Android绘图系列(一)——自定义View基础
这个系列主要是介绍下Android自定义View和Android绘图机制,自己能力有限,如果在介绍过程中有什么错误,欢迎指正
一.自定义View常用的方法
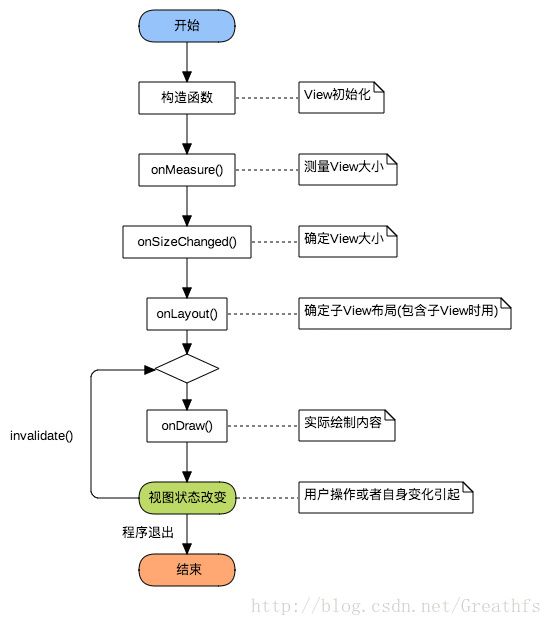
首先用一张图来表示自定义View绘制流程函数调用链(简化版),之后在分别介绍不同的方法
1.构造函数
构造函数是View的入口,可以用于初始化一些的内容,和获取自定义属性。
View的构造函数有四种重载分别如下:
public void CustomView(Context context) {}
public void CustomView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {}
public void CustomView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {}
public void CustomView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {}这里需要注意下:
有四个参数的构造函数在API21的时候才添加上,暂不考虑。
有三个参数的构造函数中第三个参数是默认的Style,这里的默认的Style是指它在当前Application或Activity所用的Theme中的默认Style,且只有在明确调用的时候才会生效,以系统中的ImageButton为例说明:
public ImageButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
//调用了三个参数的构造函数,明确指定第三个参数
this(context, attrs, com.android.internal.R.attr.imageButtonStyle);
}
public ImageButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
//此处调了四个参数的构造函数,无视即可
this(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, 0);
}注意:即使你在View中使用了Style这个属性也不会调用三个参数的构造函数,所调用的依旧是两个参数的构造函数。
由于三个参数的构造函数第三个参数一般不用,暂不考虑,第三个参数的具体用法会在以后用到的时候详细介绍。
排除了两个之后,只剩下一个参数和两个参数的构造函数,他们的详情如下:
//一般在直接New一个View的时候调用。
public void CustomView(Context context) {}
//一般在layout文件中使用的时候会调用,关于它的所有属性(包括自定义属性)都会包含在attrs中传递进来。
public void CustomView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {}以下方法调用的是一个参数的构造函数:
//在Avtivity中
CustomView view = new CustomView(this);以下方法调用的是两个参数的构造函数:
//在layout文件中 - 格式为: 包名.View名
<com.hfs.study.CustomView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>2.onFinishInflate()
//从XML加载组件后回调
@Override
protected void onFinishInflate() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onFinishInflate();
}3.onSizeChanged()
//组件大小改变时回调
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
}4.onMeasure()
// 回调该方法进行测量
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}测量View的原因:
View的大小不仅由自身所决定,同时也会受到父控件的影响,为了我们的控件能更好的适应各种情况,一般会自己进行测量。
测量View大小使用的是onMeasure函数,我们可以从onMeasure的两个参数中取出宽高的相关数据:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int widthsize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); //取出宽度的确切数值
int widthmode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); //取出宽度的测量模式
int heightsize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); //取出高度的确切数值
int heightmode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); //取出高度的测量模式
}从上面可以看出 onMeasure 函数中有 widthMeasureSpec 和 heightMeasureSpec 这两个 int 类型的参数, 毫无疑问他们是和宽高相关的, 但它们其实不是宽和高, 而是由宽、高和各自方向上对应的测量模式来合成的一个值:
测量模式一共有三种, 被定义在 Android 中的 View 类的一个内部类View.MeasureSpec中:
