Tensorflow_07B_读取 TFRecord 与反序列化过程
Brief 概述
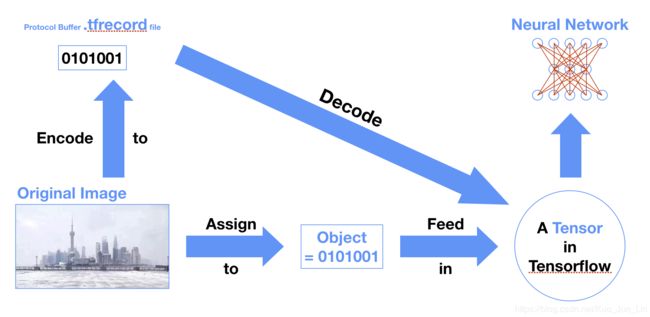
前一个章节描述如何使用 Tensorflow 的函数把数据序列化后,妥善构建一个数据结构并把数据放入 protocol buffer 文档中保存成二进制的格式,这也是上一章节中如下图最左边肩头的环节:
保存好的 .tfrecord 文档就好比我们的子弹,已经把作为火药的原始数据妥善的包装到了弹壳当中随时准备产生作用,这一节将描述如何把这些子弹装入机枪中,而这把机枪就是 Tensorflow 的框架,是一个解译 (decode) 数据结构的过程,并在每次成功解译后,都打印出结果来比对其正确性。
Read TFRecord 读取数据 (官网代码)
理解完整的数据结构与储存方式后,接着就是如何读取已经储存的数据。同样的,根据两种不同的储存方式,也有两种读取方法,如下陈列:
- tf.parse_single_example()
- tf.parse_single_sequence_example()
1. Decode Data using tf.parse_single_example()
Step 1-1
定义哪些路径下的 .tfrecord 数据文档准备被读取,是字符串形式,并且使用一个列表打包每一个路径,每个路径都做为一个列表里面的单元,如下代码:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
data_path=['example.tfrecord']Step 1-2
tf.train.string_input_producer() 方法来创建一个队列,解析第一步给到的路径集列表,该队列是一个 FIFO 队列,此方法还有 num_epochs 与 shuffle 参数提供调用,让我们调整是否随机排布数据顺序,代码如下:
queued_filename = tf.train.string_input_producer(data_path,
shuffle=False,
num_epochs=None)Step 1-3
接着使用 tf.TFRecordReader() 方法来创建一个读取的物件并读取内容,如下代码:
reader = tf.TFRecordReader()
key, serialized_example = reader.read(queued_filename)
# The generated objects are all tf Tensors.
# ReaderReadV2(key=,
# value=)
Step 1-4
需要先创建一个解析器,用来解析 .tfrecord 里面的数据,因此使用 tf.parse_single_example() ,但是解析前必须重新给一个定义的 features 数据格式,其中尤其注意 !!! 标签的名字 和 数据格式 !!! 必须严格一模一样的定义,定义方式有两种如下陈列:
- tf.FixedLenFeature(shape, dtype, default_value): 回传的是 Tensor,含有预设好的数据格式与 "一个" 张量值,对应好了 dtype 数据类型。
- shape: 类似 reshape 的功能,可以重塑储存数据的维度
- dtype: 必须是 tf.float32, tf.int64, tf.string 其中一种
- default_value: 如果 feature 没有值,那它就是预设值
- tf.VarLenFeature(dtype): 回传的是 SparTensor 多个张量,可以用方法 indices, values, dense_shape 来呼叫个别的值,并且只预先使用 dtype 设定该些值的数据类型。
实际代码如下:
read_features = {
'name': tf.FixedLenFeature(shape=[], dtype=tf.string),
'tall': tf.FixedLenFeature(shape=[1,], dtype=tf.float32),
'age': tf.VarLenFeature(dtype=tf.int64),
'email': tf.VarLenFeature(dtype=tf.string),
'gender': tf.VarLenFeature(dtype=tf.string)
}
read_data = tf.parse_single_example(serialized=serialized_example,
features=read_features)
print('read_data: ', read_data)
print('\nname: ', read_data['name'])read_data: {'age':, 'email': , 'gender': , 'name': , 'tall': } name: Tensor("ParseSingleExample/ParseSingleExample:9", shape=(), dtype=string)
Step 1-4 - Remind
完成了步骤四之后,原先那些 Bytes 形式的数据储存时转换二进制的动作,已经可以开始在这一步反转换回来了,不过切记此时的数据还是留存在 Tensorflow 中的 Tensor,一般的模块如 numpy 中的 frombuffer 或 fromstring 函数是无法解析此时此刻的数据的。
Tensorflow 提供了几种解析数据的方法,如下:
tf.decode_raw(): 适合把二进制的任意类型数据转换成 "数字类型" 的状态,例如用矩阵表示的图像数据解码的过程则可以通过此方法转换,但是注意不能转换回文字。- tf.decode_csv()
- tf.image_decode_jpeg()
