linux kernel 配置与编译
linux内核的配置与编译过程
选择九鼎s5pv210开发板移植的Linux内核,下载地址为:
链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1sl15QMD 密码:by3o
1.首先检查Makefile
查看Makefile主要看一下Makefile中的两个变量:ARCH与CROSS_COMPILE;
(1)主要是检查交叉编译工具链有没有设置对。
CROSS_COMPILE ?= /usr/local/arm/arm-2009q3/bin/arm-none-linux-gnueabi-
(2)确认ARCH = arm。主要目的是为了编译时能找到arch/arm目录。
2.配置过程
(1)配置主要通过两步进行:
第一步,make xx_defconfig,在九鼎x210开发板中是make x210ii_qt_defconfig,如果在配置信息最后一行看到configuration written to .config这句,表明把所有的配置选项都写到.config文件中。
第二步,make menuconfig,在这个图形界面进行配置。
(2)make xx_defconfig和make menuconfig相配合
make xxx_defconfig这一步其实是参考别人已经做好的,这样做有很多好处:减少很多工作量,避开了很多自己不懂的配置项(譬如对内存管理的、调度系统的等模块的配置项),我们只用管自己需要管的。
其实make x210ii_qt_defconfig就相当于:cp arch/arm/configs/x210ii_qt_defconfig .config
在arch/arm/configs目录下有很多xxx_defconfig,这些文件都是别人手工配置好适合一定的开发板的.config文件后自己把.config文件保存过去的
make menuconfig其实就是读取第一步得到的.config,然后给我们一个图形化的界面,让我们可以更加容易的找到自己想要修改的配置项,然后更改配置。
(3)make menuconfig注意事项
执行之后的图形界面如图所示:
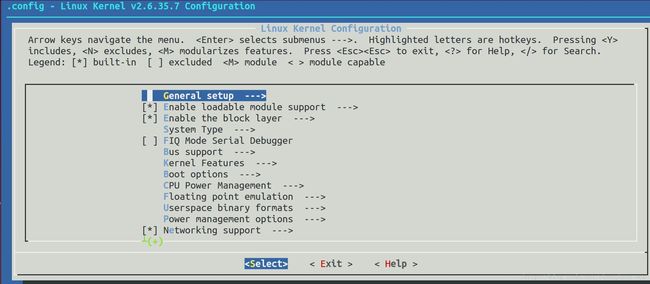
1.用法:
箭头按键导航整个菜单;
回车按键选择子菜单(注意选项后面有 —>的选项才是有子菜单的,没有这个标识的没有子菜单);
高亮的字母是热键(快捷键);
键盘按键Y、N、M三个按键的作用分别是将选中模块编入、去除、模块化,在menuconfig中选项前面的括号里,*表示编入,空白表示去除,M表示模块化;
双击ESC表示退出;
按下”?“按键可以显示帮助信息;
按下”/“按键可以输入搜索内容来全局搜索信息(类似于vi中的搜索);
[]不可以模块化,<>的才可以模块化。
2.menuconfig的工作原理
a. menuconfig显示的菜单内容是由内核源码树各个目录下的Kconfig文件来支持的。Kconfig文件中按照一定的格式包含了一个又一个的配置项,每一个配置项在make menuconfig中都会成为一个菜单项目。而且menuconfig中显示的菜单目录结构和源码目录中的Kconfig的目录结构是一样的。在相应的Kconfig文件中删除一个config项,则再次make menuconfig时这个项目已经看不到了。
b. menuconfig读取/写入.config文件
menuconfig的菜单内容来自于Kconfig文件,但是每一个菜单的选择结果(Y、N、M)却不是保存在Kconfig文件中的。Kconfig文件是不变的,Kconfig文件只是决定有没有这个菜单项,并不管这个菜单项的选择结果。menuconfig工作时在我们make menuconfig打开时,他会读取.config文件,并且用.config文件中的配置选择结果来初始化menuconfig中各个菜单项的选择值。
总结:菜单项的项目内容从Kconfig文件来,菜单项的选择值从.config文件来。
3.Kconfig文件分析
几乎在大部分的目录下都有一个Kconfig文件,随便找一个Kconfig文件进行分析,比如\kernel\drivers\net\wireless目录下的Kconfig文件,内容如下:
menuconfig WLAN
bool "Wireless LAN"
depends on !S390
depends on NET
select WIRELESS
default y
---help---
This section contains all the pre 802.11 and 802.11 wireless
device drivers. For a complete list of drivers and documentation
on them refer to the wireless wiki:
http://wireless.kernel.org/en/users/Drivers
if WLAN
config PCMCIA_RAYCS
tristate "Aviator/Raytheon 2.4GHz wireless support"
depends on PCMCIA
select WIRELESS_EXT
select WEXT_SPY
select WEXT_PRIV
---help---
Say Y here if you intend to attach an Aviator/Raytheon PCMCIA
(PC-card) wireless Ethernet networking card to your computer.
