Python实战异步爬虫(协程)+分布式爬虫(多进程)
引言:我们在写爬虫时常会遇到这样的问题,当需要爬取多个URL时,写一个普通的基于
requests库的爬虫程序爬取时间会很长。因为是顺序请求网页的,而网页请求和获得响应过程比较耗费时间,程序不得不等待获得当前网页响应后才能进行下一个URL的爬取,使得总耗时较多。对于这样的多任务,可以使用基于多进程(multiprocessing)和基于Asyncio库的异步(协程)爬虫增强并发性,加速爬虫。
Talk is cheap,show me the picture!
在讲解之前,我们先来通过一幅图看清多进程和协程的爬虫之间的原理及其区别。(图片来源于网络)
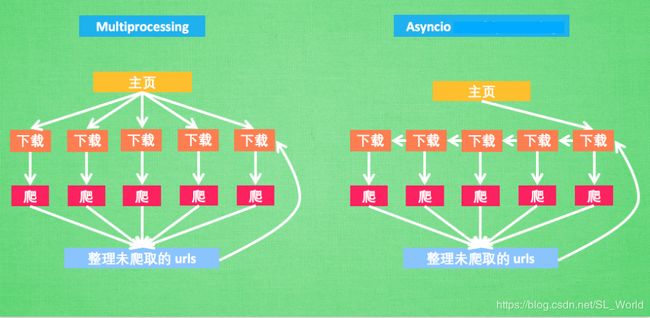
这里,异步爬虫不同于多进程爬虫,它使用单线程(即仅创建一个事件循环,然后把所有任务添加到事件循环中)就能并发处理多任务。在轮询到某个任务后,当遇到耗时操作(如请求URL)时,挂起该任务并进行下一个任务,当之前被挂起的任务更新了状态(如获得了网页响应),则被唤醒,程序继续从上次挂起的地方运行下去。极大的减少了中间不必要的等待时间。
- 对于协程(Asyncio库)的原理及实现请见:《Python异步IO之协程(详解)》
- 对于多进程的知识讲解及实现请见:《廖雪峰-Python多进程》
在有了Asyncio异步IO库实现协程后,我们还需要实现异步网页请求。因此,aiohttp库应运而生。
使用aiohttp库实现异步网页请求
在我们写普通的爬虫程序时,经常会用到requests库用以请求网页并获得服务器响应。而在协程中,由于requests库提供的相关方法不是可等待对象(awaitable),使得无法放在await后面,因此无法使用requests库在协程程序中实现请求。
在此,官方专门提供了一个aiohttp库,用来实现异步网页请求等功能,简直就是异步版的requests库,当然需要我们手动安装该库(如下所示)。
>>> pip3 install aiohttp
【基础实现】:在官方文档中,推荐使用ClientSession()函数来调用网页请求等相关方法。
首先,我们需要引入aiohttp模块。
import aiohttp
然后,我们在协程中使用ClientSession()的get()或request()方法来请求网页。(其中async with是异步上下文管理器,其封装了异步实现等功能)
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.get('http://httpbin.org/get') as resp:
print(resp.status)
print(await resp.text())
ClientSession()除了有请求网页的方法,官方API还提供了其他HTTP常见方法。
session.request(method='GET', url='http://httpbin.org/request')
session.post('http://httpbin.org/post', data=b'data')
session.put('http://httpbin.org/put', data=b'data')
session.delete('http://httpbin.org/delete')
session.head('http://httpbin.org/get')
session.options('http://httpbin.org/get')
session.patch('http://httpbin.org/patch', data=b'data')
如欲看完整的aiohttp使用方法,请见官方文档。
【案例】
【任务】:爬取2018年AAAI顶会中10篇论文的标题。
【已知】:10个论文页面URL。如欲提前看所有代码请见:GitHub
urls = [
'https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16488',
'https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16583',
'https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16380',
'https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16911',
'https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16581',
'https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16674',
'https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16112',
'https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/17343',
'https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16659',
'https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16449',
]
