TensorFlow实战10:ResNet实现及时间测评
1.ResNet简介
ResNet(Residual Neural Network)是由微软研究院的Kaiming He等4名华人提出的,一般我们把ResNet称作是残差网。在ILSVRC 2015的比赛中,Kaiming He等人通过使用Residual Units(残差单元)训练了152层神经网络(名副其实的深度学习了!)赢得了冠军。在比赛中的top-5的错误率为3.57%,同时参数量比VGGNet低,效果非常突出。
ResNet最初的灵感出自一个问题:在不断加深神经网络,会出现一个degradation的问题,即准确率会限=先上升然后达到饱和,再持续增加深度则会导致准确率下降。有小伙伴说这是不是因为过拟合了?然而这并不是过拟合问题,因为误差啊不仅仅在测试集上增大,在训练集误差也增加了。
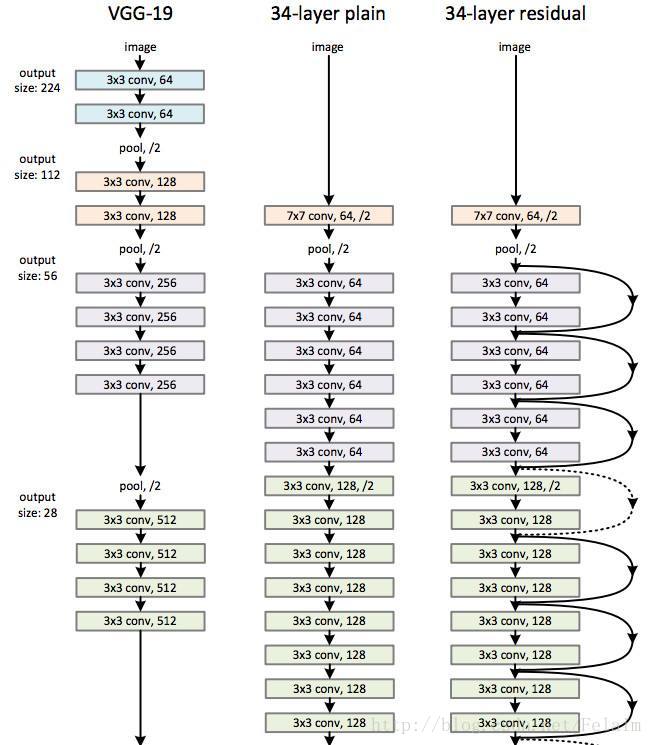
可以看到上图最右端就是使用残差网络构成的34层残差网络。黑色的箭头会跳过两个卷积层直接作为输入给间隔两层的神经网络。相当于在卷积层之间架设了一座高架桥。
ResNet残差学习模块现在也有很多种,甚至可以根据项目要求自己定义。上图显示的就是两层和三层对应的学习模块。
2.ResNet的代码实现
#coding:utf-8
#导入对应的库
import collections
import tensorflow as tf
import time
import math
from datetime import datetime
slim = tf.contrib.slim
#定义了一个block类
class Block(collections.namedtuple('Bolck', ['scope', 'init_fn', 'args'])):
'A named tuple describing a ResNet block.'
