TX-LCN分布式事务框架源码解析(基于lcn模式下的异常流程源码分析)
前一篇文章我们讲了lcn模式下的正常流程是如何运作的。这篇讲下在发生异常时框架是怎么进行回滚的,同样调用链还是A>B>C
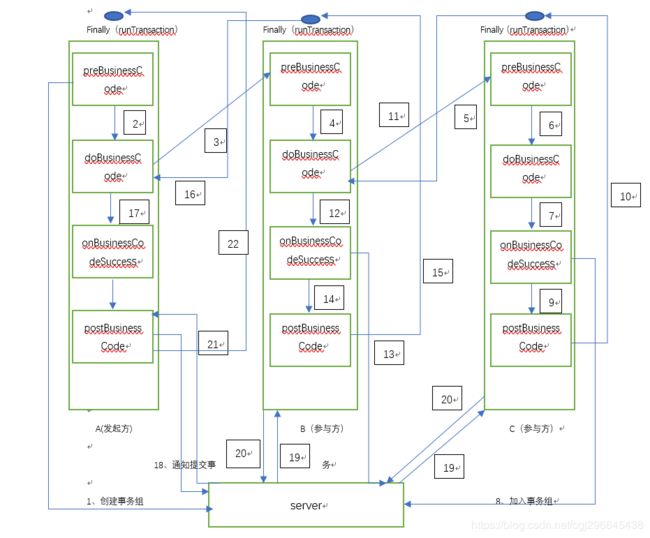
正常流程图是这样的,前一个模块的doBusinessCode执行的是后一个模块的所有逻辑。我们从后向前看
C模块的所有的代码执行都在B模块的doBusinessCode方法中。B模块的代码执行都在A模块的doBusinessCode方法中。
C模块
C模块业务代码如下(B模块此代码相同处理类相同。)
1、此方法会抛出Throwable 类型的异常
2、此方法会catch住两种异常TransactionException 与 Throwable 异常,并抛出。
public Object transactionRunning(TxTransactionInfo info) throws Throwable {
// 1. 获取事务类型
String transactionType = info.getTransactionType();
// 2. 获取事务传播状态
DTXPropagationState propagationState = propagationResolver.resolvePropagationState(info);
// 2.1 如果不参与分布式事务立即终止
if (propagationState.isIgnored()) {
return info.getBusinessCallback().call();
}
// 3. 获取本地分布式事务控制器
DTXLocalControl dtxLocalControl = txLcnBeanHelper.loadDTXLocalControl(transactionType, propagationState);
// 4. 织入事务操作
try {
// 4.1 记录事务类型到事务上下文
Set transactionTypeSet = globalContext.txContext(info.getGroupId()).getTransactionTypes();
transactionTypeSet.add(transactionType);
dtxLocalControl.preBusinessCode(info);
// 4.2 业务执行前
txLogger.txTrace(
info.getGroupId(), info.getUnitId(), "pre business code, unit type: {}", transactionType);
// 4.3 执行业务
Object result = dtxLocalControl.doBusinessCode(info);
// 4.4 业务执行成功
txLogger.txTrace(info.getGroupId(), info.getUnitId(), "business success");
dtxLocalControl.onBusinessCodeSuccess(info, result);
return result;
} catch (TransactionException e) {
txLogger.error(info.getGroupId(), info.getUnitId(), "before business code error");
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
// 4.5 业务执行失败
txLogger.error(info.getGroupId(), info.getUnitId(), Transactions.TAG_TRANSACTION,
"business code error");
dtxLocalControl.onBusinessCodeError(info, e);
throw e;
} finally {
// 4.6 业务执行完毕
dtxLocalControl.postBusinessCode(info);
}
} C模块由于是最后一个模块不再去调用其他接口,它的doBusinessCode只是执行本地数据库操作,此doBusinessCode方法会抛出Throwable异常,如果C模块的本地数据库操作失败报错,则会被catch住去执行下面代码
catch (Throwable e) {
// 4.5 业务执行失败
txLogger.error(info.getGroupId(), info.getUnitId(), Transactions.TAG_TRANSACTION,
"business code error");
dtxLocalControl.onBusinessCodeError(info, e);
throw e;
}public void onBusinessCodeError(TxTransactionInfo info, Throwable throwable) {
try {
//清理事务,即回滚本地数据库连接
transactionCleanTemplate.clean(info.getGroupId(), info.getUnitId(), info.getTransactionType(), 0);
} catch (TransactionClearException e) {
log.error("{} > clean transaction error." , Transactions.LCN);
}
}如果本地数据库操作成功,C模块会去joinGroup加入事务组。(异步检测也是处理异常的,后面再讲)
public void joinGroup(String groupId, String unitId, String transactionType, TransactionInfo transactionInfo)
throws TransactionException {
try {
txLogger.txTrace(groupId, unitId, "join group > transaction type: {}", transactionType);
