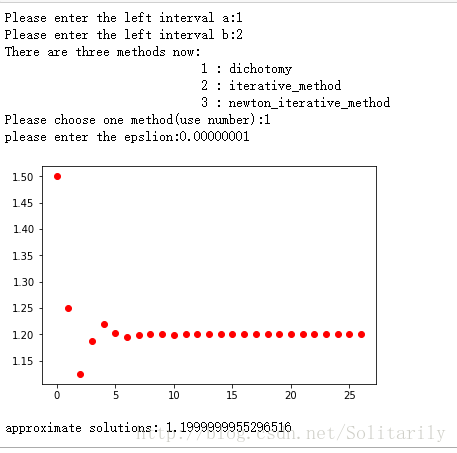
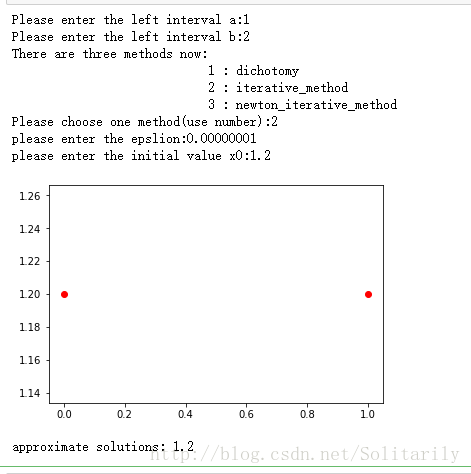
方程求根(二分法和牛顿迭代法)
一、实验内容
- 以方程:x3-0.2x2-0.2x-1.2=0为例,编写程序求方程的根
- 编写二分法、迭代法、牛顿法程序,分析运行结果
二、代码(python)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#计算原函数值
def compute_function_value(x):
return x**3-0.2*(x**2)-0.2*x-1.2
#计算迭代式的值
def compute_iteration_value(x):
return -0.05*(x**3)+0.01*(x**2)+1.01*x+0.06
#计算牛顿迭代式的值
def compute_newton_iteration_value(x):
return x-(x**3-0.2*(x**2)-0.2*x-1.2)/(3*(x**2)-0.4*x-0.2)
#用零点定理判断区间是否有根
def zero_theorem(x1,x2):
r=(compute_function_value(x1)*compute_function_value(x2))
if(r<=0):
return True
else:
return False
'''
二分法
a:左区间
b:右区间
cache_x:缓存每次迭代的x值
epslion:精度
'''
def dichotomy(a,b,cache_x,epslion):
k=1
while((b-a)>=epslion or k==1):
mid=(a+b)/2.0
cache_x.append(mid)
if(compute_function_value(mid)*compute_function_value(b)<0):
a=mid
else:
b=mid
k=k+1
return mid
'''
迭代法
x0:初值
cache_x:缓存每次迭代的x值
epslion:精度
'''
def iterative_method(x0,cache_x,epslion):
cache_x.append(x0) #缓存初值
x1=compute_iteration_value(x0) #计算迭代式的值并赋给x1
cache_x.append(x1) #缓存
#判断,不满足精度则循环
while(abs(x1-x0)>epslion):
x0=x1
x1=compute_iteration_value(x0)
cache_x.append(x1)
return x1 #返回最后结果
#牛顿迭代法
def newton_iterative_method(x0,cache_x,epslion):
cache_x.append(x0) #缓存初值
x1=compute_newton_iteration_value(x0) #计算牛顿迭代式的值并赋给x1
cache_x.append(x1) #缓存
#判断,不满足精度则循环
while(abs(x1-x0)>epslion):
x0=x1
x1=compute_newton_iteration_value(x0)
cache_x.append(x1)
return x1 #返回最后结果
#主控程序
def main():
cache_x=[] #保存x的每次的值,以便绘图
a=float(input("Please enter the left interval a:")) #输入左区间a
b=float(input("Please enter the left interval b:")) #输入右区间b
#有根情况
if(zero_theorem(a,b)):
#选择菜单
choose=int(input("There are three methods now: \n\
1 : dichotomy\n\
2 : iterative_method\n\
3 : newton_iterative_method\nPlease choose one method(use number):"))
epslion=float(input("please enter the epslion:")) #输入精度
#各种选择情况
if(choose==1):
x1=dichotomy(a,b,cache_x,epslion)
elif(choose==2):
x0=float(input("please enter the initial value x0:"))
x1=iterative_method(x0,cache_x,epslion)
else:
x0=float(input("please enter the initial value x0:"))
x1=newton_iterative_method(x0,cache_x,epslion)
#绘图
plt.plot(cache_x,'or')
plt.show()
print('approximate solutions:',x1)
else: #无根情况
print('The equation has no root in the interval')
if __name__=='__main__':
main()
三、实验结果
同一精度(0.00000001)下: