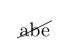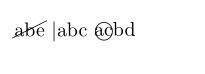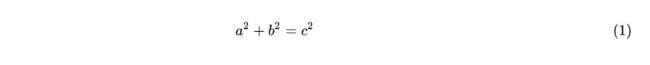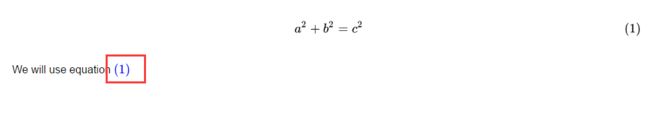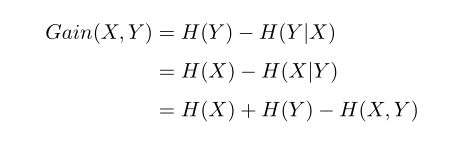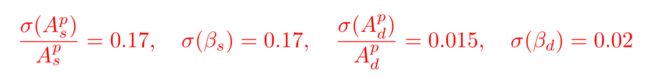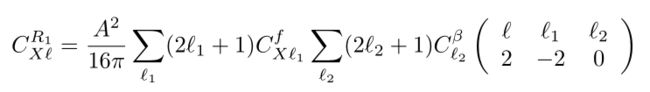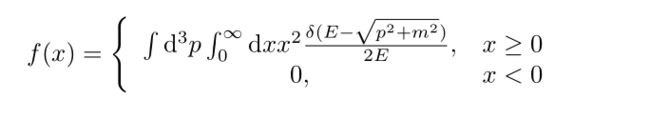WinEdt(latex)教程详细笔记
本文持续更新…
目录
- 本文持续更新...
- 0 包文件
- 1.字体
- 1.1 字体大小
- 1.2 字体加粗
- 1.3 字体显示形式
- 1.3.1 删除字体
- 1.3.2 其他形式
- 2.分段机制
- 3.空格
- 4.自动补全
- 5.数学模式与文本模式
- 5.1 行内公式和行间公式
- 5.2 数学公式编号
- 手动编号
- 自动编号
- 为知笔记
- Latex
- 马克飞象
- 5.3 数学公式对齐
- 5.4 公式之间空格
- 6.输入函数
- 7.矩阵和大括号
- 8.分段函数
- 9.加载宏包doc文档
- 10.输入中文以及宏包安装
- 11.插入图片
- 12.表格
- 12.1普通表格
- 调整表格和标题/标注的距离
- 多行
- 12.2合并行列
- 1,合并行
- 2,合并列
- 3,行列都存在
- 12.3表格下标注释和字体大小设置
- 设置表格(字体)大小
- 彩色表格和字体
- 彩色表格
- 彩色字体
- 12.4 图片表格并列
- 12.5 图片和图片并列
- 12.6 表格和表格并列
- 两个表格并列
- 多个表格并列
- 13.交叉引用(corss-reference)
- 14.文章布局
- (1)页面大小
- (2)页眉页脚
- (3)列举
- (4)参考文献
- A.手动输入
- B.使用Bibtex
- 15.超链接
- 16.插入代码
- 17.目录生成
- 18. 段落空行, 换行和首部缩进
本文是笔者初学WinEdt用以编辑Latex的笔记,只涉及一些简单问题,详细请参考百度文库(点点这几个字看看~~)
本文的主要参考文献是ta
0 包文件
这里主要给出本文所有的头文件,即需要使用的包。在运行本文中的事例之前在开头复制以下代码
% !Mode::"TeX:UTF-8"
%\documentclass[prd,aps,onecolumn,preprintnumbers,amsmath,amssymb,superscriptaddress]{article}
\documentclass{article}
%\usepackage[UTF8]{ctex}
\usepackage{listings}
\usepackage{amsthm}
\usepackage{amsmath}
\usepackage{amssymb}
\usepackage{subfigure}
\usepackage{graphicx}
\usepackage{hyperref}
\usepackage[table]{xcolor}
\usepackage{fancyhdr}
\usepackage{footnote}
\usepackage{lastpage}
%\usepackage{pythonhighlight}
\usepackage{indentfirst}
\usepackage{multirow}
\usepackage{authblk}
\usepackage{comment}
\usepackage{url}
\usepackage{float}
\usepackage{cite}
\usepackage{caption}
%\usepackage{graphix}
\setlength{\parindent}{1em}
%\pagestyle{fancy}
%设置页面大小
%\chead{LSPE}
%\rhead{\thesection}
%\cfoot{Page \thepage of \pageref{LastPage}}
\usepackage[top=2.54cm, bottom=2.54cm, left=3.18cm,right=3.18cm]{geometry}
1.字体
1.1 字体大小
1 设置latex/winedt代码中字体大小
options—options interface—Font schemes—Font双击从右边找到FONT_SIZE将10改为自己想要的,如14----保存—右键单击左边之前的Font----Load Script—结束
2 设置文章字体大小
\tiny
\scriptsize
\footnotesize
\small
\normalsize
\large
\Large
\LARGE
\huge
\Huge
比如:
{\small Hello word}
花括号框住的地方都变小
1.2 字体加粗
文本加粗
\textbf{这里放文本}
既要加粗又要变小:(为毛感觉有点邪恶~~ 2333333 认真脸)
{\textbf{\small Hello word}}
数学符号加粗
$\boldsymbol 直接接数学符号 $
1.3 字体显示形式
1.3.1 删除字体
\usepackage{cancel}
\cancel{abc}
1.3.2 其他形式
\cancel{abe}
\textbar{abc}
\textcircled{acbd}
2.分段机制
1, 在原码中空一行,则生成的pdf会换行
2, 在文后使用双斜杠\
3, 使用命令
\newparas
举例:
Life is too short so that I use python\\
me too.
Life is too short so that I use python
me too.
Life is too short so that I use python
\newparas
me too.