reliableMessenger.joinGroup(groupId, unitId, transactionType, DTXLocalContext.transactionState(globalContext.dtxState(groupId)));
txLogger.txTrace(groupId, unitId, "join group message over.");
// 异步检测
dtxChecking.startDelayCheckingAsync(groupId, unitId, transactionType);
// 缓存参与方切面信息
aspectLogger.trace(groupId, unitId, transactionInfo);
} catch (RpcException e) {
dtxExceptionHandler.handleJoinGroupMessageException(Arrays.asList(groupId, unitId, transactionType), e);
} catch (LcnBusinessException e) {
dtxExceptionHandler.handleJoinGroupBusinessException(Arrays.asList(groupId, unitId, transactionType), e);
}
txLogger.txTrace(groupId, unitId, "join group logic over");
}public void joinGroup(String groupId, String unitId, String unitType, int transactionState) throws RpcException, LcnBusinessException {
JoinGroupParams joinGroupParams = new JoinGroupParams();
joinGroupParams.setGroupId(groupId);
joinGroupParams.setUnitId(unitId);
joinGroupParams.setUnitType(unitType);
joinGroupParams.setTransactionState(transactionState);
MessageDto messageDto = request(MessageCreator.joinGroup(joinGroupParams));
//加入事务组失败,抛出异常
if (!MessageUtils.statusOk(messageDto)) {
throw new LcnBusinessException(messageDto.loadBean(Throwable.class));
}
}这里会catch异常一个是RpcException 异常即和服务端连接不成功,第二个是LcnBusinessException 异常这个异常是在加入事务组失败的情况下抛出的。
对于RpcException异常框架的处理是直接抛出
public void handleJoinGroupMessageException(Object params, Throwable ex) throws TransactionException {
throw new TransactionException(ex);
}对于LcnBusinessException异常是先清理本地事务,回滚连接然后抛出异常
public void handleJoinGroupBusinessException(Object params, Throwable ex) throws TransactionException {
List paramList = (List) params;
String groupId = (String) paramList.get(0);
String unitId = (String) paramList.get(1);
String unitType = (String) paramList.get(2);
try {
transactionCleanTemplate.clean(groupId, unitId, unitType, 0);
} catch (TransactionClearException e) {
txLogger.error(groupId, unitId, "join group", "clean [{}]transaction fail.", unitType);
}
throw new TransactionException(ex);
}总结下C模块
1、本地数据库操作异常和加入事务组失败会进行本地数据库连接回滚
2、针对于在加入事务组时和服务端连接、通信失败是直接抛出异常的(基本不可能除非所有的服务端都不可用)
3、只要C模块出现异常都会向B模块抛出Throwable
B模块
B模块和C模块代码一模一样,只是B模块的doBussinessCode是所有的C模块流程与本地操作。
上面说过C模块只要出错或者本地数据库操作失败,都会被B模块的catch Throwable 所捕获到,处理逻辑和C模块一样清理本地事务,回滚连接。
也和C模块同样会启动异步检测程序,会有RpcException与LcnBusinessException处理也和C模块一致。
A模块
A模块会先进行创建事务组,但是由于业务是在之后执行的,则创建事务组只是做抛出异常。A模块catch住后都没有做其他的操作。
A模块的异常处理都放在postBusinessCode方法中。
public void notifyGroup(String groupId, String unitId, String transactionType, int state) {
try {
txLogger.txTrace(
groupId, unitId, "notify group > transaction type: {}, state: {}.", transactionType, state);
