基于aidl机制的binder连接池的实现
Aidl(Android interface definition language)是一种android内部进程间通信(ipc:Inter-Process Communication)接口的描述语言,通过它我们可以定义进程间的通信接口,Aidl是最常用的ipc的方式;
Binder是什么呢?借鉴任玉刚的解读:binder是Android中的一个类,实现了IBinder接口;从ipc角度来说,binder是Android中的一种ipc方式;从Android framework角度来说,binder是ServiceManager连接各种manager(ActivityManager、WindowManager等)和相应的ManagerService的桥梁;从Android应用层来说,binder是客户端与服务端进行通信的媒介,当bindService的时候,服务端会返回一个包含了服务端业务调用的Binder对象,客户端就可以获取服务端条国内的服务或者数据,这里的服务包括普通服务和基于aidl的服务;
Aidl与binder的关系是什么?Aidl的本质是系统为我们提供了一种快速实现binder的工具,仅此而已;
进入正题之前,先来回顾一下aidl的大致流程:首先创建一个Service和aidl接口,接着创建一个类继承自aidl接口中的Stub类并实现其中的抽象方法,在service的onbind方法中返回这个类的对象,然后客户端就可以绑定服务端service,建立连接之后就可以访问远程服务端的方法了;
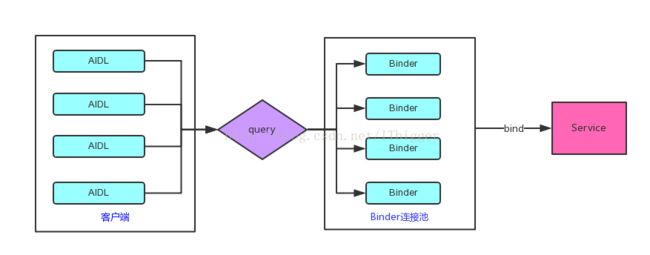
再来看看开发过程中可能遇到的一种场景:公司的项目做的非常之大了,有10个不同的业务模块都需要使用aidl来进行ipc,该怎么处理呢?一种最简单的思路就是:按照aidl的实现方式一个个来吧,需要创建10个service,如果是100个aidl,那么我们就创建100个service,但是我们不能无限制的增加service,servece是四大组件之一,是一种系统资源,太多的service会使我们的应用看起来非常的重量级,哎,算了,这种思路肯定是没有实际应用价值的,于是binder连接池千呼万唤始出来。
简单分析一下Binder连接池的工作机制:每个业务模块创建自己的aidl接口并实现此接口,不同业务模块之间不能有耦合,所有实现细节单独开发,然后向服务端提供自己唯一标识和对应的binder对象,对于服务端来说,只需要一个service就可以了,服务端提欧共一个queryBinder接口,这个接口能够根据不同业务模块的特征来返回相应的binder对象给客户端,不同业务模块拿到所需的binder对象后就可以进行远程方法的调用了;
接下来我们走起一个具体的实例:
首先,提供两个aidl接口(IsecurityCenter,ICompute);
package com.curry.ipc.binderpool;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
interface IsecuriteCenter {
/**
* Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters
* and return values in AIDL.
*/
String encrypt(String content);
String decrypt(String content);
}package com.curry.ipc.binderpool;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
interface ICompute {
/**
* Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters
* and return values in AIDL.
*/
int add(int a,int b);
}package com.curry.ipc.binderpool;
import android.os.RemoteException;
/**
* Created by Curry on 2017/9/11.
*/
public class SecuriteCenterImpl extends IsecuriteCenter.Stub {
private static final char SECRET_CODE='^';
@Override
public String encrypt(String content) throws RemoteException {
return "hallo android";
}
@Override
public String decrypt(String content) throws RemoteException {
return "hallo world";
}
}package com.curry.ipc.binderpool;
import android.os.RemoteException;
/**
* Created by Curry on 2017/9/11.
*/
public class ComputeImpl extends ICompute.Stub{
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) throws RemoteException {
return a+b;
}
}首先,为binder连接池创建aidl接口IbinderPool;
// IBinderPool.aidl
package com.curry.ipc.binderpool;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
interface IBinderPool {
/**
* Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters
* and return values in AIDL.