这些函数保证数据转换的过程中还是在张量的状态完成,维持数据处理的高效率。
# If we use this to transform binary data into tf.string,
# some Errors would pop up like this below.
NAME = tf.decode_raw(read_data['name'], tf.string)TypeError: Value passed to parameter 'out_type' has DataType string not in list of allowed values: float16, float32, float64, int32, uint16, uint8, int16, int8, int64
# If we want to use another tools to deal the the data format here,
# tensors can only be deposited in Tensorflow framewrok.
NAME = np.fromstring(read_data['name'], dtype='U4')TypeError: a bytes-like object is required, not 'Tensor'
Step 1-5
最后开启 tf.Session() 绘话,并在其中放入 tf.train.start_queue_runners() 方法运行,算是一种在 Tensorflow 当中一种宣告说已经有一个本来序列化的数据要开始被读取了,接着打印当初封装的数据结果,下面由两个打印的方法分别使用 tf.InteractiveSession() 与 tf.Session() 方法,自行参考。
int_sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=int_sess, coord=coord)
tf.train.start_queue_runners(int_sess)
for name, tensor in read_data.items():
print('{}: {}\n'.format(name, tensor.eval()))
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)age: SparseTensorValue(indices=array([[0]]), values=array([28]), dense_shape=array([1])) email: SparseTensorValue(indices=array([[0]]), values=array([b'[email protected]'], dtype=object), dense_shape=array([1])) gender: SparseTensorValue(indices=array([[0]]), values=array([b'M\x00\x00\x00a\x00\x00\x00l\x00\x00\x00e\x00\x00\x00'], dtype=object), dense_shape=array([1])) name: b'J\x00\x00\x00a\x00\x00\x00m\x00\x00\x00e\x00\x00\x00s\x00\x00\x00' tall: [1.78]
p.s. 切记使用 .eval( ) 的时候,开启的 sess 必须是用 InteractiveSession( ) 方法开启的才不会报错。
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
print('name: ', sess.run(read_data['name']))
print('tall: ', sess.run(read_data['tall']))
print('age: ', sess.run(read_data['age']))
print('age: ', sess.run(read_data['age']).indices)
print('age: ', sess.run(read_data['age']).values)
print('age: ', sess.run(read_data['age']).dense_shape)
print('age: ', type(sess.run(read_data['age']).values))
print('email: ', sess.run(read_data['email']).values[0].decode('utf-8'))
GENDER = sess.run(read_data['gender'].values[0])
print('gender: ', np.frombuffer(GENDER, dtype='U4'))
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)name: b'J\x00\x00\x00a\x00\x00\x00m\x00\x00\x00e\x00\x00\x00s\x00\x00\x00' tall: [1.78] age: SparseTensorValue(indices=array([[0]]), values=array([28]), dense_shape=array([1])) age: [[0]] age: [28] age: [1] age:email: [email protected] gender: ['Male']
# int_sess.close()
# sess.close()
##########################################################################
# ERROR:tensorflow:Exception in QueueRunner:
# Enqueue operation was cancelled
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------
# In order to prevent the ERROR shown above from the executing sessions,
# we should add "tf.train.Coordinator()" and the corresponding
# coord methods after .run execution.2. Decode Data using tf.parse_single_sequence_example()
其传入的参数分为两个,分别是装了一般张量值的 context_features 与装了列表的 sequence_features,完整代码如下:
reader = tf.TFRecordReader()
queue_seq_file = tf.train.string_input_producer(['sequence_example.tfrecord'],
shuffle=True,
num_epochs=None)