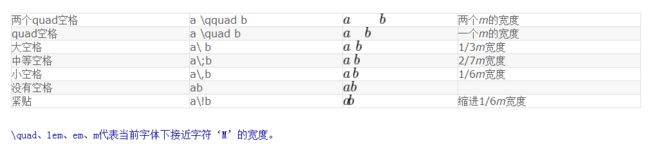
3.空格
当然直接空一格也是可以得到一个空格的,如下:
$a$, $b$, $c$.
$a,\ b,\ c.$
The first three letter are a, b, c.
结果为:

所以如果要空格直接按空格键即可,即上面代码的1和3方式
4.自动补全
快捷键:Ctrl+Enter
5.数学模式与文本模式
5.1 行内公式和行间公式
引入数学宏包{amssyb},American mathematics society symbol.例句如下
% !Mode::"TeX:UTF-8"
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{amssymb}
\begin{document}
\section{symbol}
1+1=2, $$1+1=2$$, $I know 1+1=2,$
This is in text mode, $This is in math mode,$ $This\ is\ in\ math\ in\ mode.$
\end{document}
结果如下:

对行内公式和行间公式总结如下:
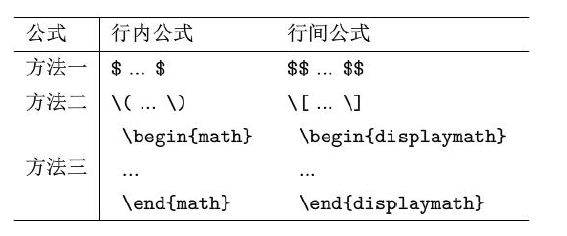
上面的方法是无法给公式编号的
5.2 数学公式编号
手动编号
通过采用\tag来编号,当引用公式时手动输入。缺点是当更改公式里的编号时引用中的编号不能自动更改,其二,不同通过点击引用的编号回到公式
$$y=1+e^x \tag{1.1}$$
我们今天要讨论这个方程$(1.1)$
(1.1) y = 1 + e x y=1+e^x \tag{1.1} y=1+ex(1.1)
我们今天要讨论这个方程 ( 1.1 ) (1.1) (1.1)
这个好处是在处理文章比较长,有很多节,如写书等时,可以手动写(1.1),(2.1)(2.1.1)等公式,而自动则是(1)(2)这样排序,没有分小节。
自动编号
建立公式环境,如下:
\begin{equation}\label{加入标记}
xxx
\end{equation}
不同的平台渲染不一样,比如为知笔记, latex等可以通过以下方法渲染自动编号
为知笔记
$$\begin{equation}\label{my_equ1}
a^2+b^2=c^2
\end{equation}$$
We will use equation \eqref{my_equ1}
Latex
对于latex而言,不需要$$这样的符号
\begin{equation}\label{time_pixel}
t_\text{pix}=\frac{\Delta T}{N_\text{pix}}\times N_\text{det}.
\end{equation}
Substituting \autoref{time_pixel}
马克飞象
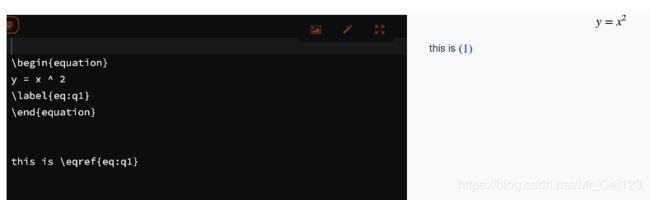
(马克飞象有时候渲染会失败,跟官方人员问过,给的办法是:失败的时候重新打开就可以看到自动编号,但是遗憾的是,当你尝试改动时又会出错,因此官方建议先编写完,再渲染,这样就不会去动它了。。。。呵呵哒。)
5.3 数学公式对齐
采用{aligned}如下:
\begin{equation}\label{information gain}
\begin{aligned}
Gain(X,Y)&=H(Y)-H(Y|X)\\
&=H(X)-H(X|Y)\\
&=H(X)+H(Y)-H(X,Y)
\end{aligned}
\end{equation}
\begin{equation}\label{lagrangian}
\begin{aligned}
w_{ij}&=\frac{1}{(N_i+R_i)(N_j+R_j)\frac{1}{2}(1+\delta_{ij})}\\
Var[\mathbb{\hat{C}}_\ell]&=\frac{2}{2\ell+1}\left(\sum_{i,j,j\ge i}\frac{1}{(N_i+R_i)(N_j+R_j)\frac{1}{2}(1+\delta_{ij})}\right)^{-1}
\end{aligned}
\end{equation}
5.4 公式之间空格
没有空格
\begin{equation}\label{add_prior}
\frac{\sigma(A_s^p)}{A_s^p}=0.17, \sigma(\beta_s)=0.17, \frac{\sigma(A_d^p)}{A_d^p}=0.015, \sigma(\beta_d)=0.02
\end{equation}
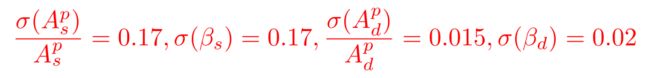
发现上面的公式之间挨得太近了,想要空格,可以使用第3部分提到的空格方法,将上面的代码增加\quad:
\begin{equation}\label{add_prior}
\frac{\sigma(A_s^p)}{A_s^p}=0.17,\quad \sigma(\beta_s)=0.17,\quad \frac{\sigma(A_d^p)}{A_d^p}=0.015,\quad \sigma(\beta_d)=0.02
\end{equation}
6.输入函数
输入函数前面加斜杠""
如:
$\frac{10}{11}, \sqrt[3]{x^2+1}, \ldots, \sin x, \cos x.$
结果如下:
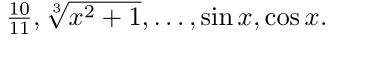