| 模式 | 二进制数值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| UNSPECIFIED | 00 | 即精确值模式,当控件的layout_width属性或layout_height属性指定为具体数值时,例如android:layout_width=”100dp”,或者指定为match_parent属性时,系统使用的是EXACTLY 模式。 |
| EXACTLY | 01 | 即最大值模式,当控件的layout_width属性或layout_height属性指定为warp_content时,控件大小一般随着控件的子控件或者内容的变化而变化,此时控件的尺寸只要不超过父控件允许的最大尺寸即可。 |
| AT_MOST | 10 | 表示子View具体大小没有尺寸限制,但是存在上限,上限一般为父View大小。 |
MeasureSpec类
Android系统给我们提供了一个设计小而强的工具类———MeasureSpec类
1、MeasureSpe描述了父View对子View大小的期望。里面包含了测量模式和大小。
2、MeasureSpe类把测量模式和大小组合到一个32位的int型的数值中,其中高2位表示模式,低30位表示大小而在计算中使用位运算的原因是为了提高并优化效率。
3、我们可以通过以下方式从MeasureSpec中提取模式和大小,该方法内部是采用位移计算。
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);也可以通过MeasureSpec的静态方法把大小和模式合成,该方法内部只是简单的相加。
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(specSize,specMode);注意:
如果对View的宽高进行修改了,不要调用super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);要调用setMeasuredDimension(widthsize,heightsize); 这个函数。
5.onLayout()
// 回调该方法来确定显示的位置
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int left, int right,
int bottom) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom);
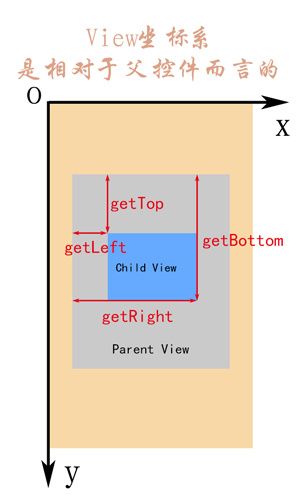
}四个参数分别为:
| 名称 | 说明 | 对应的函数 |
|---|---|---|
| left | View左侧距父View左侧的距离 | getLeft(); |
| top | View顶部距父View顶部的距离 | getTop(); |
| right | View右侧距父View左侧的距离 | getRight(); |
| bottom | View底部距父View顶部的距离 | getBottom(); |
6.onTouchEvent()
// 监听到触摸时间时回调
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}7.onDraw()
// 绘图
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDraw(canvas);
}二.画笔Paint和画布Canvas简单介绍
1.Paint属性
setAntiAlias(); //设置画笔的锯齿效果
setColor(); //设置画笔的颜色
setARGB(); //设置画笔的A、R、G、B值
setAlpha(); //设置画笔的Alpha值
setTextSize(); //设置字体的尺寸
setStyle(); //设置画笔的风格(空心或实心)
setStrokeWidth(); //设置空心边框的宽度
getColor(); //获取画笔的颜色2.Canvas属性
//绘制直线
canvas.drawLine(float startX, float startY, float stopX, float stopY, Paint paint);
//绘制矩形
canvas.drawRect(float left, float top, float right, float bottom, Paint paint);
//绘制圆角矩形
canvas.drawRoundRect(float left, float top, float right, float bottom,float radiusX,float radiusY ,Paint paint);
//绘制圆形
canvas.drawCircle(float cx, float cy, float radius, Paint paint);
//绘制弧形,扇形
canvas.drawArc(float left, float top, float right, float bottom,float startAngle,float sweepAngle,boolean useCenter, Paint paint);
//绘制字符
canvas.drawText(String text, float x, float y, Paint paint);
//绘制图形
canvas.drawBitmap(Bitmap bitmap, float left, float top, Paint paint);
//绘制椭圆
//通过椭圆的外界矩形来绘制椭圆
canvas.drawOval(float left, float top, float right, float bottom,Paint paint);