key, serialized_sequence_exp = reader.read(queue_seq_file)
context_features = {
'name': tf.FixedLenFeature(shape=[], dtype=tf.string)
}
sequence_features = {
'Info': tf.FixedLenSequenceFeature([], dtype=tf.string),
'Number': tf.VarLenFeature(dtype=tf.float32)
}
context_data, sequence_data = \
tf.parse_single_sequence_example(serialized=serialized_sequence_exp,
context_features=context_features,
sequence_features=sequence_features)
print('context_data: ', context_data)
print('\nsequence_data: ', sequence_data)
print('\nboth types: ', type(context_data), type(sequence_data))context_data: {'name':} sequence_data: {'Number': , 'Info': } both types:
读取方式: 同样分 InteractiveSession 与 Session 两种,如下代码:
int_seq_sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
int_seq_sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
int_seq_coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=int_seq_sess,
coord=int_seq_coord)
print('Context:')
for name, tensor in context_data.items():
print('{}: {}'.format(name, tensor.eval()))
print('\nData')
for name, tensor in sequence_data.items():
print('{}: {}'.format(name, tensor.eval()))
int_seq_coord.request_stop()
int_seq_coord.join(threads)Context: name: b'J\x00\x00\x00a\x00\x00\x00m\x00\x00\x00e\x00\x00\x00s\x00\x00\x00' Data Number: SparseTensorValue(indices=array([[0, 0], [1, 0]]), values=array([ 1.78, 28. ], dtype=float32), dense_shape=array([2, 1])) Info: [b'[email protected]' b'M\x00\x00\x00a\x00\x00\x00l\x00\x00\x00e\x00\x00\x00']
seq_sess = tf.Session()
seq_sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
seq_coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=seq_sess, coord=seq_coord)
seq_name = seq_sess.run(context_data['name'])
decode_seq_name = np.frombuffer(seq_name, dtype='U5')[0]
print('name: ', seq_name)
print('decode name: ', decode_seq_name)
seq_info = seq_sess.run(sequence_data['Info'])
decode_email = seq_info[0].decode('utf-8')
decode_gender = np.frombuffer(seq_info[1], dtype='U4')
print('\ninfo: ', seq_info)
print('decode email: ', decode_email)
print('decode gender: ', decode_gender)
seq_num = seq_sess.run(sequence_data['Number'])
print('\nnumber: ', seq_num)
print('number values: ', seq_num.values)
seq_coord.request_stop()
seq_coord.join(threads)name: b'J\x00\x00\x00a\x00\x00\x00m\x00\x00\x00e\x00\x00\x00s\x00\x00\x00' decode name: James info: [b'[email protected]' b'M\x00\x00\x00a\x00\x00\x00l\x00\x00\x00e\x00\x00\x00'] decode email: [email protected] decode gender: ['Male'] number: SparseTensorValue(indices=array([[0, 0], [1, 0]]), values=array([ 1.78, 28. ], dtype=float32), dense_shape=array([2, 1])) number values: [ 1.78 28. ]
int_seq_sess.close()
seq_sess.close()
##########################################################################
# ERROR:tensorflow:Exception in QueueRunner:
# Enqueue operation was cancelled
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------
# In order to prevent the ERROR shown above from the executing sessions,
# we should add "tf.train.Coordinator()" and the corresponding
# coord methods after .run execution.但上面的过程就直接把数据解析出来还原成本来的样子,并没有如概述所说的放入机枪准备发射,原因是要检查所有过程的正确性和简洁性,后面章节接着描述如何完成快速引入数据的流程。