语音识别之端点检测
在之前呢我们已经把portaudio平台搭好了,可以采集声音信号并播放了。那么接下来呢我们就来做一些实质性的东西——自适应端点检测。那么什么是自适应端点检测呢?也就是采集声音信号的时候,开始说话到说话结束,我们把这一段声音信号采集下来进行处理。不然那么多信号都去处理,没有声音也处理那就浪费了很多的空间以及浪费了CPU去做后续的操作。后面的功夫是省了,但是前面的工作就多了。天下可没有白费的午餐!接下来我就大概说一下我的做法吧。
1、基础
采样频率的设置:我们人耳一般可以听到的频率最高就是16000HZ。根据采样定理,一般采样频率要是这个的两倍才不会发生混叠。所以我们在通话的时候采样频率一般是8Khz,带宽就需要16Khz。这样就基本可以使得通话的体验非常到位,还原度非常高!不是说采样频率越高声音的效果就越好,这是一个trade-off。这一次我们采样就用16Khz,这样其实已经可以把基本的声音采下来。因为人耳对于低频还是更加敏感!现在的高保真就是44.1Khz的采样率。在经过量化(均匀量化和非均匀量化)就可以进行保存。怎么把采集到的信号进行数字化变成非均匀量化比如Mu律。请参考:
http://www.speech.cs.cmu.edu/comp.speech/Section2/Q2.7.html
声音采集时遇到的问题:在进行声音采集的时候有噪声,我们得小减小噪声的影响;以及还有回声。
声音采集的方式:直接对已有的声音(已经录制好的)进行处理;以及现场录制。这样的工具有:Windows recorder,Adobe audition,Linux的arecord。
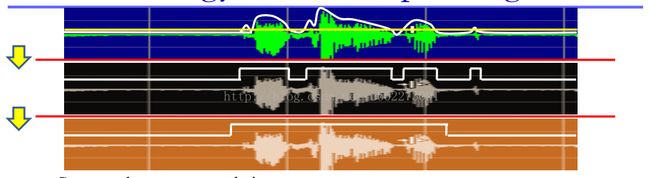
声音保存的方式:如下图。一般是PCM之后才好做进一步的处理。
声音采集时序考虑的参数:采样频率,量化方式,通道,存储。
声音采集时的两种模式:阻塞(自己设定时间,不管有没有数据都要回来)和回调(有有效的数据的时候才会调用这个函数返回数据),这两种在Portaudio里面都有对应的代码。在这里你大概也想到了我们应该使用的就是回调才能实现我们的功能。
语言处理的模式:Push和Pull。在这里的话,这两个东西正好和阻塞和回调差不多对应。
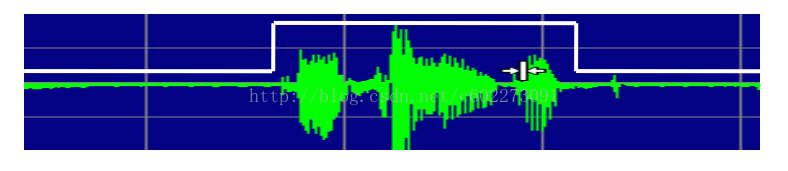
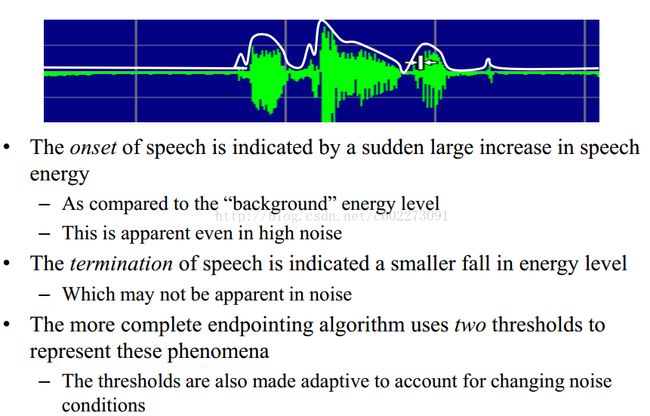
端点检测:实现效果如下图:一般来说人说话是突然说的,然后我们还要判断什么时候结束。
2、算法
具体实现的步骤如下图:
- 判别:计算每个时刻的能量,设定一个阈值k,如果大于它,我们认为是1(1表示该点是语言),否则就是0。能量计算的公式就是:

- 平滑:小于100ms的silien我们认为是语音的部分,大于250ms的语言我们才认为是语言。在截取的语音信号前后多截出250ms。这个的前提是比较安静,如果不安静的话那么就得另当别论,看外界影响有多大。
- 算法一:先来一个比较简单的算法
- 算法二:更复杂一些的算法
3、代码
捕获声音信号并转化:
#include
#include
#include //function log
#include //kbhit()
#include "portaudio.h"
#include "readwave.h" //WriteWave()
/* #define SAMPLE_RATE (17932) // Test failure to open with this value. */
//SAMPLE_RATE, FRAMES_PER_BUFFER, NUM_SECONDS, NUM_CHANNELS are modified by Yao Canwu
#define SAMPLE_RATE (16000)
#define FRAMES_PER_BUFFER (400)
#define NUM_SECONDS (60)
#define NUM_CHANNELS (1)
/* #define DITHER_FLAG (paDitherOff) */
#define DITHER_FLAG (0) /**/
/** Set to 1 if you want to capture the recording to a file. */
#define WRITE_TO_FILE (0)
/* Select sample format. */
#if 0
#define PA_SAMPLE_TYPE paFloat32
typedef float SAMPLE;
#define SAMPLE_SILENCE (0.0f)
#define PRINTF_S_FORMAT "%.8f"
#elif 1
#define PA_SAMPLE_TYPE paInt16
typedef short SAMPLE;
#define SAMPLE_SILENCE (0)
#define PRINTF_S_FORMAT "%d"
#elif 0
#define PA_SAMPLE_TYPE paInt8
typedef char SAMPLE;
#define SAMPLE_SILENCE (0)