一、测试普通爬虫程序
下面是一个普通的同步代码,实现顺序爬取10个URL的title。
import time
from lxml import etree
import requests
urls = [
'https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16488',
'https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16583',
# 省略后面8个url...
]
'''
提交请求获取AAAI网页,并解析HTML获取title
'''
def get_title(url,cnt):
response = requests.get(url) # 提交请求,获取响应内容
html = response.content # 获取网页内容(content返回的是bytes型数据,text()获取的是Unicode型数据)
title = etree.HTML(html).xpath('//*[@id="title"]/text()') # 由xpath解析HTML
print('第%d个title:%s' % (cnt,''.join(title)))
if __name__ == '__main__':
start1 = time.time()
i = 0
for url in urls:
i = i + 1
start = time.time()
get_title(url,i)
print('第%d个title爬取耗时:%.5f秒' % (i,float(time.time() - start)))
print('爬取总耗时:%.5f秒' % float(time.time()-start1))
执行结果如下:
第1个title:Norm Conflict Resolution in Stochastic Domains
第1个title爬取耗时:1.41810秒
第2个title:Algorithms for Trip-Vehicle Assignment in Ride-Sharing
第2个title爬取耗时:1.31734秒
第3个title:Tensorized Projection for High-Dimensional Binary Embedding
第3个title爬取耗时:1.31826秒
第4个title:Synthesis of Programs from Multimodal Datasets
第4个title爬取耗时:1.28625秒
第5个title:Video Summarization via Semantic Attended Networks
第5个title爬取耗时:1.33226秒
第6个title:TIMERS: Error-Bounded SVD Restart on Dynamic Networks
第6个title爬取耗时:1.52718秒
第7个title:Memory Management With Explicit Time in Resource-Bounded Agents
第7个title爬取耗时:1.35522秒
第8个title:Mitigating Overexposure in Viral Marketing
第8个title爬取耗时:1.35722秒
第9个title:Neural Link Prediction over Aligned Networks
第9个title爬取耗时:1.51317秒
第10个title:Dual Deep Neural Networks Cross-Modal Hashing
第10个title爬取耗时:1.30624秒
爬取总耗时:13.73324秒
可见,平均每请求完一个URL并解析该HTML耗时1.4秒左右。本次程序运行总耗时13.7秒。
二、测试基于协程的异步爬虫程序
下面,是使用了协程的异步爬虫程序。etree模块用于解析HTML,aiohttp是一个利用asyncio的库,它的API看起来很像请求的API,可以暂时看成协程版的requests。
import time
from lxml import etree
import aiohttp
import asyncio
urls = [
'https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16488',
'https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16583',
# 省略后面8个url...
]
titles = []
sem = asyncio.Semaphore(10) # 信号量,控制协程数,防止爬的过快
'''
提交请求获取AAAI网页,并解析HTML获取title
'''
async def get_title(url):
with(await sem):
# async with是异步上下文管理器
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session: # 获取session
async with session.request('GET', url) as resp: # 提出请求
# html_unicode = await resp.text()
# html = bytes(bytearray(html_unicode, encoding='utf-8'))
html = await resp.read() # 可直接获取bytes
title = etree.HTML(html).xpath('//*[@id="title"]/text()')
print(''.join(title))
'''
调用方
'''
def main():
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() # 获取事件循环
tasks = [get_title(url) for url in urls] # 把所有任务放到一个列表中
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks)) # 激活协程
loop.close() # 关闭事件循环
if __name__ == '__main__':
start = time.time()
main() # 调用方
print('总耗时:%.5f秒' % float(time.time()-start))
执行结果如下:
Memory Management With Explicit Time in Resource-Bounded Agents