if (globalContext.isDTXTimeout()) {
throw new LcnBusinessException("dtx timeout.");
}
state = reliableMessenger.notifyGroup(groupId, state);
transactionCleanTemplate.clean(groupId, unitId, transactionType, state);
} catch (TransactionClearException e) {
txLogger.trace(groupId, unitId, Transactions.TE, "clean transaction fail.");
} catch (RpcException e) {
dtxExceptionHandler.handleNotifyGroupMessageException(Arrays.asList(groupId, state, unitId, transactionType), e);
} catch (LcnBusinessException e) {
// 关闭事务组失败
dtxExceptionHandler.handleNotifyGroupBusinessException(Arrays.asList(groupId, state, unitId, transactionType), e.getCause());
}
txLogger.txTrace(groupId, unitId, "notify group exception state {}.", state);
}我们按情况来说
1、如果A、B、C模块都正确执行,这时notifyGroup方法的state参数为1,如果调用服务端通知清理事务连接有问题或者网络不通(请求异常) reliableMessenger.notifyGroup方法抛出RpcException 异常执行catch逻辑
catch (RpcException e) {
dtxExceptionHandler.handleNotifyGroupMessageException(Arrays.asList(groupId, state, unitId, transactionType), e);
}public void handleNotifyGroupMessageException(Object params, Throwable ex) {
// 当0 时候
List paramList = (List) params;
String groupId = (String) paramList.get(0);
int state = (int) paramList.get(1);
if (state == 0) {
handleNotifyGroupBusinessException(params, ex);
return;
}
//1的情况
String unitId = (String) paramList.get(2);
String transactionType = (String) paramList.get(3);
try {
//清理本地事务
transactionCleanTemplate.cleanWithoutAspectLog(groupId, unitId, transactionType, state);
} catch (TransactionClearException e) {
txLogger.error(groupId, unitId, "notify group", "{} > cleanWithoutAspectLog transaction error.", transactionType);
}
// 上报Manager,上报直到成功.
tmReporter.reportTransactionState(groupId, null, TxExceptionParams.NOTIFY_GROUP_ERROR, state);
}private MessageDto request(MessageDto messageDto, long timeout, String whenNonManagerMessage) throws RpcException {
for (int i = 0; i < rpcClient.loadAllRemoteKey().size() + 1; i++) {
try {
String remoteKey = rpcClient.loadRemoteKey();
MessageDto result = rpcClient.request(remoteKey, messageDto, timeout);
log.debug("request action: {}. TM[{}]", messageDto.getAction(), remoteKey);
return result;
} catch (RpcException e) {
if (e.getCode() == RpcException.NON_TX_MANAGER) {
throw new RpcException(e.getCode(), whenNonManagerMessage + ". non tx-manager is alive.");
}
}
}
throw new RpcException(RpcException.NON_TX_MANAGER, whenNonManagerMessage + ". non tx-manager is alive.");
}会先提交本地事务(状态为1),然后会和服务端通信进行记录事务状态,可能有人会问你这都请求不到服务端,这里怎么会通信成功呢?我们都知道实际上我们的服务端部署多台,分布式事务只是选取一台来操作事务,如果其中一台不能正常工作,会选择其他服务器。上面的request方法就是根据此客户端连接的所有的服务端进行通信。
服务端接收到状态为1的消息后,会在t_tx_exception表中插入一条数据,state值为1表示要提交事务。但是这里A模块提交了本地事务了,B、C模块还没提交这是怎么搞的?