#define PRINTF_S_FORMAT "%d"
#else
#define PA_SAMPLE_TYPE paUInt8
typedef unsigned char SAMPLE;
#define SAMPLE_SILENCE (128)
#define PRINTF_S_FORMAT "%d"
#endif
typedef struct
{
int frameIndex; /* Index into sample array. */
int maxFrameIndex;
SAMPLE *recordedSamples;
}
paTestData;
//calculate the energy in decibe of a frame segment
//added by Yao Canwu
float energyPerSampleInDecibe(const SAMPLE *ptr)
{
float energy = 0.0f;
SAMPLE temp;
for (unsigned long i = 0; i threshold) isSpeech = true;
return isSpeech;
}
/* This routine will be called by the PortAudio engine when audio is needed.
** It may be called at interrupt level on some machines so don't do anything
** that could mess up the system like calling malloc() or free().
*/
static int recordCallback(const void *inputBuffer, void *outputBuffer,
unsigned long framesPerBuffer,
const PaStreamCallbackTimeInfo* timeInfo,
PaStreamCallbackFlags statusFlags,
void *userData)
{
paTestData *data = (paTestData*)userData;
const SAMPLE *rptr = (const SAMPLE*)inputBuffer;
SAMPLE *wptr = &data->recordedSamples[data->frameIndex * NUM_CHANNELS];
long framesToCalc;
long i;
int finished;
unsigned long framesLeft = data->maxFrameIndex - data->frameIndex;
(void)outputBuffer; /* Prevent unused variable warnings. */
(void)timeInfo;
(void)statusFlags;
(void)userData;
if (framesLeft < framesPerBuffer)
{
framesToCalc = framesLeft;
finished = paComplete;
}
else
{
framesToCalc = framesPerBuffer;
finished = paContinue;
}
if (inputBuffer == NULL)
{
for (i = 0; iframeIndex += framesToCalc;
/* calculate the initial background and initial level,
** which will be used for classify frame
** Added by Yao Canwu
*/
if (data->frameIndex == 0)
{
level = energyPerSampleInDecibe(&data->recordedSamples[0]);
background = 0.0f;
SAMPLE temp;
for (i = 0; i < 10 * framesPerBuffer; i++)
{
temp = data->recordedSamples[i];
background += temp * temp;
}
background = log(background);
}
//Silence in 4 seconds means the end of audio capture
if (classifyFrame(rptr)) count = 0;
else count++;
//printf("count = %d\n", count);
if (count >= 80) data->maxFrameIndex = data->frameIndex;
return finished;
}
/* This routine will be called by the PortAudio engine when audio is needed.