Please read the file for
details.
To compile this driver as a module, choose M here: the module will be
called ray_cs. If unsure, say N.
config LIBERTAS_THINFIRM
tristate "Marvell 8xxx Libertas WLAN driver support with thin firmware"
depends on MAC80211
select FW_LOADER
---help---
A library for Marvell Libertas 8xxx devices using thinfirm.
config LIBERTAS_THINFIRM_DEBUG
bool "Enable full debugging output in the Libertas thin firmware module."
depends on LIBERTAS_THINFIRM
---help---
Debugging support.
config LIBERTAS_THINFIRM_USB
tristate "Marvell Libertas 8388 USB 802.11b/g cards with thin firmware"
depends on LIBERTAS_THINFIRM && USB
---help---
A driver for Marvell Libertas 8388 USB devices using thinfirm.
config AIRO
tristate "Cisco/Aironet 34X/35X/4500/4800 ISA and PCI cards"
depends on ISA_DMA_API && (PCI || BROKEN)
select WIRELESS_EXT
select CRYPTO
select WEXT_SPY
select WEXT_PRIV
---help---
This is the standard Linux driver to support Cisco/Aironet ISA and
PCI 802.11 wireless cards.
It supports the new 802.11b cards from Cisco (Cisco 34X, Cisco 35X
- with or without encryption) as well as card before the Cisco
acquisition (Aironet 4500, Aironet 4800, Aironet 4800B).
This driver support both the standard Linux Wireless Extensions
and Cisco proprietary API, so both the Linux Wireless Tools and the
Cisco Linux utilities can be used to configure the card.
The driver can be compiled as a module and will be named "airo".
config ATMEL
tristate "Atmel at76c50x chipset 802.11b support"
depends on (PCI || PCMCIA)
select WIRELESS_EXT
select WEXT_PRIV
select FW_LOADER
select CRC32
---help---
A driver 802.11b wireless cards based on the Atmel fast-vnet
chips. This driver supports standard Linux wireless extensions.
Many cards based on this chipset do not have flash memory
and need their firmware loaded at start-up. If yours is
one of these, you will need to provide a firmware image
to be loaded into the card by the driver. The Atmel
firmware package can be downloaded from
config PCI_ATMEL
tristate "Atmel at76c506 PCI cards"
depends on ATMEL && PCI
---help---
Enable support for PCI and mini-PCI cards containing the
Atmel at76c506 chip.
config PCMCIA_ATMEL
tristate "Atmel at76c502/at76c504 PCMCIA cards"
depends on ATMEL && PCMCIA
select WIRELESS_EXT
select FW_LOADER
select CRC32
---help---
Enable support for PCMCIA cards containing the
Atmel at76c502 and at76c504 chips.
config AT76C50X_USB
tristate "Atmel at76c503/at76c505/at76c505a USB cards"
depends on MAC80211 && USB
select FW_LOADER
---help---
Enable support for USB Wireless devices using Atmel at76c503,
at76c505 or at76c505a chips.
config AIRO_CS
tristate "Cisco/Aironet 34X/35X/4500/4800 PCMCIA cards"
depends on PCMCIA && (BROKEN || !M32R)
select WIRELESS_EXT
select WEXT_SPY
select WEXT_PRIV
select CRYPTO
select CRYPTO_AES
---help---
This is the standard Linux driver to support Cisco/Aironet PCMCIA
802.11 wireless cards. This driver is the same as the Aironet
driver part of the Linux Pcmcia package.
It supports the new 802.11b cards from Cisco (Cisco 34X, Cisco 35X
- with or without encryption) as well as card before the Cisco
acquisition (Aironet 4500, Aironet 4800, Aironet 4800B). It also
supports OEM of Cisco such as the DELL TrueMobile 4800 and Xircom
802.11b cards.
This driver support both the standard Linux Wireless Extensions
and Cisco proprietary API, so both the Linux Wireless Tools and the
Cisco Linux utilities can be used to configure the card.
config PCMCIA_WL3501
tristate "Planet WL3501 PCMCIA cards"
depends on EXPERIMENTAL && PCMCIA
select WIRELESS_EXT
select WEXT_SPY
help
A driver for WL3501 PCMCIA 802.11 wireless cards made by Planet.
It has basic support for Linux wireless extensions and initial
micro support for ethtool.
config PRISM54
tristate 'Intersil Prism GT/Duette/Indigo PCI/Cardbus (DEPRECATED)'
depends on PCI && EXPERIMENTAL
select WIRELESS_EXT
select WEXT_SPY
select WEXT_PRIV
select FW_LOADER
---help---
This enables support for FullMAC PCI/Cardbus prism54 devices. This
driver is now deprecated in favor for the SoftMAC driver, p54pci.
p54pci supports FullMAC PCI/Cardbus devices as well. For details on
the scheduled removal of this driver on the kernel see the feature
removal schedule:
Documentation/feature-removal-schedule.txt
For more information refer to the p54 wiki:
http://wireless.kernel.org/en/users/Drivers/p54
Note: You need a motherboard with DMA support to use any of these cards
When built as module you get the module prism54
config USB_ZD1201
tristate "USB ZD1201 based Wireless device support"
depends on USB
select WIRELESS_EXT
select WEXT_PRIV
select FW_LOADER
---help---
Say Y if you want to use wireless LAN adapters based on the ZyDAS
ZD1201 chip.