可以看到,虽然在上面代码每个逗号之后都输入了空格,但得到的pdf文档并没有逗号,而英文中是习惯在逗号,句号等符号之后加空格的,这个时候可以将上面代码改为:
$\frac{10}{11},$ $\sqrt[3]{x^2+1},$ $\ldots,$ $\sin x,$ $\cos x.$
即每个函数单独用美元符号分开,并在两者之间加符号。
$\sum_{n=1}^{\infty}$
$$\sum_{n=1}^{\infty}$$
$$\lim_{n \to \infty}(1+\frac{1}{n})^n = e,$$
$$\int_{-\infty}^{+\infty}\frac{\sin x}{x} \mathrm{d}x=I$$
$\alpha,\beta,\gamma,\delta\epsilon\varepsilon\xi\pi\rho\sigma\eta\theta\phi\varphi\omega$
$\Gamma\Phi$
$|A|,\|a\|,\vec{a},\overleftarrow{AB},\tilde{x},\widetilde{xyz},sin,\mathrm{sin}$
$\mathbb{AB},\mathbf{abAB}$
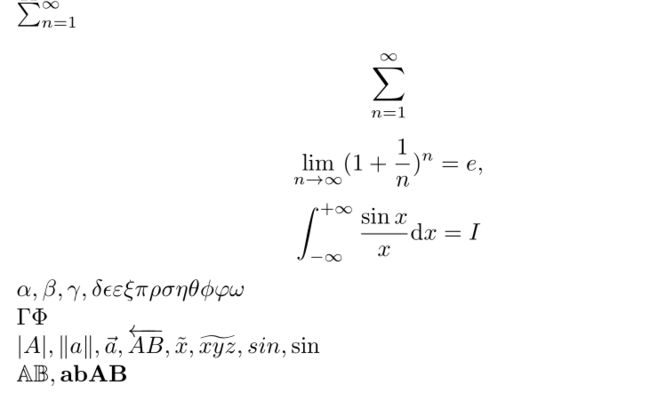
(1)第一行是行内公式和第二行的行间公式是不一样的,这是出于文本美观的目的。
(2)\mathrm{d}那儿是为了和x不同,因为d是直立的而不是变量,而x是变量,这里mathrm=math roman
(3)剩下的看到gamma等希腊字母第一个字母大写则表示输出的文本是大写,这里值得注意的是:alpha,beta,varepsilon等是没有大写形式的,因为其大写形式就是ABE,不能输入\Alpha,\Beta…
(4)mathbb=math blackboard, mathbf=math boldface
实际上第行中的括号应该是大括号而不是小括号,细节见下节。
7.矩阵和大括号
先看矩阵
\begin{equation}
\left(
\begin{array}{ccc}
a_{11}& a_{12} & a_{13} \\
a_{21} & a_{22} & a_{23} \\
a_{31} & a_{32} & a_{33}
\end{array}
\right)
\end{equation}
如果需要写 “函数=矩阵” 的形式,只需要在\left前加入即可,如:
\begin{equation}
f=
\left(
\begin{array}{ccc}
a_{11}& a_{12} & a_{13} \\
a_{21} & a_{22} & a_{23} \\
a_{31} & a_{32} & a_{33}
\end{array}
\right)
\end{equation}

(这里不要纠结颜色,因为我都改为红色了)
(1)以上begin{equation}开始了一个公式环境,在这个环境中可以直接输入变量、函数等而不需要加$符号,上面等同于
$$ \left(
\begin{array}{ccc}
a_{11}& a_{12} & a_{13} \\
a_{21} & a_{22} & a_{23} \\
a_{31} & a_{32} & a_{33}
\end{array}
\right)$$
(2)\left( and \right) are left bracket and right bracket. 能够通过括号内的内容自动改变括号大小。所以上面6中的第三行应该改为:
$$\lim_{n \to +\infty}\left(1+\frac{1}{n}\right)^n=e$$
(3)符号&是用来分隔列的,同一行不同列之间的元素用&分隔开
(4){ccc}是array中必选参数,为center,center,center,表示三列都居中,
(5)\是强制换行符号
\begin{equation}\label{Cx1}
C_{X\ell}^{R_1}=\frac{A^2}{16\pi}\sum_{\ell_1}(2\ell_1+1)C_{X\ell_1}^f\sum_{\ell_2}(2\ell_2+1)C_{\ell_2}^\beta\left(
\begin{array}{ccc}
\ell&\ell_1&\ell_2\\
2&-2&0
\end{array}
\right)
\end{equation}
\begin{equation}\label{Cx1}
C_{X\ell}^{R_1}=\frac{A^2}{16\pi}\sum_{\ell_1}(2\ell_1+1)C_{X\ell_1}^f\sum_{\ell_2}(2\ell_2+1)C_{\ell_2}^\beta\left(
\begin{array}{ccc}
\ell&\ell_1&\ell_2\\
2&-2&0
\end{array}
\right)
\left(
\begin{array}{ccc}
\ell&\ell_1&\ell_2\\
2&-2&0
\end{array}
\right)
\end{equation}
8.分段函数
分段函数是在矩阵的基础之上的,比如如下的分段函数
\begin{equation}
f(x)=
\left\{
\begin{array}{cc}
\int \mathrm{d}^3p\int_{0}^{\infty}\mathrm{d}x x^2 \frac{\delta(E-\sqrt{p^2+m^2})}{2E} , & x \geq 0 \\
0,& x < 0
\end{array}
\right.