** It may be called at interrupt level on some machines so don't do anything
** that could mess up the system like calling malloc() or free().
*/
static int playCallback(const void *inputBuffer, void *outputBuffer,
unsigned long framesPerBuffer,
const PaStreamCallbackTimeInfo* timeInfo,
PaStreamCallbackFlags statusFlags,
void *userData)
{
paTestData *data = (paTestData*)userData;
SAMPLE *rptr = &data->recordedSamples[data->frameIndex * NUM_CHANNELS];
SAMPLE *wptr = (SAMPLE*)outputBuffer;
unsigned int i;
int finished;
unsigned int framesLeft = data->maxFrameIndex - data->frameIndex;
(void)inputBuffer; /* Prevent unused variable warnings. */
(void)timeInfo;
(void)statusFlags;
(void)userData;
if (framesLeft < framesPerBuffer)
{
/* final buffer... */
for (i = 0; iframeIndex += framesLeft;
finished = paComplete;
}
else
{
for (i = 0; iframeIndex += framesPerBuffer;
finished = paContinue;
}
return finished;
}
/*******************************************************************/
int main(void)
{
PaStreamParameters inputParameters,
outputParameters;
PaStream* stream;
PaError err = paNoError;
paTestData data;
int i;
int totalFrames;
int numSamples;
int numBytes;
SAMPLE max, val;
double average;
printf("patest_record.c\n"); fflush(stdout);
data.maxFrameIndex = totalFrames = NUM_SECONDS * SAMPLE_RATE; /* Record for a few seconds. */
data.frameIndex = 0;
numSamples = totalFrames * NUM_CHANNELS;
numBytes = numSamples * sizeof(SAMPLE);
data.recordedSamples = (SAMPLE *)malloc(numBytes); /* From now on, recordedSamples is initialised. */
if (data.recordedSamples == NULL)
{
printf("Could not allocate record array.\n");
goto done;
}
for (i = 0; idefaultLowInputLatency;
inputParameters.hostApiSpecificStreamInfo = NULL;
//set a keyboard hit to start recording. Added by Yao Canwu
printf("Press any key to start recording\n");
while (!kbhit()){}
/* Record some audio. -------------------------------------------- */
err = Pa_OpenStream(
&stream,
&inputParameters,
NULL, /* &outputParameters, */
SAMPLE_RATE,
FRAMES_PER_BUFFER,
paClipOff, /* we won't output out of range samples so don't bother clipping them */
recordCallback,
&data);
if (err != paNoError) goto done;
err = Pa_StartStream(stream);
if (err != paNoError) goto done;
printf("\n=== Now start recording!!\n"); fflush(stdout);
/* Pa_IsStreamActive: Determine whether the stream is active. A stream
is active after a successful call to Pa_StartStream(), until it becomes
inactive either as a result of a call to Pa_StopStream() or Pa_AbortStream(),
or as a result of a return value other than paContinue from the stream callback.
