TensorFlow实现FCN
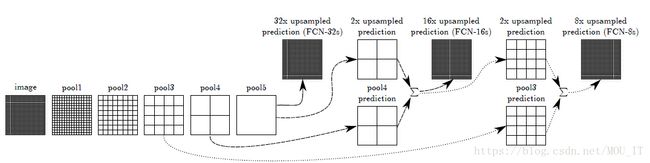
FCN的网络结构:
FCN全名叫做全卷机神经网络,它在经典的VGGNet的基础上,把VGG网络最后的全连接层全部去掉,换为卷积层。为了能对图像进行分割,FCN对卷积后的结果进行了反卷积,生成和原图一样的尺寸输出,然后经过softmax就能对每个像素进行分类。具体的网络结果如下:
论文参考《Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation》,代码实现参考:https://github.com/shekkizh/FCN.tensorflow
代码详解:
代码的实现有四个python文件,分别是FCN.py、BatchDatasetReader.py、TensorFlowUtils.py、read_MITSceneParsingData.py。将这四个文件放在一个当前目录 . 下,然后去这里下载VGG网络的权重参数,下载好后的文件路径为./Model_zoo/imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat,然后去这里下载训练会用到的数据集,并解压到路径: ./Data_zoo/MIT_SceneParsing/ADEChallengeData2016。训练时把FCN.py中的全局变量mode该为“train”,运行该文件。测试时改为“visualize”运行即可。
FCN.py为主文件,代码如下:
from __future__ import print_function
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import TensorflowUtils as utils
import read_MITSceneParsingData as scene_parsing
import datetime
import BatchDatsetReader as dataset
from six.moves import xrange
batch_size=2 # batch 大小
logs_dir="logs/"
data_dir= "Data_zoo/MIT_SceneParsing/" # 存放数据集的路径,需要提前下载
data_name="ADEChallengeData2016"
learning_rate=1e-4 # 学习率
model_path="Model_zoo/imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat" # VGG网络参数文件,需要提前下载
debug= False
mode='train' # 训练模式train | visualize
MODEL_URL = 'http://www.vlfeat.org/matconvnet/models/beta16/imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat' #训练好的VGGNet参数
MAX_ITERATION = int(1e5 + 1) # 最大迭代次数
NUM_OF_CLASSESS = 151 # 类的个数
IMAGE_SIZE = 224 # 图像尺寸
# 根据载入的权重建立原始的 VGGNet 的网络
def vgg_net(weights, image):
layers = (
'conv1_1', 'relu1_1', 'conv1_2', 'relu1_2', 'pool1',
'conv2_1', 'relu2_1', 'conv2_2', 'relu2_2', 'pool2',
'conv3_1', 'relu3_1', 'conv3_2', 'relu3_2', 'conv3_3','relu3_3', 'conv3_4', 'relu3_4', 'pool3',
'conv4_1', 'relu4_1', 'conv4_2', 'relu4_2', 'conv4_3','relu4_3', 'conv4_4', 'relu4_4', 'pool4',
'conv5_1', 'relu5_1', 'conv5_2', 'relu5_2', 'conv5_3','relu5_3', 'conv5_4', 'relu5_4'
)
net = {}
current = image
for i, name in enumerate(layers):
kind = name[:4]
if kind == 'conv':
kernels, bias = weights[i][0][0][0][0]
# matconvnet: weights are [width, height, in_channels, out_channels]
# tensorflow: weights are [height, width, in_channels, out_channels]
kernels = utils.get_variable(np.transpose(kernels, (1, 0, 2, 3)), name=name + "_w")
bias = utils.get_variable(bias.reshape(-1), name=name + "_b")
current = utils.conv2d_basic(current, kernels, bias)
print ("当前形状:",np.shape(current))
elif kind == 'relu':
current = tf.nn.relu(current, name=name)
if debug:
utils.add_activation_summary(current)
elif kind == 'pool':
current = utils.avg_pool_2x2(current)
print ("当前形状:",np.shape(current))
net[name] = current
return net
# FCN的网络结构定义,网络中用到的参数是迁移VGG训练好的参数
def inference(image, keep_prob):
"""
Semantic segmentation network definition
:param image: input image. Should have values in range 0-255
:param keep_prob:
:return:
"""
# 加载模型数据
print ("原始图像:",np.shape(image))
model_data = utils.get_model_data(model_path)
mean = model_data['normalization'][0][0][0]
mean_pixel = np.mean(mean, axis=(0, 1))
weights = np.squeeze(model_data['layers'])
# 图像预处理
processed_image = utils.process_image(image, mean_pixel)
print ("预处理后的图像:",np.shape(processed_image))
with tf.variable_scope("inference"):
# 建立原始的VGGNet-19网络
print ("开始建立VGG网络:")
image_net = vgg_net(weights, processed_image)
# 在VGGNet-19之后添加 一个池化层和三个卷积层
conv_final_layer = image_net["conv5_3"]
print ("VGG处理后的图像:",np.shape(conv_final_layer))
pool5 = utils.max_pool_2x2(conv_final_layer)
print ("pool5:",np.shape(pool5))
W6 = utils.weight_variable([7, 7, 512, 4096], name="W6")
b6 = utils.bias_variable([4096], name="b6")
conv6 = utils.conv2d_basic(pool5, W6, b6)
relu6 = tf.nn.relu(conv6, name="relu6")
if debug:
utils.add_activation_summary(relu6)
relu_dropout6 = tf.nn.dropout(relu6, keep_prob=keep_prob)
print ("conv6:",np.shape(relu_dropout6))
W7 = utils.weight_variable([1, 1, 4096, 4096], name="W7")
b7 = utils.bias_variable([4096], name="b7")
conv7 = utils.conv2d_basic(relu_dropout6, W7, b7)
relu7 = tf.nn.relu(conv7, name="relu7")
if debug:
utils.add_activation_summary(relu7)
relu_dropout7 = tf.nn.dropout(relu7, keep_prob=keep_prob)
print ("conv7:",np.shape(relu_dropout7))
W8 = utils.weight_variable([1, 1, 4096, NUM_OF_CLASSESS], name="W8")
b8 = utils.bias_variable([NUM_OF_CLASSESS], name="b8")
conv8 = utils.conv2d_basic(relu_dropout7, W8, b8)
print ("conv8:",np.shape(conv8))
# annotation_pred1 = tf.argmax(conv8, dimension=3, name="prediction1")
# 对卷积后的结果进行反卷积操作
deconv_shape1 = image_net["pool4"].get_shape()
W_t1 = utils.weight_variable([4, 4, deconv_shape1[3].value, NUM_OF_CLASSESS], name="W_t1")
b_t1 = utils.bias_variable([deconv_shape1[3].value], name="b_t1")
conv_t1 = utils.conv2d_transpose_strided(conv8, W_t1, b_t1, output_shape=tf.shape(image_net["pool4"]))
fuse_1 = tf.add(conv_t1, image_net["pool4"], name="fuse_1")
print ("pool4 and de_conv8 ==> fuse1:",np.shape(fuse_1)) # (14, 14, 512)
deconv_shape2 = image_net["pool3"].get_shape()
W_t2 = utils.weight_variable([4, 4, deconv_shape2[3].value, deconv_shape1[3].value], name="W_t2")
b_t2 = utils.bias_variable([deconv_shape2[3].value], name="b_t2")
conv_t2 = utils.conv2d_transpose_strided(fuse_1, W_t2, b_t2, output_shape=tf.shape(image_net["pool3"]))
fuse_2 = tf.add(conv_t2, image_net["pool3"], name="fuse_2")
print ("pool3 and deconv_fuse1 ==> fuse2:",np.shape(fuse_2)) # (28, 28, 256)
shape = tf.shape(image)
deconv_shape3 = tf.stack([shape[0], shape[1], shape[2], NUM_OF_CLASSESS])
W_t3 = utils.weight_variable([16, 16, NUM_OF_CLASSESS, deconv_shape2[3].value], name="W_t3")
b_t3 = utils.bias_variable([NUM_OF_CLASSESS], name="b_t3")
conv_t3 = utils.conv2d_transpose_strided(fuse_2, W_t3, b_t3, output_shape=deconv_shape3, stride=8)
print ("conv_t3:",[np.shape(image)[1],np.shape(image)[2],NUM_OF_CLASSESS]) # (224,224,151)
annotation_pred = tf.argmax(conv_t3, dimension=3, name="prediction") # (224,224,1)
return tf.expand_dims(annotation_pred, dim=3), conv_t3
# 返回优化器
def train(loss_val, var_list):
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate)
grads = optimizer.compute_gradients(loss_val, var_list=var_list)
if debug:
# print(len(var_list))
for grad, var in grads:
utils.add_gradient_summary(grad, var)
return optimizer.apply_gradients(grads)
# 主函数,返回优化器的操作步骤
def main(argv=None):
keep_probability = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name="keep_probabilty")
image = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3], name="input_image")
annotation = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 1], name="annotation")
print("setting up vgg initialized conv layers ...")
# 定义好FCN的网络模型
pred_annotation, logits = inference(image, keep_probability)
# 定义损失函数,这里使用交叉熵的平均值作为损失函数
loss = tf.reduce_mean((tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,
labels=tf.squeeze(annotation, squeeze_dims=[3]),
name="entropy")))
# 定义优化器
trainable_var = tf.trainable_variables()
if debug:
for var in trainable_var:
utils.add_to_regularization_and_summary(var)
train_op = train(loss, trainable_var)
# 加载数据集
print("Setting up image reader...")
train_records, valid_records = scene_parsing.read_dataset(data_dir,data_name)
print("训练集的大小:",len(train_records))
print("验证集的大小:",len(valid_records))
print("Setting up dataset reader")
image_options = {'resize': True, 'resize_size': IMAGE_SIZE}
if mode == 'train':
train_dataset_reader = dataset.BatchDatset(train_records, image_options)
validation_dataset_reader = dataset.BatchDatset(valid_records, image_options)
# 开始训练模型
sess = tf.Session()
print("Setting up Saver...")
saver = tf.train.Saver()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(logs_dir)
if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:
saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
print("Model restored...")
if mode == "train":
for itr in xrange(MAX_ITERATION):
train_images, train_annotations = train_dataset_reader.next_batch(batch_size)
print (np.shape(train_images),np.shape(train_annotations))
feed_dict = {image: train_images, annotation: train_annotations, keep_probability: 0.85}
sess.run(train_op, feed_dict=feed_dict)
print ("step:",itr)
if itr % 10 == 0:
train_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict=feed_dict)
print("Step: %d, Train_loss:%g" % (itr, train_loss))
if itr % 500 == 0:
valid_images, valid_annotations = validation_dataset_reader.next_batch(batch_size)
valid_loss= sess.run(loss, feed_dict={image: valid_images, annotation: valid_annotations,
keep_probability: 1.0})
print("%s ---> Validation_loss: %g" % (datetime.datetime.now(), valid_loss))
saver.save(sess, logs_dir + "model.ckpt", itr)
elif mode == "visualize":
valid_images, valid_annotations = validation_dataset_reader.get_random_batch(batch_size)
pred = sess.run(pred_annotation, feed_dict={image: valid_images, annotation: valid_annotations,
keep_probability: 1.0})
valid_annotations = np.squeeze(valid_annotations, axis=3)
pred = np.squeeze(pred, axis=3)
for itr in range(batch_size):
utils.save_image(valid_images[itr].astype(np.uint8), logs_dir, name="inp_" + str(5+itr))
utils.save_image(valid_annotations[itr].astype(np.uint8), logs_dir, name="gt_" + str(5+itr))
utils.save_image(pred[itr].astype(np.uint8), logs_dir, name="pred_" + str(5+itr))
print("Saved image: %d" % itr)
if __name__ == "__main__":
tf.app.run()BatchDatasetReader.py主要用于制作数据集batch块,代码如下:
#coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
import scipy.misc as misc
# 批量读取数据集的类
class BatchDatset:
files = []
images = []
annotations = []
image_options = {}
batch_offset = 0
epochs_completed = 0
def __init__(self, records_list, image_options={}):
"""
Intialize a generic file reader with batching for list of files
:param records_list: list of file records to read -
sample record:
{'image': f, 'annotation': annotation_file, 'filename': filename}
:param image_options: A dictionary of options for modifying the output image
Available options:
resize = True/ False
resize_size = #size of output image - does bilinear resize
color=True/False
"""
print("Initializing Batch Dataset Reader...")