\end{equation}
9.加载宏包doc文档
当我们使用一个宏包比如amsmath,想要得到说明文时可以如下操作:
在控制台上点击终端cmd窗口,输入tex xxx(xxx是宏包名,如amsmath)回车即可。
终端按钮如下图:
10.输入中文以及宏包安装
输入中文需要用到ctex包,这是专门针对中文而设计的包,使用时在前面将
\document{article}
改为
\document[UTF8]{ctexart}
即可,(有的不需要加方括号中的内容),或者\document{article}不变,在其下加入一个宏包为
\usepackage[UTF8]{ctex}
此外,中文包还可以使用
\usepackage{CJK}
当然,前提是已经安装ctex宏包,通常情况都会自动安装好,如果没有安装可以如下(笔者用的是Tex live)
开始—tex live—tex live manager—找到ctex—点击安装
值得注意的是:宏包已经都不需要网上下载安装,而是直接从库上安装缺少的宏包,方法就是上面的方法。
11.插入图片
插入图片可以引用命令:
\ref{fig} or \autoref{fig}
前者只给图片序号,而后者为Figure + 序号
插入图片需要加载宏包
\usepackage{graphicx}
或
\usepackage{graphics}
建议前者。
插入图片的环境为:
\begin{figure}[ht]
\centering
\includegraphics[width=10cm]{hh}
\caption{这个是图片}\label{bbb}
\end{figure}
解释:
(1)第一句begin{figure}代表开始插入图片,后面的[ht]是可选参数,表示here, top。如果去掉[ht]表示默认的htbp,分别表示“这里,顶部,底部,换一页”(here, top, bottom, page)
(2)第二句是图片居中,否则自动靠左
(3)[width=10cm] (有些people不需要加cm,是已经设置单位是cm了,还可以有in英尺),可选的参数还有如下(可参考DreamSeeking的文献):
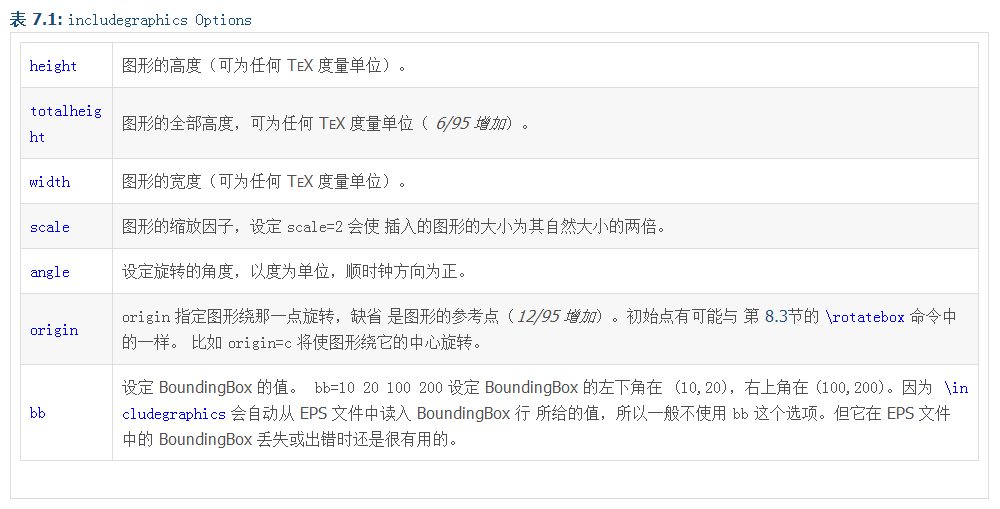
第三行最后的{hh}表示插入的图片的名字,因此插入的图片一定要放在工作目录下,并命名为hh.xxx(xxx表示后缀,如png,jpg,eps等)
当然也有不在工作目录下的方法,这个google一下by yourself.在此不累赘。(好吧,让我再告诉你好了,其实就是使用绝对路径
\includegraphics[width=10cm]{D:/software/tex/hh.png}
当然,.png后缀可以不写)注意,绝对路径中是用的左斜杠“/”而不是右斜杠。
此外如果图片比较多,最好的方法是在当前工作路径下单独建一个文件夹,命名为fig.然后将图片都放进去,此后要使用里面的图片时只需要使用路径加载即可,这是相对路径方法,如下:
\includegraphics[width=10cm]{fig/hh}
(4)caption{这个是图片}表示对图片的描述,将出现在图片的底下。label{bbb}表示对这张图片的标签,相当于给定了这张图片的名字。图片较多时,建议使用容易看懂的名字,如label{fig.sub.1}。这个label的作用是方便以后引用这个图时只需要用其标签就可以,比如
see,figure\ref{fig.sub.1} or \autoref{fig.sub.1}
结果就是:see,figure x(x表示刚刚插入的图的序号,如图3)
(5)这样插入的图片是一个浮动图,也就是latex自动找到最好的位置来放置此图,而不是你代码设置的地方,想要得到不浮动的图可以将
\includegraphics[width=10cm]{fig/hh}
这句单独提取出来放置想要放的代码中即可,但这个时候是不能加
\caption{xxx}
这一句的,也就是没法加入标题。如果要给不浮动的图形加标题,那么可以看看nonfloat 包或者自己google(这回是朕是真的不打算给你找了)。
12.表格
12.1普通表格
表格制作可以参考这个 and 这个(点一下试试),后者是英文。
简单说明:
表格制作可以使用tabular,简单一个图如下:
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|}
\hline
% after \\: \hline or \cline{col1-col2} \cline{col3-col4} ...
Name & score \\
\hline
小明 & 50 \\
小华 & 45 \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
结果如下
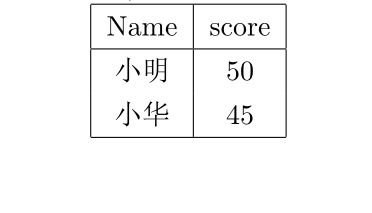
讲解:
(1)第一句是tabular表格的开始,参数{|c|c|}中的第一个|表示表格中的左边竖,第二、三个分别是中间和右边的竖。而c表示表格中的字体居中,l(left)和r(right)表示表格中字体靠左和靠右。可以尝试将{|c|c|}改为{c|c}即不要两边的竖线。
(2)\hline(horizontal line)表示画一条水平线
(3)%是注释,\是换行,\hline可以紧接在\后,如下表示:
\\ \hline
会显得更紧凑。
当然,这个表格是不浮动的,和图片一样,如果想加入\caption的话,可以构成浮动的图片(但毕竟可以写标题了呀,想想还是赚的)。这个时候需要用到table环境。如下
\begin{table}
\centering
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|}
\hline
% after \\: \hline or \cline{col1-col2} \cline{col3-col4} ...