*/
IBinder queryBinder(int binderCode);
}
然后,为binder连接池创建远程service并实现ibinderpool;
public class BinderPoolService extends Service {
private static final String Tag="BinderPoolService";
private Binder mBinderPool=new BinderPool.BinderPoolImpl();
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
}
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mBinderPool;
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
}
}接着,就是binder连接池的具体实现了;
public class BinderPool {
private static final String Tag="BinderPool";
public static final int BINDER_NONE=-1;
public static final int BINDER_COMPUTE=0;
public static final int BINDER_SECURITY=1;
private Context mContext;
private IBinderPool mBinderPool;
private static volatile BinderPool mInstance;
private CountDownLatch mLatch;
private BinderPool(Context context){
mContext=context.getApplicationContext();
connectBinderPoolService();//第一次测试的时候竟然忘记了调用连接的方法,我了个擦
}
public static BinderPool getmInstance(Context context){
if (mInstance==null){
synchronized (BinderPool.class){
if (mInstance==null){
mInstance=new BinderPool(context);
}
}
}
return mInstance;
}
private synchronized void connectBinderPoolService(){
mLatch=new CountDownLatch(1);
Intent service=new Intent(mContext,BinderPoolService.class);
mContext.bindService(service,mBinderPoolConnection,Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
try {
mLatch.await();
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public IBinder queryBinder(int binderCode){
IBinder binder=null;
try {
if (mBinderPool!=null){
binder=mBinderPool.queryBinder(binderCode);
}
}catch (RemoteException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return binder;
}
private ServiceConnection mBinderPoolConnection=new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
mBinderPool=IBinderPool.Stub.asInterface(service);
try {
mBinderPool.asBinder().linkToDeath(deathRecipient,0);
}catch (RemoteException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
mLatch.countDown();
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
};
private IBinder.DeathRecipient deathRecipient=new IBinder.DeathRecipient() {
@Override
public void binderDied() {
mBinderPool.asBinder().unlinkToDeath(deathRecipient,0);
mBinderPool=null;
connectBinderPoolService();
}
};
public static class BinderPoolImpl extends IBinderPool.Stub{
public BinderPoolImpl(){
super();
}
@Override
public IBinder queryBinder(int binderCode) throws RemoteException {
IBinder binder=null;
switch (binderCode){
case BINDER_COMPUTE:
binder=new ComputeImpl();
break;
case BINDER_SECURITY:
binder=new SecuriteCenterImpl();
break;
default:
break;
}
return binder;
}
}
}最后,就是见证奇迹的时刻了,新建一个Main5Activity来验证一下效果;
public class Main5Activity extends AppCompatActivity {
public IsecuriteCenter mSecurityCenter;
public ICompute computeCenter;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main4);
new Thread(r).start();
// i = new Intent(this, BookManagerService.class);
// bindService(i, connection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
private Runnable r=new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
doWork();
}
};
private void doWork(){
BinderPool binderPool=BinderPool.getmInstance(Main5Activity.this);
IBinder securityBinder=binderPool.queryBinder(BinderPool.BINDER_SECURITY);
if (securityBinder==null){
return;
}
mSecurityCenter=(IsecuriteCenter)SecuriteCenterImpl.asInterface(securityBinder);
Log.d(Tag,"visit security");
String msg="hallo android";
Log.d(Tag,"content:"+msg);
try {
String password=mSecurityCenter.encrypt(msg);
Log.d(Tag,"content1:"+password);
Log.d(Tag,"content11:"+mSecurityCenter.decrypt(password));
}catch (RemoteException E){
E.printStackTrace();
}
Log.d(Tag,"visit compute");
IBinder computeBinder=binderPool.queryBinder(BinderPool.BINDER_COMPUTE);
if (securityBinder==null){
return;
}
computeCenter=(ICompute)ComputeImpl.asInterface(computeBinder);
try {
Log.d(Tag,"compute:"+computeCenter.add(3,9));
}catch (RemoteException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} }来看看代表成功的log;
09-11 19:12:15.217 3685-3698/? D/Main5Activity: visit security
09-11 19:12:15.217 3685-3698/? D/Main5Activity: content:hallo android
09-11 19:12:15.237 3685-3698/? D/Main5Activity: content1:hallo android
09-11 19:12:15.237 3685-3698/? D/Main5Activity: content11:hallo world
09-11 19:12:15.237 3685-3698/? D/Main5Activity: visit compute
09-11 19:12:15.237 3685-3698/? D/Main5Activity: compute:12本文的思路和案例来源于任玉刚的《Android开发艺术探索》,没读过的同学推荐读读此书。