print(image_options)
self.files = records_list
self.image_options = image_options
self._read_images()
def _read_images(self):
self.__channels = True
# 读取训练集图像
self.images = np.array([self._transform(filename['image']) for filename in self.files])
self.__channels = False
# 读取label的图像,由于label图像是二维的,这里需要扩展为三维
self.annotations = np.array(
[np.expand_dims(self._transform(filename['annotation']), axis=3) for filename in self.files])
print (self.images.shape)
print (self.annotations.shape)
# 把图像转为 numpy数组
def _transform(self, filename):
image = misc.imread(filename)
if self.__channels and len(image.shape) < 3: # make sure images are of shape(h,w,3)
image = np.array([image for i in range(3)])
if self.image_options.get("resize", False) and self.image_options["resize"]:
resize_size = int(self.image_options["resize_size"])
resize_image = misc.imresize(image,[resize_size, resize_size], interp='nearest')
else:
resize_image = image
return np.array(resize_image)
def get_records(self):
return self.images, self.annotations
def reset_batch_offset(self, offset=0):
self.batch_offset = offset
def next_batch(self, batch_size):
start = self.batch_offset
self.batch_offset += batch_size
if self.batch_offset > self.images.shape[0]:
# Finished epoch
self.epochs_completed += 1
print("****************** Epochs completed: " + str(self.epochs_completed) + "******************")
# Shuffle the data
perm = np.arange(self.images.shape[0])
np.random.shuffle(perm)
self.images = self.images[perm]
self.annotations = self.annotations[perm]
# Start next epoch
start = 0
self.batch_offset = batch_size
end = self.batch_offset
return self.images[start:end], self.annotations[start:end]
def get_random_batch(self, batch_size):
indexes = np.random.randint(0, self.images.shape[0], size=[batch_size]).tolist()
return self.images[indexes], self.annotations[indexes]TensorFlowUtils.py主要定义了一些工具函数,如变量初始化、卷积反卷积操作、池化操作、批量归一化、图像预处理等,代码如下:
#coding=utf-8
# Utils used with tensorflow implemetation
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import scipy.misc as misc
import os, sys
from six.moves import urllib
import tarfile
import zipfile
import scipy.io
# 下载VGG模型的数据
def get_model_data(file_path):
if not os.path.exists(file_path):
raise IOError("VGG Model not found!")