In the latter case, the stream is considered inactive after the last buffer has finished playing. */
while ((err = Pa_IsStreamActive(stream)) == 1)
{
Pa_Sleep(1000);
printf("index = %d\n", data.frameIndex); fflush(stdout);
}
if (err < 0) goto done;
err = Pa_CloseStream(stream);
if (err != paNoError) goto done;
//Write wave to file in wav formate. Added by Yao Canwu
printf("Waiting to save into file...\n");
char *path = "audio.wav";
WriteWave(path, data.recordedSamples, data.maxFrameIndex, SAMPLE_RATE);
printf("Save successfully!\n");
/* Write recorded data to a file. */
#if WRITE_TO_FILE
{
FILE *fid;
fid = fopen("recorded.raw", "wb");
if (fid == NULL)
{
printf("Could not open file.");
}
else
{
fwrite(data.recordedSamples, NUM_CHANNELS * sizeof(SAMPLE), totalFrames, fid);
fclose(fid);
printf("Wrote data to 'recorded.raw'\n");
}
}
#endif
/* Playback recorded data. -------------------------------------------- */
data.frameIndex = 0;
outputParameters.device = Pa_GetDefaultOutputDevice(); /* default output device */
if (outputParameters.device == paNoDevice) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: No default output device.\n");
goto done;
}
outputParameters.channelCount = 1; /* stereo output */
outputParameters.sampleFormat = PA_SAMPLE_TYPE;
outputParameters.suggestedLatency = Pa_GetDeviceInfo(outputParameters.device)->defaultLowOutputLatency;
outputParameters.hostApiSpecificStreamInfo = NULL;
printf("\n=== Now playing back. ===\n"); fflush(stdout);
err = Pa_OpenStream(
&stream,
NULL, /* no input */
&outputParameters,
SAMPLE_RATE,
FRAMES_PER_BUFFER,
paClipOff, /* we won't output out of range samples so don't bother clipping them */
playCallback,
&data);
if (err != paNoError) goto done;
if (stream)
{
err = Pa_StartStream(stream);
if (err != paNoError) goto done;
printf("Waiting for playback to finish.\n"); fflush(stdout);
while ((err = Pa_IsStreamActive(stream)) == 1) Pa_Sleep(100);
if (err < 0) goto done;
err = Pa_CloseStream(stream);
if (err != paNoError) goto done;
printf("Done.\n"); fflush(stdout);
}
done:
Pa_Terminate();
if (data.recordedSamples) /* Sure it is NULL or valid. */
free(data.recordedSamples);
if (err != paNoError)
{
fprintf(stderr, "An error occured while using the portaudio stream\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Error number: %d\n", err);
fprintf(stderr, "Error message: %s\n", Pa_GetErrorText(err));
err = 1; /* Always return 0 or 1, but no other return codes. */
}
system("pause");
return err;
}
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "readwave.h"
bool WaveRewind(FILE *wav_file, WavFileHead *wavFileHead)
{
char riff[8],wavefmt[8];
short i;
rewind(wav_file);
fread(wavFileHead,sizeof(struct WavFileHead),1,wav_file);
for ( i=0;i<8;i++ )
{
riff[i]=wavFileHead->RIFF[i];
wavefmt[i]=wavFileHead->WAVEfmt_[i];
}
riff[4]='\0';
wavefmt[7]='\0';
if ( strcmp(riff,"RIFF")==0 && strcmp(wavefmt,"WAVEfmt")==0 )
return true; // It is WAV file.
else
{
rewind(wav_file);
return(false);
}
}
short *ReadWave(const char *wavFile, int *numSamples, int *sampleRate )
{
FILE *wavFp;
WavFileHead wavHead;
short *waveData;
long numRead;
wavFp = fopen(wavFile, "rb");
if (!wavFp)
{
printf("\nERROR:can't open %s!\n", wavFile);
exit(0);
}
if (WaveRewind(wavFp, &wavHead) == false)
{
printf("\nERROR:%s is not a Windows wave file!\n", wavFile);
exit(0);
}
waveData = new short [wavHead.RawDataFileLength/sizeof(short)];
