也可用于回归问题
2.1.2 交叉熵
该损失函数使用要求为输入的 Yˆ,Y Y ^ , Y 均为概率值,因此我们的输出层应使用softmax函数作为激活函数,这样就可以获得概率值,同时,一般还要求Y(即label)进行one-hot label转换,比如我们有0,1,2这3个label,经过转换后变为100,010,001,这对应3个输出神经元,正好与softmax的输出对应然后就可以使用交叉熵计算损失值了,损失值越小, Yˆ,Y Y ^ , Y 的概率分布越相近。
2.2 梯度下降
2.2.1 基于sigmoid函数和最小平方误差的分析
梯度下降是神经网络更新参数常用的方法,我们把上面的图拿下来参考着看

这里我们分别将隐含层、输出层的输出称为 ho h o 和 yo y o
首先我们令h的输入值为 α α ,y的输入值为 β β ,梯度更新的参数估计式为:
其中 η η 为学习率(learning rate),E为通过损失函数计算出的损失值,那么 我们对输出层的权重 wh1y1 w h 1 y 1 为例子计算梯度:
我们可以看出 ∂β1∂wh1y1=ho1 ∂ β 1 ∂ w h 1 y 1 = h o 1
由于使用最小平方误差损失函数,因此 ∂E∂yoˆ1=yoˆ1−y1 ∂ E ∂ y o ^ 1 = y o ^ 1 − y 1
上面说过sigmoid函数有个很好的性质,因此 ∂yoˆ1∂β1=∂sigmoid(β1)∂β1=yoˆ1(1−yoˆ1) ∂ y o ^ 1 ∂ β 1 = ∂ s i g m o i d ( β 1 ) ∂ β 1 = y o ^ 1 ( 1 − y o ^ 1 )
我们定义梯度式
我们就可以推得
同理可以推得
于是参数更新就可以写为: wh1y1=wh1y1+Δwh1y1 w h 1 y 1 = w h 1 y 1 + Δ w h 1 y 1 和 by1=by1+Δby1 b y 1 = b y 1 + Δ b y 1
现在我们来看隐含层,具体以权重 wx1h1 w x 1 h 1 为例子计算梯度:
我们定义梯度式
则
同理
上面我们都是在具体的网络中分析具体的权重的梯度,现在我们广义一下,在一个3层网络中,我们设该网络有K个输入神经元,Q个隐含神经元,J个输出神经元
则梯度值计算如下:
对于有多个隐含层而言,实际上每一层的形式都类似于 eq e q ,只需要将 hoq h o q 替换为当前w对应的节点输出值, ∑Jj=1whqyjgj ∑ j = 1 J w h q y j g j 替换为 下一层的梯度值和 下一层与当前计算的节点连接的权值的积和即可。
2.2.2 基于softmax函数和交叉熵的分析
上面说的sigmoid函数如果用在输出层的话,只能用于2分类问题,面对多分类问题的话,输出层会有多个神经元,此时就需要用softmax函数将输出层的输出转变为概率输出,使用softmax的同时通常还会采用交叉熵作为损失函数。
前面我们推导了sigmoid函数和MSE下的输出层梯度式:
这里梯度式包含了sigmoid和MSE的梯度,将其替换为softmax和交叉熵的梯度即可
我们先计算交叉熵的梯度,交叉熵的计算公式为:
由于Y为经过one-hot label处理后的label,其形式为只含有一个1的向量,剩下的都为0,因此该计算公式可以简化为
yˆl y ^ l 为label Y中非零的y下标 l l 对应于 Yˆ Y ^ 下的值,那么就有:
对于softmax的求导我们就要分情况讨论了:
当计算的输出节点标号 j j 等于 l l 时:
当计算的输出节点标号 j j 不等于 l l 时:
然后我们将两个梯度乘起来可以获得:
其中 yˆol y ^ o l 为label Y中非零的y下标 l l 对应于 Yˆ Y ^ 下的值
在处理多分类问题时只需要将输出层的计算改为softmax和交叉熵,前面的隐含层依旧使用sigmoid即可
3. python实现
我们这里使用python3.6实现了隐含层自定义且可以设置多层隐含层的DNN,隐含层激活函数为sigmoid,输出层激活函数为softmax,损失函数为交叉熵,使用的数据集为sklearn.datasets中的手写数字集,该数据集的样本是64维的,是从8*8的图像转换为64维的向量,我们对训练集进行中心化,并将中心化的参数(均值和均方差)记录用于对测试集进行中心化。(常见陷阱. 在进行数据的预处理时(比如计算数据均值),我们只能在训练数据上进行,然后应用到验证/测试数据上。如果我们对整个数据集-整个数据集的均值,然后再进行训练/验证/测试数据的分割的话,这样是不对的。正确做法是计算训练数据的均值,然后分别把它从训练/验证/测试数据中减去。)
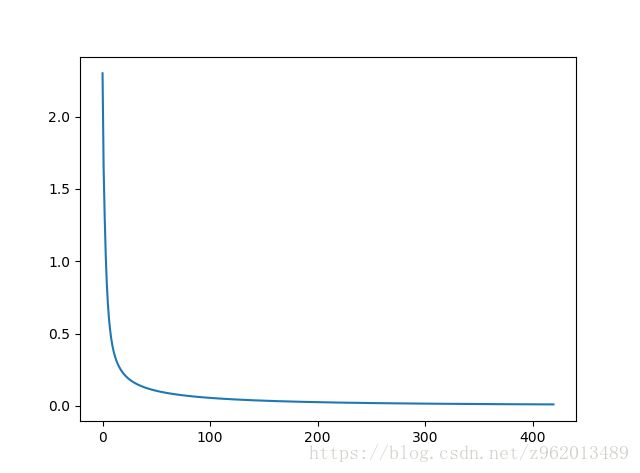
这里将前1000个样本作为训练集,后700多个作为测试集,最后训练准确率有93.34%,这里的网络我们设置为输入层64个神经元,隐含层为128和64个神经元,输出为10个神经元,学习率0.005,损失函数目标值为0.01,损失函数曲线如下,横坐标为迭代次数:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class BPNN:
def __init__(self, nn_shape=[2, 4, 1]):
self.W = [] # 权重
self.B = [] # 阈值
self.O = [] # 各神经元节点输出
self.grads = [] # bp算法中误差与神经节点输入的微分(梯度项)
self.mean = np.zeros(nn_shape[2])
self.mean = self.mean.reshape((1, nn_shape[2]))
self.W_shape = [] # 存储各矩阵的shape以便reshape时使用
self.B_shape = []
self.O_shape = []
self.grads_shape = []
self.errs = [] # 记录每次迭代的误差误差
for index in range(len(nn_shape) - 1): # 初始化W,B,O,grads矩阵
self.W.append(2 * np.random.random([nn_shape[index], nn_shape[index + 1]]) - 1)
self.W[index] = self.W[index].reshape([nn_shape[index], nn_shape[index + 1]])
self.W_shape.append(self.W[index].shape)
self.B.append(2 * np.random.random(nn_shape[index + 1]) - 1)
self.B[index] = self.B[index].reshape(1, nn_shape[index + 1])
self.B_shape.append(self.B[index].shape)
self.O.append(np.zeros(nn_shape[index + 1]))
self.O[index] = self.O[index].reshape(1, nn_shape[index + 1])
self.O_shape.append(self.O[index].shape)
self.grads.append(np.zeros(nn_shape[index + 1]))
self.grads[index] = self.grads[index].reshape(1, nn_shape[index + 1])
self.grads_shape.append(self.grads[index].shape)
self.y_hat = self.O[-1]
self.y_hat = self.y_hat.reshape(self.O[-1].shape)
print('建立{}层神经网络网络'.format(len(nn_shape)))
print(self.W_shape)
print(self.B_shape)
print(self.O_shape)
print(self.grads_shape)
def sigmoid(self, x):
'''
x为1*n向量
'''
return 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-x))
def sigmoid_derivate(self, x):
'''
x为1*n向量
'''
return x * (1 - x)
def error(self, y, y_hat):
err = y - y_hat
return 0.5 * err.dot(err.T)
def cross_entropy(self, y, y_hat):
tmp = np.argwhere(y == 1)
return -np.log(y_hat[0, tmp[0, 1]])
def softmax(self, x):
'''
x为1*n向量
'''
exp_all = np.exp(x)
return exp_all / np.sum(exp_all)
def update_output(self, x, x_istest=False):
'''
更新各神经元的输出值,x为n*1向量
'''
if x_istest == True:
x = (x - self.mean) / self.var
for index in range(len(self.O)):
if index == 0:
self.O[index] = self.sigmoid(
x.dot(self.W[index]) + self.B[index])
elif index == len(self.O) - 1:
self.O[index] = self.softmax(
self.O[index - 1].dot(self.W[index]) + self.B[index])
else:
self.O[index] = self.sigmoid(
self.O[index - 1].dot(self.W[index]) + self.B[index])
self.O[index] = self.O[index].reshape(self.O_shape[index])
self.y_hat = self.O[-1]
self.y_hat = self.y_hat.reshape(self.O[-1].shape)
return self.y_hat
def update_grads(self, y):
'''
更新梯度值,y为p*1向量
'''
for index in range(len(self.grads) - 1, -1, -1):
if index == len(self.grads) - 1:
'''#该代码用来计算使用均方误差和sigmoid函数的二分类问题
self.grads[index] = self.sigmoid_derivate(
self.O[index]) * (y - self.O[index])
'''
tmp = np.argwhere(y == 1)
for index_g in range(self.grads[index].shape[1]):
if index_g == tmp[0, 1]:
self.grads[index][0, index_g] = 1 - self.O[index][0, index_g]
else:
self.grads[index][0, index_g] = - self.O[index][0, index_g]
else: # 链式法则计算隐含层梯度
self.grads[index] = self.sigmoid_derivate(
self.O[index]) * self.W[index + 1].dot(self.grads[index + 1].T).T