data = scipy.io.loadmat(file_path)
return data
def save_image(image, save_dir, name, mean=None):
"""
Save image by unprocessing if mean given else just save
:param mean:
:param image:
:param save_dir:
:param name:
:return:
"""
if mean:
image = unprocess_image(image, mean)
misc.imsave(os.path.join(save_dir, name + ".png"), image)
def get_variable(weights, name):
init = tf.constant_initializer(weights, dtype=tf.float32)
var = tf.get_variable(name=name, initializer=init, shape=weights.shape)
return var
def weight_variable(shape, stddev=0.02, name=None):
# print(shape)
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=stddev)
if name is None:
return tf.Variable(initial)
else:
return tf.get_variable(name, initializer=initial)
def bias_variable(shape, name=None):
initial = tf.constant(0.0, shape=shape)
if name is None:
return tf.Variable(initial)
else:
return tf.get_variable(name, initializer=initial)
def get_tensor_size(tensor):
from operator import mul
return reduce(mul, (d.value for d in tensor.get_shape()), 1)
def conv2d_basic(x, W, bias):
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding="SAME")
return tf.nn.bias_add(conv, bias)
def conv2d_strided(x, W, b):
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding="SAME")
return tf.nn.bias_add(conv, b)
def conv2d_transpose_strided(x, W, b, output_shape=None, stride = 2):
# print x.get_shape()
# print W.get_shape()
if output_shape is None:
output_shape = x.get_shape().as_list()
output_shape[1] *= 2
output_shape[2] *= 2
output_shape[3] = W.get_shape().as_list()[2]
# print output_shape
conv = tf.nn.conv2d_transpose(x, W, output_shape, strides=[1, stride, stride, 1], padding="SAME")
return tf.nn.bias_add(conv, b)
def leaky_relu(x, alpha=0.0, name=""):
return tf.maximum(alpha * x, x, name)
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding="SAME")
def avg_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.avg_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding="SAME")
def local_response_norm(x):
return tf.nn.lrn(x, depth_radius=5, bias=2, alpha=1e-4, beta=0.75)
def batch_norm(x, n_out, phase_train, scope='bn', decay=0.9, eps=1e-5):
"""
Code taken from http://stackoverflow.com/a/34634291/2267819
"""
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
beta = tf.get_variable(name='beta', shape=[n_out], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.0)
, trainable=True)
gamma = tf.get_variable(name='gamma', shape=[n_out], initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(1.0, 0.02),
trainable=True)
batch_mean, batch_var = tf.nn.moments(x, [0, 1, 2], name='moments')
ema = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(decay=decay)
def mean_var_with_update():
ema_apply_op = ema.apply([batch_mean, batch_var])
with tf.control_dependencies([ema_apply_op]):
return tf.identity(batch_mean), tf.identity(batch_var)
mean, var = tf.cond(phase_train,
mean_var_with_update,
lambda: (ema.average(batch_mean), ema.average(batch_var)))
normed = tf.nn.batch_normalization(x, mean, var, beta, gamma, eps)
return normed
def process_image(image, mean_pixel):
return image - mean_pixel
def unprocess_image(image, mean_pixel):
return image + mean_pixel
def bottleneck_unit(x, out_chan1, out_chan2, down_stride=False, up_stride=False, name=None):
"""
Modified implementation from github ry?!
"""
def conv_transpose(tensor, out_channel, shape, strides, name=None):
out_shape = tensor.get_shape().as_list()
in_channel = out_shape[-1]
kernel = weight_variable([shape, shape, out_channel, in_channel], name=name)
shape[-1] = out_channel
return tf.nn.conv2d_transpose(x, kernel, output_shape=out_shape, strides=[1, strides, strides, 1],
padding='SAME', name='conv_transpose')
def conv(tensor, out_chans, shape, strides, name=None):
in_channel = tensor.get_shape().as_list()[-1]
kernel = weight_variable([shape, shape, in_channel, out_chans], name=name)
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, kernel, strides=[1, strides, strides, 1], padding='SAME', name='conv')