Name & score \\
\hline
小明 & 50 \\
小华 & 45 \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
\caption{这是一个表格}
\end{table}
同样的\centering是表格居中,否则居左。其他都讲过了,很easy.最后可以使用caption宏包,这个需要自行google。
在表格中换行
比如两个表格(table)是要构成一个table的,想统一做一个说明,而不是每个table单独说明,此时需要将两个表格分开,这个时候可以用命令:
\vspace{0.35cm} #表示上下空0.35cm的空间
比如
\begin{table}
\centering
%\footnotesize
Case 0: 95+150
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline
$r$ & $\sigma_r(\sigma_F=1)$ & $\sigma_r(\sigma_F=0.1)$ & $\sigma_r(\sigma_F=0.01)$ & $N_{95}$ & $N_{150}$\\
\hline
0.01 & 0.01094 & 0.00228 & 0.00106 & 8701 & 1299 \\
0 & 0.01084 & 0.00216 & 0.00091 & 8701 & 1299 \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
\vspace{0.35cm} #空0.35cm
Case 1: 41+95+150
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline
$r$ & $\sigma_r(\sigma_F=1)$ & $\sigma_r(\sigma_F=0.1)$ & $\sigma_r(\sigma_F=0.01)$ & $N_{95}$ & $N_{150}$\\
\hline
0.01 & 0.00787 & 0.00203 & 0.00106 & 8701 & 1299 \\
0 & 0.01084 & 0.00216 & 0.00091 & 8701 & 1299 \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
\caption{table 1}\label{anser1}
\end{table}

如果要改变字体大小,只要在第二行即\centering下加入改变字体大小的代码即可,(如我已经注释掉的\footnotesize),更多字体大小的代码见第一部分。
调整表格和标题/标注的距离
可以使用以下两个命令,关于调节距离多少,可以尝试调节里面的数字
\setlength{\abovecaptionskip}{0.cm}
\setlength{\belowcaptionskip}{-0.9cm}
多行
现在要将上面的tabe2设置为如下形式,即对应r=0.01有多个 σ F \sigma_F σF可选。
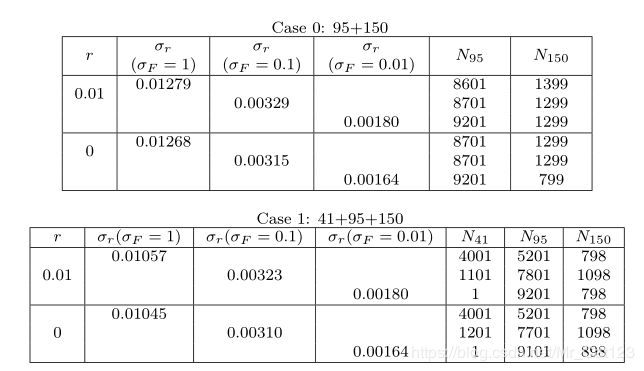
代码如下:
\begin{table}
\centering
\footnotesize
Case 0: 95+150
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline
\multirow{2}{0.25cm}{\centering $r$} & \multirow{2}{1.2cm}{\centering $\sigma_r$\\$(\sigma_F=1)$} & \multirow{2}{1.4cm}{\centering $\sigma_r$\\$(\sigma_F=0.1)$} & \multirow{2}{1.6cm}{\centering $\sigma_r$\\$(\sigma_F=0.01)$} & \multirow{2}{1cm}{\centering $N_{95}$} & \multirow{2}{1cm}{\centering $N_{150}$}\\
& & & & & \\
\hline
\multirow{2}*{0.01} & 0.01279 & & & 8601 & 1399 \\
& & 0.00329 & & 8701 & 1299 \\
& & & 0.00180 & 9201 & 1299 \\
\hline
\multirow{2}*{0} & 0.01268 & & & 8701 & 1299 \\
& & 0.00315 & &8701 & 1299\\
& & & 0.00164 & 9201 & 799 \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
\vspace{0.35cm}
Case 1: 41+95+150
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline
$r$ & $\sigma_r(\sigma_F=1)$ & $\sigma_r(\sigma_F=0.1)$ & $\sigma_r(\sigma_F=0.01)$ & $N_{41}$ & $N_{95}$ & $N_{150}$\\
\hline
& 0.01057 & & & 4001 & 5201 & 798 \\
0.01 & & 0.00323 & & 1101 & 7801 & 1098 \\
& & & 0.00180 & 1 & 9201 & 798 \\
\hline
& 0.01045 & & & 4001 & 5201 & 798 \\
0 & & 0.00310 & & 1201 & 7701 & 1098 \\
& & & 0.00164 & 1 & 9101 & 898 \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
\caption{table 1}\label{anser1}
\end{table}
12.2合并行列
1,合并行
使用
\multirow{n}*{text} #n表示要合并的行数,*是必须的,否则无法编译成功,text是此行中要输入的内容
注意,使用\multirow一定要在导言区,也就是在最开头使用包\usepackage{multirow}
举例如下:
% !Mode::"TeX:UTF-8"
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage[UTF8]{ctex}
\usepackage{listings}
\usepackage{amsthm}
\usepackage{amsmath}
\usepackage{amssymb}
\usepackage{graphicx}
\usepackage{hyperref}
\usepackage[table]{xcolor}
\usepackage{fancyhdr}
\usepackage{lastpage}
\usepackage{pythonhighlight}
\pagestyle{fancy}
\usepackage{enumitem}
\setlist[trivlist]{topsep=\baselineskip}
\usepackage{multirow}
%这里以上都是导言区
\begin{document}
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|}
\hline
\multirow{3}*{朕} & 尚书省 & 工部 刑部 兵部 礼部 户部 吏部 \\
\cline{2-3}
& 中书省 & ... \\
\cline{2-3}
& 门下省 & ... \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
\end{document}
得到如下图:

上面中 \cline{a-b}表示从第a列画一条到第b列的线,与\hline的区别在于可以指定线的起始位置。
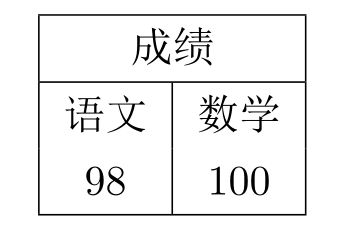
2,合并列
使用
\multicolumn{n}{x}{text} #n为合并列的数量,x为字体的排版样式,比如r,l,c分别表示右对齐,左对齐,居中,text为内容