#定义了一个下采样函数
def subsample(inputs, factor, scope = None):
if factor == 1:
return inputs
else:
return slim.max_pool2d(inputs, [1, 1], stride = factor, scope = scope)
#定义conv2d_same函数创建卷积层
def conv2d_same(inputs, num_outputs, kernel_size, stride, scope = None):
if stride == 1:
return slim.conv2d(inputs, num_outputs, kernel_size, stride = 1, padding = 'SAME', scope = scope)
else:
pad_total = kernel_size - 1
pad_beg = pad_total // 2
pad_end = pad_total - pad_beg
inputs = tf.pad(inputs, [[0, 0], [pad_beg, pad_end], [pad_beg, pad_end], [0, 0]])
return slim.conv2d(inputs, num_outputs, kernel_size, stride = stride, padding = 'VALID', scope = scope)
#定义堆叠blocks的函数
#@这个符号用于装饰器中,用于修饰一个函数,把被修饰的函数作为参数传递给装饰器
@slim.add_arg_scope
def stack_blocks_dense(net, blocks, outputs_collections = None):
for block in blocks:
with tf.variable_scope(block.scope, 'block', [net]) as sc:
for i, unit in enumerate(block.args):
with tf.variable_scope('unit_%d' %(i + 1), values = [net]):
unit_depth, unit_depth_bottleneck, unit_stride = unit
net = block.unit_fn(net, depth = unit_depth,
unit_depth_bottleneck = unit_depth_bottleneck,
stride = unit_stride)
net = slim.utils.collect_named_outputs(outputs_collections, sc.name, net)
return net
#创建ResNet通用的arg_scope
def resnet_arg_scope(is_training = True,
weight_decay = 0.0001,
batch_norm_decay = 0.997,
batch_norm_epsilon = 1e-5,
batch_norm_scale = True):
batch_norm_params = {
'is_training': is_training,
'decay': batch_norm_decay,
'epsilon': batch_norm_epsilon,
'scale': batch_norm_scale,
'updates_collections': tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS,
}
with slim.arg_scope(
[slim.conv2d],
weights_regularizer = slim.l2_regularizer(weight_decay),
weights_initializer = slim.variance_scaling_initializer(),
activation_fn = tf.nn.relu,
normalizer_fn = slim.batch_norm,
normalizer_params = batch_norm_params):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.batch_norm], **batch_norm_params):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.max_pool2d], padding = 'SAME') as arg_sc:
return arg_sc
#定义bottleneck残差学习单元
@slim.add_arg_scope
def bottleneck(inputs, depth, depth_bottleneck, stride, outputs_collections = None, scope = None):
with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'bottleneck_v2', [inputs]) as sc:
depth_in = slim.utils.last_dimension(inputs.get_shape(), min_rank = 4)
preact = slim.batch_norm(inputs, activation_fn = tf.nn.relu, scope = 'preact')
if depth == depth_in:
shortcut = subsample(inputs, stride, 'shortcut')
else:
shortcut = slim.conv2d(preact, depth, [1, 1], stride = stride, normalizer_fn = None, activation_fn = None, scope = 'shortcut')
residual = slim.conv2d(preact, depth_bottleneck, [1, 1], stride = 1, scope = 'conv1')
residual = conv2d_same(residual, depth_bottleneck, 3, stride, scope = 'conv2')
residual = slim.conv2d(residual, depth, [1, 1], stride = 1, normalizer_fn = None, activation_fn = None, scope = 'conv3')
output = shortcut + residual
return slim.utils.collect_named_outputs(outputs_collections, sc.name, output)
#定义生成ResNet V2主函数
def resnet_v2(inputs, blocks, num_classes = None, global_pool = True, include_root_block = True, reuse = None, scope = None):
with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'resnet_v2', [inputs], reuse = reuse) as sc:
end_points_collection = sc.original_name_scope + '_end_points'
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, bottleneck, stack_blocks_dense], outputs_collections = end_points_collection):
net = inputs
if include_root_block:
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d], activation_fn = None, normalizer_fn = None):
net = conv2d_same(net, 64, 7, stride = 2, scope = 'conv1')