还记得前面提到的异步检测程序吗?
// 异步检测
dtxChecking.startDelayCheckingAsync(groupId, unitId, transactionType);public void startDelayCheckingAsync(String groupId, String unitId, String transactionType) {
txLogger.taskTrace(groupId, unitId, "start delay checking task");
ScheduledFuture scheduledFuture = scheduledExecutorService.schedule(() -> {
try {
TxContext txContext = globalContext.txContext(groupId);
if (Objects.nonNull(txContext)) {
synchronized (txContext.getLock()) {
txLogger.taskTrace(groupId, unitId, "checking waiting for business code finish.");
txContext.getLock().wait();
}
}
int state = reliableMessenger.askTransactionState(groupId, unitId);
txLogger.taskTrace(groupId, unitId, "ask transaction state {}", state);
if (state == -1) {
txLogger.error(this.getClass().getSimpleName(), "delay clean transaction error.");
onAskTransactionStateException(groupId, unitId, transactionType);
} else {
transactionCleanTemplate.clean(groupId, unitId, transactionType, state);
aspectLogger.clearLog(groupId, unitId);
}
} catch (RpcException e) {
onAskTransactionStateException(groupId, unitId, transactionType);
} catch (TransactionClearException | InterruptedException e) {
txLogger.error(this.getClass().getSimpleName(), "{} clean transaction error.", transactionType);
}
}, clientConfig.getDtxTime(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
delayTasks.put(groupId + unitId, scheduledFuture);
}这个定时任务会按周期性的去调用服务端查询t_tx_exception中的state信息,然后按照state进行提交事务或者回滚事务(这里是提交)。mysql绝对可用。
如果发生业务异常LcnBusinessException,表示服务端在通知B、C客户端提交事务失败,同样服务端会写表t_tx_exception的state为1(提交事务),然后A客户端也提交事务
2、如果C模块报错则,C、B模块已回滚。这种情况下无论是什么异常只要A模块回滚即可。
请求异常回滚
//请求异常回滚
public void handleNotifyGroupMessageException(Object params, Throwable ex) {
// 当0 时候
List paramList = (List) params;
String groupId = (String) paramList.get(0);
int state = (int) paramList.get(1);
if (state == 0) {
handleNotifyGroupBusinessException(params, ex);
return;
}public void handleNotifyGroupBusinessException(Object params, Throwable ex) {
List paramList = (List) params;
String groupId = (String) paramList.get(0);
int state = (int) paramList.get(1);
String unitId = (String) paramList.get(2);
String transactionType = (String) paramList.get(3);
//用户强制回滚.
if (ex instanceof UserRollbackException) {
state = 0;
}
if ((ex.getCause() != null && ex.getCause() instanceof UserRollbackException)) {
state = 0;
}
// 结束事务
try {
transactionCleanTemplate.clean(groupId, unitId, transactionType, state);
} catch (TransactionClearException e) {
txLogger.error(groupId, unitId, "notify group", "{} > clean transaction error.", transactionType);
}
}事务异常回滚
public void handleNotifyGroupBusinessException(Object params, Throwable ex) {
List paramList = (List) params;
String groupId = (String) paramList.get(0);
int state = (int) paramList.get(1);
String unitId = (String) paramList.get(2);
String transactionType = (String) paramList.get(3);
//用户强制回滚.
if (ex instanceof UserRollbackException) {
state = 0;
}
if ((ex.getCause() != null && ex.getCause() instanceof UserRollbackException)) {
state = 0;
}
// 结束事务
try {
transactionCleanTemplate.clean(groupId, unitId, transactionType, state);
} catch (TransactionClearException e) {
txLogger.error(groupId, unitId, "notify group", "{} > clean transaction error.", transactionType);
}
}3、如果B或C模块异常则只能通过通知B、C进行回滚,如果通知失败则失败,靠客户端A无法处理。
注:由于服务端是高可用上述的一些异常基本不存在