Leetcode 407. Trapping Rain Water II 收集雨水2 解题报告
1 解题思想
我看了下题目,发现比预想中的简单,加之我比较烂,所以其实我还是没做,只是看懂了上回贴的代码,然后做了一下注释,现在我来讲下题目。
首先请看下上一题,上一题是2D的这题是3D的:
Leetcode #42. Trapping Rain Water 雨水收集 解题报告
题目的意思,就是给定了一个矩阵,代表一些木头桩,高度不一样,所以下雨的时候能够保存住一些水,现在问说能够收集多少雨水?
所谓的能收集雨水,就是要中间低,四边高,围起来才行,这就是核心idea和题目42一样。
所以这题的思想是:
1、构造一个优先队列,每次都取出高度最矮的一个。
2、首先将四周的桩都加入,因为记得四周是无法盛水的
3、每次从优先队列中取出一个最矮的cell,若他比未访问过的四周的四个高了delta h,那么总的盛水量多加delta h,否则不加,注意四周只要一访问过下次就不能访问了。
- 因为若当前cell被取出,且其某个邻居cell-n高度低于cell,那么可以得出:cell-n的邻居里面最矮的就是cell,所以cell可以决定cell-n的盛水量。
2 原题
Given an m x n matrix of positive integers representing the height of each unit cell in a 2D elevation map, compute the volume of water it is able to trap after raining.
Note:
Both m and n are less than 110. The height of each unit cell is greater than 0 and is less than 20,000.
Example:
Given the following 3x6 height map:
[
[1,4,3,1,3,2],
[3,2,1,3,2,4],
[2,3,3,2,3,1]
]
Return 4.
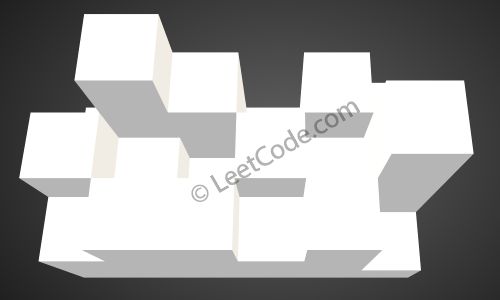
The above image represents the elevation map [[1,4,3,1,3,2],
[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]] before the rain.
After the rain, water are trapped between the blocks. The total volume of water trapped is 4.
3 参考代码
修改于于:https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/60371/java-version
public class Solution {
public int trapRainWater(int[][] heightMap) {
//一个单元格用一个Cell来表示
class Cell{
int x, y,h;
Cell(int x, int y, int height){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
h = height;
}
}
if (heightMap == null || heightMap.length == 0 || heightMap[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int m = heightMap.length;
int n = heightMap[0].length;
//优先队列,每次按照优先度输出队列,而不是按照顺序,这里是每次输出最矮的哪一个
PriorityQueue| pq = new PriorityQueue<>((v1,v2)->v1.h - v2.h);
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];
//将四周初始化为访问过的,周围的一边是怎么都没法盛水的
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
visited[0][i] = true;
visited[m-1][i] = true;
pq.offer(new Cell(0, i, heightMap[0][i]));
pq.offer(new Cell(m-1, i, heightMap[m-1][i]));
}
for(int i = 1; i < m-1; i++){
visited[i][0] = true;
visited[i][n-1] = true;
pq.offer(new Cell(i, 0, heightMap[i][0]));
pq.offer(new Cell(i, n-1, heightMap[i][n-1]));
}
//四个方向
int[] xs = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int[] ys = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int sum = 0;
//开始计算收集到的雨水,每次取出符合条件最矮的按个,然后计算差值,就是当前单元格可以容纳的了
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Cell cell = pq.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = cell.x + xs[i];
int ny = cell.y + ys[i];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && !visited[nx][ny]) {
visited[nx][ny] = true;
sum += Math.max(0, cell.h - heightMap[nx][ny]);
pq.offer(new Cell(nx, ny, Math.max(heightMap[nx][ny], cell.h)));
}
}
}
return sum;
}
}
|