例子
\begin{document}
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|}
\hline
\multicolumn{2}{|c|}{成绩} \\
\hline
语文 & 数学 \\
98 & 100 \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
\end{document}
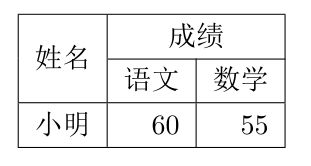
3,行列都存在
\begin{document}
\begin{tabular}{|c|r|r|}
\hline
\multirow{2}*{姓名} & \multicolumn{2}{c|}{成绩} \\
\cline{2-3}
& 语文 & 数学 \\
\hline
小明 & 60 & 55 \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
\end{document}
12.3表格下标注释和字体大小设置
给定一个表格后,表下可能会有表格的介绍,而介绍的字体通常比文章字体小,可以用
\small{}
\begin{table}
\centering
\rowcolors[\hline]{2}{orange}{red!30!yellow}
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|}
\rowcolor{red!20}
Name & score \\
小明 & 50 \\
小华 & 45 \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
\caption{\small{This is a simple table for testing}}
\end{table}
设置表格(字体)大小
同样,可以通过\small来修改,但是放置的位置和上面不同,而是放在\begin{table}之后,如:
\begin{table}
\centering
\small #改变表格字体大小,同时表格大小也会变
\rowcolors[\hline]{2}{orange}{red!30!yellow}
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|}
\rowcolor{red!20}
Name & score \\
小明 & 50 \\
小华 & 45 \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
\caption{\small{This is a simple table for testing}}
\end{table}
此外还有
\tiny
\scriptsize
\footnotesize
\small
\normalsize
\large
\Large
\LARGE
\huge
\Huge
彩色表格和字体
彩色表格
彩色表格需要用到宏包
\usepackage{xcolor}
没有需要按照上面的方法先安装。因为是针对表格,所以需要支持表格,使用时要如下:
\usepackage[table]{xcolor}
上面的例子可以加入彩色如下:
...
\usepackage[table]{xcolor}
...
...
\begin{table}
\centering
\rowcolors[\hline]{2}{orange}{red!30!yellow}
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|}
\rowcolor{red!20}
Name & score \\
小明 & 50 \\
小华 & 45 \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
\caption{这是一个表格}
\end{table}
结果为:
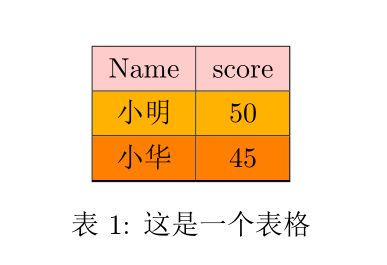
说明:
(1)第一行使用宏包xcolor,并支持table
(2)
\rowcolors[\hline]{2}{orange}{red!30!yellow}
这里是表示行颜色的设置,\hline表示每行都加横线,后面表示从第二行开始奇数行用orange颜色,偶数行用30%红色和30%黄色的混合,也可以写成{red!30yellow!30}
(3)因为我们是从第二行开始加颜色,所以第一行要单独加颜色,如下
\rowcolor{red!20}
如果没有则是白色。如果想要单独每行自行设置,也可以如下单独每行设置颜色
\begin{table}
\centering
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|}
\hline
\rowcolor{red!20}
Name & score \\
\hline
\rowcolor{yellow}
小明 & 50 \\
\hline \rowcolor{orange}
小华 & 45 \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
\caption{这是一个表格}
\end{table}
彩色字体
同样是xcolor包
{\color{violet}{哇,这是我的第一个 \LaTeX{} Article!}}

这一行是通过一个大花括号括起来的(即最左和最后的括号),如果没有则整篇文章都是这种颜色的字体,括起来后就只有这一句话是这个颜色。
更多颜色设置见官网 and it’s pdf article
12.4 图片表格并列
可以参考 https://tex.stackexchange.com/questions/377998/how-to-make-table-and-figure-side-by-side-appear-at-the-same-height
\begin{figure} %开始图片(图片和表格合成一个大的图片,这里指的是整体的大图片)
\begin{minipage}[b]{.5\linewidth} %开辟一个小页面,即用来放第一个图片
\centering
\includegraphics[width=6cm]{Figure_1.eps}
\caption{Image}
\end{minipage}%
\begin{minipage}[b]{.5\linewidth} %开辟第二个小页面,用来放表格
\centering
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|}
\hline
aa & bb \\ \hline
cc & dd \\ \hline
\end{tabular}
\captionof{table}{Table}
\end{minipage}
%\caption{pic and table side by side}
\end{figure}
注意上面表格和图片合成了一个大的图片,同时可以对上面两个一起写注释,即将上面的
%\caption{pic and table side by side}
去掉注释即可
12.5 图片和图片并列
受上面的启发,我们可以将两张图片并列
\begin{document}
\begin{figure}
\begin{minipage}[b]{.5\linewidth}
\centering
\includegraphics[width=6cm]{large_full.eps}
\caption{Image}
\end{minipage}%
\begin{minipage}[b]{.5\linewidth}
\centering
\includegraphics[width=6cm]{large_part}
\caption{image2}
\end{minipage}
\end{figure}
\end{document}
\begin{figure}[htb]
\centering
\subfigure[]{\includegraphics[width=6.5cm]{large_part.eps}} %[ ]里面不填就会默认为(a)
\quad
\subfigure[]{\includegraphics[width=6.5cm]{large_full.eps}} %[ ]里面不填默认为(b)