self.grads[index] = self.grads[index].reshape(
self.grads_shape[index])
def update_WB(self, x, learning_rate):
for index in range(len(self.W)):
if index == 0:
self.W[index] += learning_rate * x.T.dot(self.grads[index])
self.B[index] -= learning_rate * self.grads[index]
else:
self.W[index] += learning_rate * self.O[index - 1].T.dot(self.grads[index])
self.B[index] -= learning_rate * self.grads[index]
self.B[index] = self.B[index].reshape(self.B_shape[index])
def preprocess(self, X, method='centring'):
self.mean = np.mean(X, axis=0)
self.var = X.var()
X = (X - self.mean) / self.var
if method == 'centring':
return X
def fit(self, X, Y, Preprocess=True, method='centring', thre=0.03, learning_rate=0.001, max_iter=1000):
'''
将样本和label输入,X,Y中的样本均为行向量
'''
if Preprocess == True:
X = self.preprocess(X, method=method)
err = np.inf
count = 0
while err > thre:
err = 0
for index in range(X.shape[0]):
x = X[index, :].reshape((1, -1))
y = Y[index, :].reshape((1, -1))
self.update_output(x)
x = X[index, :].reshape((1, -1))
self.update_grads(y)
self.update_WB(x, learning_rate=learning_rate)
err += self.cross_entropy(y, self.y_hat)
err /= index + 1
self.errs.append(err)
count += 1
if count > max_iter:
print("超过最大迭代次数{}".format(max_iter))
break
print(count)
print(err)
def one_hot_label(self, Y):
'''
将label转化为0001形式,若label有3种,则转化为100,010,001
这里的label必须从0开始
'''
category = list(set(Y[:, 0]))
Y_ = np.zeros([Y.shape[0], len(category)])
for index in range(Y.shape[0]):
Y_[index, Y[index, 0]] = 1
return Y_
if __name__ == '__main__':
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
digits = load_digits()
X = digits.data
Y = digits.target
X = X.reshape(X.shape)
Y = Y.reshape(Y.shape[0], 1)
bp = BPNN([64, 128, 64, 10])#建立神经网络对象
Y = bp.one_hot_label(Y)
train_data = X[:1000, :]
train_label = Y[:1000, :]
test_data = X[1000:-1, :]
test_label = Y[1000:-1, :]
bp.fit(train_data, train_label, Preprocess=True,thre=0.01, learning_rate=0.005, max_iter=1000)#构建网络
count = 0
for i in range(test_data.shape[0]):
x = test_data[i].reshape(1, 64)
pre = bp.update_output(x, x_istest=True)
y = test_label[i].reshape(1, 10)
a = np.where(pre == np.max(pre))
b = np.where(y == np.max(y))
if a[1][0] == b[1][0]:
count += 1
print('准确率:{}'.format(count / test_label.shape[0]))
plt.plot(bp.errs)
plt.show()参考文献:
https://blog.csdn.net/cppjava_/article/details/68921869
http://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1579651272863719116&wfr=spider&for=pc
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/25723112
https://blog.csdn.net/elaine_bao/article/details/50889856
周志华《机器学习》