Norm Conflict Resolution in Stochastic Domains
Video Summarization via Semantic Attended Networks
Tensorized Projection for High-Dimensional Binary Embedding
Algorithms for Trip-Vehicle Assignment in Ride-Sharing
Dual Deep Neural Networks Cross-Modal Hashing
Neural Link Prediction over Aligned Networks
Mitigating Overexposure in Viral Marketing
TIMERS: Error-Bounded SVD Restart on Dynamic Networks
Synthesis of Programs from Multimodal Datasets
总耗时:2.43371秒
可见,本次我们使用协程爬取10个URL只耗费了2.4秒,效率是普通同步程序的8~12倍。
【解释】:
request获取的text()返回的是网页的Unicode型数据,content和read()返回的是bytes型数据。而etree.HTML(html)接收的参数需是bytes类型,所以①可以通过resp.read()直接获取bytes;②若使用text()则需要通过先把Unicode类型数据转换成比特数组对象,再转换成比特对象, 即bytes(bytearray(html_unicode, encoding='utf-8'))。- 发起请求除了可以用上述
session.request('GET', url)也可以用session.get(url),功能相同。 - 如果同时做太多的请求,链接有可能会断掉。所以需要使用
sem = asyncio.Semaphore(10),Semaphore是限制同时工作的协同程序数量的同步工具。 async with是异步上下文管理器,不解的请看Python中的async with用法。
三、测试基于多进程的分布式爬虫程序
下面,我们测试多进程爬虫程序,由于我的电脑CPU是4核,所以这里进程池我就设的4。
import multiprocessing
from multiprocessing import Pool
import time
import requests
from lxml import etree
urls = [
'https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16488',
'https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16583',
# 省略后面8个url...
]
'''
提交请求获取AAAI网页,并解析HTML获取title
'''
def get_title(url,cnt):
response = requests.get(url) # 提交请求
html = response.content # 获取网页内容
title = etree.HTML(html).xpath('//*[@id="title"]/text()') # 由xpath解析HTML
print('第%d个title:%s' % (cnt,''.join(title)))
'''
调用方
'''
def main():
print('当前环境CPU核数是:%d核' % multiprocessing.cpu_count())
p = Pool(4) # 进程池
i = 0
for url in urls:
i += 1
p.apply_async(get_title, args=(url, i))
p.close()
p.join() # 运行完所有子进程才能顺序运行后续程序
if __name__ == '__main__':
start = time.time()
main() # 调用方
print('总耗时:%.5f秒' % float(time.time()-start))
执行结果:
当前环境CPU核数是:4核
第2个title:Algorithms for Trip-Vehicle Assignment in Ride-Sharing
第1个title:Norm Conflict Resolution in Stochastic Domains
第4个title:Synthesis of Programs from Multimodal Datasets
第3个title:Tensorized Projection for High-Dimensional Binary Embedding
第5个title:Video Summarization via Semantic Attended Networks
第6个title:TIMERS: Error-Bounded SVD Restart on Dynamic Networks
第7个title:Memory Management With Explicit Time in Resource-Bounded Agents
第8个title:Mitigating Overexposure in Viral Marketing
第9个title:Neural Link Prediction over Aligned Networks
第10个title:Dual Deep Neural Networks Cross-Modal Hashing
总耗时:5.01228秒
可见,多进程分布式爬虫也比普通同步程序要快很多,本次运行时间5秒。但比协程略慢。
【时间对比】:
对于上例中10个URL的爬取时间,下面整理成了表格。
| CPU核数\实现方式 | 普通同步爬虫 | 多进程爬虫 | 异步爬虫 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4核 | 13.7秒 | 5.0秒 | 2.4秒 |
其中增加多进程中进程池Pool(n)的n可加速爬虫,下图显示了消耗的时间(单位.秒)和Pool()参数的关系。
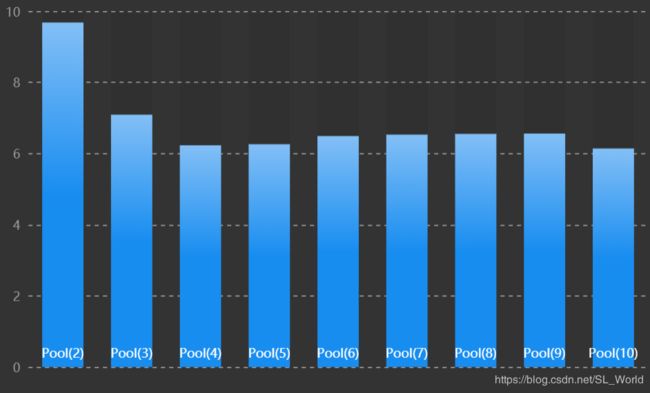
如果你以为到这里就结束了,那你就要错过最精彩的东西了:)
四、测试-异步结合多进程-爬虫程序
由于解析HTML也需要消耗一定的时间,而aiohttp和asyncio均未提供相关解析方法。所以可以在请求网页的时使用异步程序,在解析HTML使用多进程,两者配合使用,效率更高哦~!
【请求网页】:使用协程。
【解析HTML】:使用多进程。
from multiprocessing import Pool
import time
from lxml import etree
import aiohttp
import asyncio
urls = [
'https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16488',
'https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16583',
# 省略后面8个url...
]
htmls = []
titles = []
sem = asyncio.Semaphore(10) # 信号量,控制协程数,防止爬的过快
'''
提交请求获取AAAI网页html
'''
async def get_html(url):
with(await sem):
# async with是异步上下文管理器
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session: # 获取session
async with session.request('GET', url) as resp: # 提出请求
html = await resp.read() # 直接获取到bytes
htmls.append(html)
print('异步获取%s下的html.' % url)
'''
协程调用方,请求网页
'''
def main_get_html():
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() # 获取事件循环
tasks = [get_html(url) for url in urls] # 把所有任务放到一个列表中
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks)) # 激活协程
loop.close() # 关闭事件循环
'''
使用多进程解析html
'''
def multi_parse_html(html,cnt):
title = etree.HTML(html).xpath('//*[@id="title"]/text()')
titles.append(''.join(title))
print('第%d个html完成解析-title:%s' % (cnt,''.join(title)))
'''
多进程调用总函数,解析html
'''
def main_parse_html():
p = Pool(4)
i = 0
for html in htmls:
i += 1
p.apply_async(multi_parse_html,args=(html,i))
p.close()
p.join()
if __name__ == '__main__':
start = time.time()
main_get_html() # 调用方
main_parse_html() # 解析html
print('总耗时:%.5f秒' % float(time.time()-start))
执行结果如下:
异步获取https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16380下的html.
异步获取https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16674下的html.
异步获取https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16583下的html.
异步获取https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16911下的html.
异步获取https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/17343下的html.
异步获取https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16449下的html.
异步获取https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16488下的html.
异步获取https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16659下的html.
异步获取https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16581下的html.
异步获取https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/viewPaper/16112下的html.
第3个html完成解析-title:Algorithms for Trip-Vehicle Assignment in Ride-Sharing
第1个html完成解析-title:Tensorized Projection for High-Dimensional Binary Embedding
第2个html完成解析-title:TIMERS: Error-Bounded SVD Restart on Dynamic Networks
第4个html完成解析-title:Synthesis of Programs from Multimodal Datasets
第6个html完成解析-title:Dual Deep Neural Networks Cross-Modal Hashing
第7个html完成解析-title:Norm Conflict Resolution in Stochastic Domains
第8个html完成解析-title:Neural Link Prediction over Aligned Networks
第5个html完成解析-title:Mitigating Overexposure in Viral Marketing
第9个html完成解析-title:Video Summarization via Semantic Attended Networks
第10个html完成解析-title:Memory Management With Explicit Time in Resource-Bounded Agents
【参考文献】:
[1] aiohttp官方API文档
[2] 加速爬虫: 异步加载 Asyncio
[3] python:利用asyncio进行快速抓取
[4] 使用 aiohttp 和 asyncio 进行异步请求
[5] requests的content与text导致lxml的解析问题