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], stride = 2, scope = 'pool1')
net = stack_blocks_dense(net, blocks)
net = slim.batch_norm(net, activation_fn = tf.nn.relu, scope = 'postnorm')
if global_pool:
net = tf.reduce_mean(net, [1, 2], name = 'pool5', keep_dims = True)
if num_classes is not None:
net = slim.conv2d(net, num_classes, [1, 1], activation_fn = None, normalizer_fn = None, scope = 'logits')
end_points = slim.utils.convert_collection_to_dict(end_points_collection)
if num_classes is not None:
end_points['predictions'] = slim.softmax(net, scope = 'predictions')
return net, end_points
#定义50层的ResNet
def resnet_v2_50(inputs, num_classes = None, global_pool = True, reuse = None, scope = 'resnet_v2_50'):
blocks = [
Block('block1', bottleneck, [(256, 64, 1)] * 2 + [(256, 64, 2)]),
Block('block2', bottleneck, [(512, 128, 1)] * 3 + [(512, 128, 2)]),
Block('block3', bottleneck, [(1024, 256, 1)] * 5 + [(1024, 256, 2)]),
Block('block4', bottleneck, [(2048, 1024, 1)] * 3)]
return resnet_v2(inputs, blocks, num_classes, global_pool, include_root_block = True, reuse = reuse, scope = scope)
#定义101层的ResNet
def resnet_v2_101(inputs, num_classes = None, global_pool = True, reuse = None, scope = 'resnet_v2_101'):
blocks = [
Block('block1', bottleneck, [(256, 64, 1)] * 2 + [(256, 64, 2)]),
Block('block2', bottleneck, [(512, 128, 1)] * 3 + [(512, 128, 2)]),
Block('block3', bottleneck, [(1024, 256, 1)] * 22 + [(1024, 256, 2)]),
Block('block4', bottleneck, [(2048, 512, 1)] * 3)]
return resnet_v2(inputs, blocks, num_classes, global_pool, include_root_block = True, reuse = reuse, scope = scope)
#定义152层的ResNet
def resnet_v2_152(inputs, num_classes = None, global_pool = True, reuse = None, scope = 'resnet_v2_152'):
blocks = [
Block('block1', bottleneck, [(256, 64, 1)] * 2 + [(256, 64, 2)]),
Block('block2', bottleneck, [(512, 128, 1)] * 7 + [(512, 128, 2)]),
Block('block3', bottleneck, [(1024, 256, 1)] * 35 + [(1024, 256, 2)]),
Block('block4', bottleneck, [(2048, 512, 1)] * 3)]
return resnet_v2(inputs, blocks, num_classes, global_pool, include_root_block = True, reuse = reuse, scope = scope)
#定义200层的ResNet
def resnet_v2_200(inputs, num_classes = None, global_pool = True, reuse = None, scope = 'resnet_v2_200'):
blocks = [
Block('block1', bottleneck, [(256, 64, 1)] * 2 + [(256, 64, 2)]),
Block('block2', bottleneck, [(512, 128, 1)] * 23 + [(512, 128, 2)]),
Block('block3', bottleneck, [(1024, 256, 1)] * 35 + [(1024, 256, 2)]),
Block('block4', bottleneck, [(2048, 512, 1)] * 3)]
return resnet_v2(inputs, blocks, num_classes, global_pool, include_root_block = True, reuse = reuse, scope = scope)
def time_tensorflow_run(session, target, info_string):
num_steps_burn_in = 10
total_duration = 0.0
total_duration_squared = 0.0
for i in range(num_batches + num_steps_burn_in):
start_time = time.time()
_ = session.run(target)
duration = time.time() - start_time
if i >= num_steps_burn_in:
if not i % 10:
print('%s: step %d, duration = %.3f' %(datetime.now(), i - num_steps_burn_in, duration))
total_duration += duration
total_duration_squared += duration * duration
mn = total_duration / num_batches
vr = total_duration_squared / num_batches - mn * mn
sd = math.sqrt(vr)
print('%s: %s across %d steps, %.3f +/- %.3f sec / batch' %(datetime.now(), info_string, num_batches, mn, sd))
batch_size = 32
height, width = 224, 224
inputs = tf.random_uniform((batch_size, height, width, 3))
with slim.arg_scope(resnet_arg_scope(is_training = False)):
net, end_points = resnet_v2_152(inputs, 1000)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
num_batches = 100
time_tensorflow_run(sess, net, "Forward")
哈哈,ResNet也构建好啦O(∩_∩)O