def bn(tensor, name=None):
"""
:param tensor: 4D tensor input
:param name: name of the operation
:return: local response normalized tensor - not using batch normalization :(
"""
return tf.nn.lrn(tensor, depth_radius=5, bias=2, alpha=1e-4, beta=0.75, name=name)
in_chans = x.get_shape().as_list()[3]
if down_stride or up_stride:
first_stride = 2
else:
first_stride = 1
with tf.variable_scope('res%s' % name):
if in_chans == out_chan2:
b1 = x
else:
with tf.variable_scope('branch1'):
if up_stride:
b1 = conv_transpose(x, out_chans=out_chan2, shape=1, strides=first_stride,
name='res%s_branch1' % name)
else:
b1 = conv(x, out_chans=out_chan2, shape=1, strides=first_stride, name='res%s_branch1' % name)
b1 = bn(b1, 'bn%s_branch1' % name, 'scale%s_branch1' % name)
with tf.variable_scope('branch2a'):
if up_stride:
b2 = conv_transpose(x, out_chans=out_chan1, shape=1, strides=first_stride, name='res%s_branch2a' % name)
else:
b2 = conv(x, out_chans=out_chan1, shape=1, strides=first_stride, name='res%s_branch2a' % name)
b2 = bn(b2, 'bn%s_branch2a' % name, 'scale%s_branch2a' % name)
b2 = tf.nn.relu(b2, name='relu')
with tf.variable_scope('branch2b'):
b2 = conv(b2, out_chans=out_chan1, shape=3, strides=1, name='res%s_branch2b' % name)
b2 = bn(b2, 'bn%s_branch2b' % name, 'scale%s_branch2b' % name)
b2 = tf.nn.relu(b2, name='relu')
with tf.variable_scope('branch2c'):
b2 = conv(b2, out_chans=out_chan2, shape=1, strides=1, name='res%s_branch2c' % name)
b2 = bn(b2, 'bn%s_branch2c' % name, 'scale%s_branch2c' % name)
x = b1 + b2
return tf.nn.relu(x, name='relu')read_MITSceneParsingData.py主要是用于读取数据集的数据,代码如下:
#coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
import os
import random
from six.moves import cPickle as pickle
from tensorflow.python.platform import gfile
import glob
import TensorflowUtils as utils
# DATA_URL = 'http://sceneparsing.csail.mit.edu/data/ADEChallengeData2016.zip'
DATA_URL = 'http://data.csail.mit.edu/places/ADEchallenge/ADEChallengeData2016.zip'
def read_dataset(data_dir,data_name):
pickle_filename = "MITSceneParsing.pickle"
pickle_filepath = os.path.join(data_dir, pickle_filename)
if not os.path.exists(pickle_filepath):
result = create_image_lists(os.path.join(data_dir, data_name))
print ("Pickling ...")
with open(pickle_filepath, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(result, f, pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)
else:
print ("Found pickle file!")
with open(pickle_filepath, 'rb') as f:
result = pickle.load(f)
training_records = result['training']
validation_records = result['validation']
del result
return training_records, validation_records
'''
返回一个字典:
image_list{
"training":[{'image': image_full_name, 'annotation': annotation_file, 'image_filename': },......],
"validation":[{'image': image_full_name, 'annotation': annotation_file, 'filename': filename},......]
}
'''
def create_image_lists(image_dir):
if not gfile.Exists(image_dir):
print("Image directory '" + image_dir + "' not found.")
return None
directories = ['training', 'validation']
image_list = {}
for directory in directories:
file_list = []
image_list[directory] = []
# 获取images目录下所有的图片名
file_glob = os.path.join(image_dir, "images", directory, '*.' + 'jpg')
file_list.extend(glob.glob(file_glob))
if not file_list:
print('No files found')
else:
for f in file_list:
# 注意注意,下面的分割符号,在window上为:\\,在Linux撒花姑娘为 : /
filename = os.path.splitext(f.split("\\")[-1])[0] # 图片名前缀
annotation_file = os.path.join(image_dir, "annotations", directory, filename + '.png')
if os.path.exists(annotation_file):
record = {'image': f, 'annotation': annotation_file, 'filename': filename}
image_list[directory].append(record)
else:
print("Annotation file not found for %s - Skipping" % filename)
random.shuffle(image_list[directory])
no_of_images = len(image_list[directory])
print ('No. of %s files: %d' % (directory, no_of_images))
return image_list