numRead = fread(waveData, sizeof(short), wavHead.RawDataFileLength / 2, wavFp);
assert(numRead * sizeof(short) == (unsigned long)wavHead.RawDataFileLength);
fclose(wavFp);
*numSamples = wavHead.RawDataFileLength/sizeof(short);
*sampleRate = wavHead.SampleRate;
return waveData;
}
void FillWaveHeader(void *buffer, int raw_wave_len, int sampleRate)
{
WavFileHead wavHead;
strcpy(wavHead.RIFF, "RIFF");
strcpy(wavHead.WAVEfmt_, "WAVEfmt ");
wavHead.FileLength = raw_wave_len + 36;
wavHead.noUse = 16;
wavHead.FormatCategory = 1;
wavHead.NChannels = 1;
wavHead.SampleRate = sampleRate;
wavHead.SampleBytes = sampleRate*2;
wavHead.BytesPerSample = 2;
wavHead.NBitsPersample = 16;
strcpy(wavHead.data, "data");
wavHead.RawDataFileLength = raw_wave_len;
memcpy(buffer, &wavHead, sizeof(WavFileHead));
}
void WriteWave(const char *wavFile, short *waveData, int numSamples, int sampleRate)
{
FILE *wavFp;
WavFileHead wavHead;
long numWrite;
wavFp = fopen(wavFile, "wb");
if (!wavFp)
{
printf("\nERROR:can't open %s!\n", wavFile);
exit(0);
}
FillWaveHeader(&wavHead, numSamples*sizeof(short), sampleRate);
fwrite(&wavHead, sizeof(WavFileHead), 1, wavFp);
numWrite = fwrite(waveData, sizeof(short), numSamples, wavFp);
assert(numWrite == numSamples);
fclose(wavFp);
}
void GetWavHeader(const char *wavFile, short *Bits, int *Rate,
short *Format, int *Length, short *Channels)
{
FILE *wavFp;
WavFileHead wavHead;
char *waveData;
long numRead,File_length;
wavFp = fopen(wavFile, "rb");
if (!wavFp)
{
printf("\nERROR:can't open %s!\n", wavFile);
exit(0);
}
fseek(wavFp,0,SEEK_END);
File_length=ftell(wavFp);
if (WaveRewind(wavFp, &wavHead) == false)
{
printf("\nERROR:%s is not a Windows wave file!\n", wavFile);
exit(0);
}
waveData = new char[(File_length-sizeof(struct WavFileHead))/sizeof(char)];
numRead = fread(waveData, sizeof(char), File_length-sizeof(struct WavFileHead), wavFp);
fclose(wavFp);
*Bits = wavHead.NBitsPersample;
*Format = wavHead.FormatCategory;
*Rate = wavHead.SampleRate;
*Length = (int)numRead;
*Channels = wavHead.NChannels;
delete [] waveData;
}
short *ReadWavFile(const char *wavFile, int *numSamples, int *sampleRate )
{
FILE *wavFp;
WavFileHead wavHead;
short *waveData;
long numRead,File_length;
wavFp = fopen(wavFile, "rb");
if (!wavFp)
{
printf("\nERROR:can't open %s!\n", wavFile);
exit(0);
}
fseek(wavFp,0,SEEK_END);
File_length=ftell(wavFp);
if (WaveRewind(wavFp, &wavHead) == false)
{
printf("\nERROR:%s is not a Windows wave file!\n", wavFile);
exit(0);
}
waveData = new short [(File_length-sizeof(struct WavFileHead))/sizeof(short)];
numRead = fread(waveData, sizeof(short), (File_length-sizeof(struct WavFileHead))/sizeof(short), wavFp);
fclose(wavFp);
*numSamples = (int)numRead;
*sampleRate = wavHead.SampleRate;
return waveData;
}
void ReadWav(const char *wavFile, short *waveData, int *numSamples, int *sampleRate)
{
FILE *wavFp;
WavFileHead wavHead;
long numRead;
wavFp = fopen(wavFile, "rb");
if (!wavFp)
{
printf("\nERROR:can't open %s!\n", wavFile);
exit(0);
}
if (WaveRewind(wavFp, &wavHead) == false)
{
printf("\nERROR:%s is not a Windows PCM file!\n", wavFile);
exit(0);
}
numRead = fread(waveData, sizeof(short), wavHead.RawDataFileLength/2, wavFp);
assert(numRead*sizeof(short) == (unsigned long)wavHead.RawDataFileLength);
fclose(wavFp);
*numSamples = wavHead.RawDataFileLength/sizeof(short);
*sampleRate = wavHead.SampleRate;
} 特别说明:以上截图来自于CMU的李明老师的上课PPT。