Service知识点全解析(二)——远程服务
上一章我们说了本地服务的相关知识点,本章我们一起学习下远程服务吧~
远程服务是什么?
远程服务一般适用于为其它应用程序提供公共服务的Service,这种Service即为系统常驻的Service(如:天气服务等)。
优点
1. 远程服务有自己的独立进程,不会受到其它进程的影响;
2. 可以被其它进程复用,提供公共服务;
3. 具有很高的灵活性。
缺点
1. 相对普通服务,占用系统资源较多,使用AIDL进行IPC也相对麻烦。
远程服务分为私有进程服务和公用进程服务。不过私有进程服务并没有什么实质上的作用,因为这只是在一个Activity里调用了同一个应用程序的不同进程的Service方法。而跨进程通信的真正意义是为了让应用之间数据共享,如共享远程服务Service的功能。
进程间通信名词解释
AIDL是AndroidInterface definition language的缩写,是Android接口定义语言。把Binder比作一个管道,AIDL则定义了该管道中传输数据的格式。
IPC:Inter-Process Communication,即跨进程通信。
Android系统四大组件Activity, Content Provider, Broadcast和Service均可以进行跨进程数据传输。
Activity可以隐式调用其他进程的Activity; ContentProvier可以跨进程访问其他应用中的数据;Broadcast通过广播的方式与其他应用进行通讯;Service则是通过Binder实现远程过程调用。
案例解析
案例:一个远程Service与另一个应用程序的组件(四大组件)进行跨进程通信。
服务器端(Service)
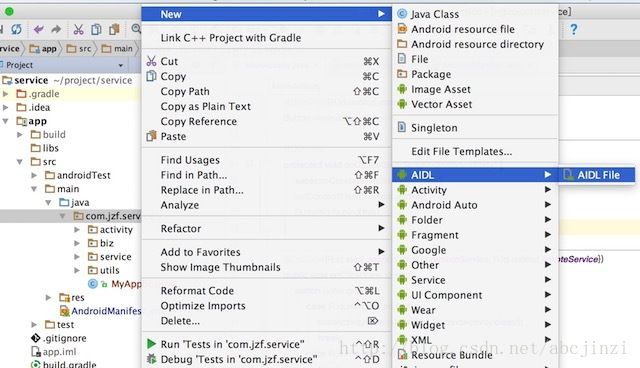
一. 创建AIDL文件,并在其中定义与客户端通信的内容(即方法),并编译(Make Project)。
在AIDL文件内,此例通过getDataFromAIDL建立通信(注意aidl支持的数据类型):
interface IMyAidlInterface {
int getDataFromAIDL(int count);
//AIDL中支持以下的数据类型
//1. 基本数据类型
//2. String 和CharSequence
//3. List 和 Map ,List和Map 对象的元素必须是AIDL支持的数据类型;
//4. AIDL自动生成的接口(需要导入-import)
//5. 实现android.os.Parcelable 接口的类(需要导入-import)
}二. 服务器端的service(即公用进程的服务):
public class SecondService extends Service {
private static String TAG = "SecondService";
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Log.d(TAG, "onBind");
return iMyAidlInterface;
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.d(TAG, "onStartCommand");
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
IMyAidlInterface.Stub iMyAidlInterface = new IMyAidlInterface.Stub() {
@Override
public int getDataFromAIDL(int count) throws RemoteException {
Log.d(TAG, "getDataFromAIDL=" + count);
count = count + 10;
return count;
}
};
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.d(TAG, "onDestroy");
}
}在此service里实现IMyAidlInterface接口,并在onBind()方法中将IMyAidlInterface.Stub的实现返回(Stub是Binder的子类)。
三,在AndroidManifest.xml中注册带有指定action的service。
...
".service.SecondService"
android:exported="true"
android:process=":remote">
//此处Intent的action必须写成“服务器端包名.aidl文件名”
"com.jzf.service.IMyAidlInterface"/>
...
这里服务端service已经配置完成。
客户端(Client)
一,开启新项目ClientApp
二,将服务端的AIDL文件所在的包复制到客户端目录下(Project/app/src/main),并进行编译。
注:记得要原封不动地复制!!什么都不要改!复制后如图:
看到了没,完全没动(还保持原项目的包名~)
三,客户端APP的activity内添加绑定事件
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements View.OnClickListener {
private static String TAG = "MainActivity";
private IMyAidlInterface iMyAidlInterface;//定义aidl接口变量
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
findViewById(R.id.get_service_data).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.ubind_service_data).setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.get_service_data:
Intent intent = new Intent("com.jzf.service.IMyAidlInterface");
intent.setPackage("com.jzf.service");
bindService(intent, serviceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
break;
case R.id.ubind_service_data:
unbindService(serviceConnection);
break;
}
}
ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
//1,使用iMyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface()方法获取服务器端返回的IBinder对象,并将IBinder对象转换成了iMyAidlInterface接口对象
iMyAidlInterface = IMyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(service);
try {
//2,通过该对象调用在iMyAidlInterface.aidl文件中定义的接口方法,从而实现跨进程通信
int count = iMyAidlInterface.getDataFromAIDL(9);
Log.d(TAG, "ClientApp内接收数据为=" + count);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
};
}远程服务进程间通信步骤
服务器端(Service)
1. 新建定义AIDL文件,并声明该服务需要向客户端提供的接口。
2. 在Service子类中实现AIDL中定义的接口方法,并定义生命周期的方法onBind()。
3. 在AndroidMainfest.xml中注册服务 & 声明为远程服务。
客户端(Client)
1. 拷贝服务端的AIDL文件到目录下。
2. 通过Intent指定服务端的服务名称和所在包,绑定远程Service(和本地服务的绑定同理)。
3. 使用Stub.asInterface接口获取服务器的Binder,根据需要调用服务提供的接口方法。
最后打印调用远程服务的方法后的log日志:
D/MainActivity: ClientApp内接收数据为=19远程服务里做了count = count + 10;——10+9=19。
服务器端(Service)源码下载
注:客户端(Client)的已经贴出来了,其他的按文档中步骤做即可实现。
下篇文章,我们一起学习IntentService~