\caption{\small{The changing of uncertainty $\sigma_r$ on tensor-to-scalar ratio $r$ with the distribution of detectors on focal plane for different frequency combinations with $r$=0.01 and $\sigma_F$=0.1. Contour (a), (b) and (c) correspond to the case 0, case 1 and case 1*, respectively. }}\label{large_fig1}
\end{figure}
12.6 表格和表格并列
两个表格并列
\begin{figure} %开始图片(表格和表格合成一个大的图片,这里指的是整体的大图片)
\begin{minipage}[b]{.5\linewidth} %开辟第一个小页面,用来放第一个表格
\centering
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline
$r$ & $\sigma_r$ & $N_{95}$ & $N_{150}$ & $N_{220}$\\
\hline
\multirow{1}*{0} & 0.00765 & 4200 & 3000 & 2800 \\
\hline
\multirow{1}*{0.01} & 0.00778 & 4200 & 3000 & 2800 \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
\captionof{table}{Table}
\end{minipage}
\begin{minipage}[b]{.5\linewidth} %开辟第二个小页面,用来放表格
\centering
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|}
\hline
aa & bb \\ \hline
cc & dd \\ \hline
\end{tabular}
\captionof{table}{Table}
\end{minipage}
\caption{table and table side by side}
\end{figure}
可以看到有三个标注,可以通过加%去掉。另外,上面图中最后标注是figure 1 xxx, 然而我们是图表,所以只要将begin{figure}和end{figure}括号改为table即可,我就不再改了。
多个表格并列
\begin{table} %开始图表
\begin{minipage}[b]{.5\linewidth} %开辟第一个小页面,用来放第一个表格
\centering
Case I, $f_\text{sky}=0.7$
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline
$r$ & $\sigma_r$ & $N_{41}$ & $N_{95}$ & $N_{220}$\\
\hline
\multirow{1}*{0} & 0.00405 & 800 & 7200 & 2000 \\
\hline
\multirow{1}*{0.01} & 0.00422 & 800 & 7200 & 2000 \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
\end{minipage}
\vspace{0.35cm} %调节表格间距
\begin{minipage}[b]{.5\linewidth} %开辟第二个小页面,用来放第二个表格
\centering
Case II, $f_\text{sky}=0.7$
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline
% \caption{The first table}
$r$ & $\sigma_r$ & $N_{30}$ & $N_{41}$ & $N_{95}$ & $N_{220}$ & $N_{270}$\\
\hline
\multirow{1}*{0} & 0.00765 & 400 & 400 & 7200 & 1000 & 1000 \\
\hline
\multirow{1}*{0.01} & 0.00778 & 400 & 400 & 7200 & 1000 & 1000 \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
\end{minipage}
\begin{minipage}[b]{.5\linewidth} %开辟第三个小页面,用来放第三个表格
\centering
Case III, $f_\text{sky}=0.05$
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline
$r$ & $\sigma_r$ & $N_{41}$ & $N_{95}$ & $N_{220}$\\
\hline
\multirow{1}*{0} & 0.00256 & 600 & 7400 & 2000 \\
\hline
\multirow{1}*{0.01} & 0.00319 & 600 & 7400 & 2000 \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
\end{minipage}
\vspace{0.35cm}
\begin{minipage}[b]{.5\linewidth} %开辟第四个小页面,用来放第四个表格
\centering
Case IV, $f_\text{sky}=0.05$
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline
% \caption{The first table}
$r$ & $\sigma_r$ & $N_{30}$ & $N_{41}$ & $N_{95}$ & $N_{220}$ & $N_{270}$\\
\hline
\multirow{1}*{0} & 0.00765 & 400 & 400 & 7200 & 1000 & 1000 \\
\hline
\multirow{1}*{0.01} & 0.00778 & 400 & 400 & 7200 & 1000 & 1000 \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
\end{minipage}
\caption{table and table side by side}
\end{table}
注意,表格之间不要出现空行,因为空行表示换一段,所以表格会打乱。
13.交叉引用(corss-reference)
关于引用部分上面已经提及了一些,上面11的(4)我们用的是\ref {xxx}这个命令。这个命令有一个缺点是它只给出图、定理等的序号,比如“如图2所示”当我们使用\ref时需要写成:
如图\ref{xxx}所示
当我们并不知道这个\ref{xxx}是图还是表格还是定理等等的时候就比较麻烦,或者我们不想输入“图”,“表格”这样的字眼,这时可以使用宏包(同样,如果没有宏包先按照上面的方法安装)
\usepackage{hyperref}
然后将\ref {xxx}改为\autoref{xxx},e.g.
......
\usepackage{hyperref}
...
...
\begin{equation}
f(x)=
\left\{
\begin{array}{cc}
\int \mathrm{d}^3p\int_{0}^{\infty}\mathrm{d}x x^2 \frac{\delta(E-\sqrt{p^2+m^2})}{2E} , & x \geq 0 \\
0,& x < 0
\end{array}
\right.
\label{myequation}
\end{equation}
We all know \autoref{myequation} is a important equation
we can get:
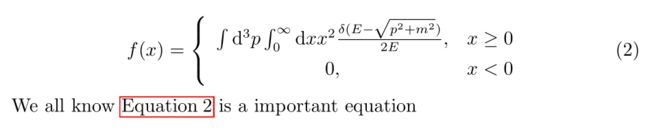
可以看到自动加了equation这个词,而且是红色方框,点击可以直接跳到公式2.
14.文章布局
(1)页面大小
使用tex得到的pdf很窄,左右空的地方很大,如果我们想让它跟微软中的word一样的页面,可以在导言部分加入以下命令
\usepackage[top=2.54cm, bottom=2.54cm, left=3.18cm,right=3.18cm]{geometry}
(2)页眉页脚
参考文献见这里
使用宏包
\usepackage{fancyhdr}
在导言部分加入
\usepackage{fancyhdr}
\pagestyle{fancy}
\lhead{wudl}
\chead{$wudl's$ $tutorial article$}
\rhead{\thesection}
\cfoot{\thepage}
上面的结果是,页眉左上边是wudl,中间是chead中的句子,右上边是章节,页脚是页码。实际还有很多可选参数,自行查找需要的。
当然上面的页码是“1”“2”“3”这样的数,如果想要A of B,即第A页共B页,则要使用lastpage宏包。
如下:
\usepackage{fancyhdr}
\usepackage{lastpage}
\pagestyle{fancy}
\lhead{wudl}
\chead{$wudl's$ $tutorial article$}
\rhead{\thesection}
\cfoot{Page \thepage of \pageref{LastPage}}
(3)列举
(4)参考文献
A.手动输入
手动输入采用thebibliography环境,手动输入适合参考文献比较少的情况
As is stated in \cite{bibitem1} blahblah\dots
\begin{thebibliography}{9}
\bibitem{bibitem1}
天朝. 朕的江山和子民[M]. 朕的天朝:天朝出版社. 2018
\bibitem{bibitem2}
blahblah(ditto)
这里\bibitem跟上面的列举中\item是一样的,上面的9表示最多可能有9条参考文献。结果为:

B.使用Bibtex
这个比较复杂,以后再补充
15.超链接
使用
hyperref
实际上面都用过这个了。
16.插入代码
参考百度知道
%导言部分
...
...
\usepackage{listings} %加入宏包
\lstset{language=Python} %Python语言
\lstset{breaklines} %自动将长的代码换行排版
\lstset{extendedchars=false} %解决代码跨页时,章节标题,页眉等汉字不显示的问题
...
...
%需要插入代码的地方
\begin{lstlisting}
放入代码
\end{lstlisting}
这样的方法是代码是没有彩色的,结果如下

解决彩色问题可以到网上找到已经修改彩色的代码,放入导言部分即可,实际上就是使用上文讲过的xcolor宏包自定义颜色。
例:自定义颜色(参考conding算子)
自定义颜色使用了listings和color两个宏包
\usepackage{listings}
\usepackage{color}
\definecolor{dkgreen}{rgb}{0,0.6,0}
\definecolor{gray}{rgb}{0.5,0.5,0.5}
\definecolor{mauve}{rgb}{0.58,0,0.82}
\lstset{ %
language=Octave, % the language of the code
basicstyle=\footnotesize, % the size of the fonts that are used for the code
numbers=left, % where to put the line-numbers
numberstyle=\tiny\color{gray}, % the style that is used for the line-numbers
stepnumber=2, % the step between two line-numbers. If it's 1, each line
% will be numbered
numbersep=5pt, % how far the line-numbers are from the code
backgroundcolor=\color{white}, % choose the background color. You must add \usepackage{color}
showspaces=false, % show spaces adding particular underscores
showstringspaces=false, % underline spaces within strings
showtabs=false, % show tabs within strings adding particular underscores
frame=single, % adds a frame around the code
rulecolor=\color{black}, % if not set, the frame-color may be changed on line-breaks within not-black text (e.g. commens (green here))
tabsize=2, % sets default tabsize to 2 spaces
captionpos=b, % sets the caption-position to bottom
breaklines=true, % sets automatic line breaking
breakatwhitespace=false, % sets if automatic breaks should only happen at whitespace
title=\lstname, % show the filename of files included with \lstinputlisting;
% also try caption instead of title
keywordstyle=\color{blue}, % keyword style
commentstyle=\color{dkgreen}, % comment style
stringstyle=\color{mauve}, % string literal style
escapeinside={\%*}{*)}, % if you want to add LaTeX within your code
morekeywords={*,...} % if you want to add more keywords to the set
}
导入模块
参考gaojiaxing 和 instant以python为例,下载python版本的hightlighting,地址点这里。下载完成要将pythonhighlight.sty和放在工作目录下。
可以有两种方法来加载自己写的python代码。其一是将python代码在python自己的编辑器中写完保存为.py文件放到工作目录下(如test.py),之后加载的时候只需要\inputpython…即可,这种方法可以节省大量的WinEdt书写空间
...
...
\usepackage{graphicx}
\usepackage{pythonhighlight}
...
...
\inputpython{test.py}{1}{41}#导入python文件test.py第一行到第41行
...
其二,可以通过
\begin{xxx}
代码
\end{xxx}
例如:
\begin{python}
#
from pyx import *
def f():
g = graph.graphxy(width=8)
g.plot(graph.data.function("y(x)=sin(x)/x", min=-15, max=15))
g.writePDFfile("function")
print r'\includegraphics{function}'
return f
\end{python}
17.目录生成
插入目录使用
\tableofcontents
注意这句话要在\begin{document}之后,end之前,例如:
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{hyperref}
\begin{document}
\tableofcontents
\section{A section}
This is a section
\paragraph{A paragraph}
This is a paragraph
\subsection{A subsection}
This is a subsection
\end{document}
\usepackage{hyerref}
如果没有这个超链接是不会有红色部分的。
18. 段落空行, 换行和首部缩进
在latex中,默认回车是不换行的,比如在latex中输入
A: Hello, how are you?
B: Hi, i'm fine.
A: Hello, how are you?\\
B: Hi, i'm fine.
另外,如果我们希望B换行之后行首缩进,比如写段落的时候希望前面缩进两个字符等,可以直接在latex中空一行
A: Hello, how are you?
B: Hi, i'm fine.
最后,如果我们希望段落之间空的行数比较多,可以使用如下两种方法: 我在此就不翻译了,链接来自:
https://tex.stackexchange.com/questions/135134/how-to-add-an-empty-line-between-paragraphs
这里需要提到的是:在定义\newcommad的时候,可以将下面的\newcommand{…}…这几行代码放在\begin{document}之前或者之后,但是笔者习惯放之前,看着比较整洁易识别。另外就是newpara是自定义的名字,你可以把它定义成任何你想要的名字。最后,使用\newcommand的时候里面的\vskip 1cm默认单位是cm,而不是inch,而第1种方法是inch.