This driver makes the adapter appear as a normal Ethernet interface,
typically on wlan0.
The zd1201 device requires external firmware to be loaded.
This can be found at http://linux-lc100020.sourceforge.net/
To compile this driver as a module, choose M here: the
module will be called zd1201.
config USB_NET_RNDIS_WLAN
tristate "Wireless RNDIS USB support"
depends on USB && EXPERIMENTAL
depends on CFG80211
select USB_USBNET
select USB_NET_CDCETHER
select USB_NET_RNDIS_HOST
---help---
This is a driver for wireless RNDIS devices.
These are USB based adapters found in devices such as:
Buffalo WLI-U2-KG125S
U.S. Robotics USR5421
Belkin F5D7051
Linksys WUSB54GSv2
Linksys WUSB54GSC
Asus WL169gE
Eminent EM4045
BT Voyager 1055
Linksys WUSB54GSv1
U.S. Robotics USR5420
BUFFALO WLI-USB-G54
All of these devices are based on Broadcom 4320 chip which is the
only wireless RNDIS chip known to date.
If you choose to build a module, it'll be called rndis_wlan.
source "drivers/net/wireless/rtl818x/Kconfig"
config ADM8211
tristate "ADMtek ADM8211 support"
depends on MAC80211 && PCI && EXPERIMENTAL
select CRC32
select EEPROM_93CX6
---help---
This driver is for ADM8211A, ADM8211B, and ADM8211C based cards.
These are PCI/mini-PCI/Cardbus 802.11b chips found in cards such as:
Xterasys Cardbus XN-2411b
Blitz NetWave Point PC
TrendNet 221pc
Belkin F5D6001
SMC 2635W
Linksys WPC11 v1
Fiberline FL-WL-200X
3com Office Connect (3CRSHPW796)
Corega WLPCIB-11
SMC 2602W V2 EU
D-Link DWL-520 Revision C
However, some of these cards have been replaced with other chips
like the RTL8180L (Xterasys Cardbus XN-2411b, Belkin F5D6001) or
the Ralink RT2400 (SMC2635W) without a model number change.
Thanks to Infineon-ADMtek for their support of this driver.
config MAC80211_HWSIM
tristate "Simulated radio testing tool for mac80211"
depends on MAC80211
---help---
This driver is a developer testing tool that can be used to test
IEEE 802.11 networking stack (mac80211) functionality. This is not
needed for normal wireless LAN usage and is only for testing. See
Documentation/networking/mac80211_hwsim for more information on how
to use this tool.
To compile this driver as a module, choose M here: the module will be
called mac80211_hwsim. If unsure, say N.
config MWL8K
tristate "Marvell 88W8xxx PCI/PCIe Wireless support"
depends on MAC80211 && PCI && EXPERIMENTAL
---help---
This driver supports Marvell TOPDOG 802.11 wireless cards.
To compile this driver as a module, choose M here: the module
will be called mwl8k. If unsure, say N.
source "drivers/net/wireless/ath/Kconfig"
source "drivers/net/wireless/b43/Kconfig"
source "drivers/net/wireless/b43legacy/Kconfig"
source "drivers/net/wireless/bcm4329/Kconfig"
source "drivers/net/wireless/hostap/Kconfig"
source "drivers/net/wireless/ipw2x00/Kconfig"
source "drivers/net/wireless/iwlwifi/Kconfig"
source "drivers/net/wireless/iwmc3200wifi/Kconfig"
source "drivers/net/wireless/libertas/Kconfig"
source "drivers/net/wireless/orinoco/Kconfig"
source "drivers/net/wireless/p54/Kconfig"
source "drivers/net/wireless/rt2x00/Kconfig"
source "drivers/net/wireless/wl12xx/Kconfig"
source "drivers/net/wireless/zd1211rw/Kconfig"
endif # WLAN
(1)#开头的行是注释行
(2)menuconfig表示菜单,config表示菜单中的一个配置项。
(3)menuconfig或者config后面空格隔开的大写字母表示的就是这个配置项的配置项名字,这个字符串前面添加CONFIG_后就构成了.config中的配置项名字。
(4)一个menuconfig后面跟着的所有config项就是这个menuconfig的子菜单。这就是Kconfig中表示的目录关系。
(5)内核源码目录树中每一个Kconfig都会source引入其所有子目录下的Kconfig,从而保证了所有的Kconfig项目都被包含进menuconfig中。这个也告诉我们:如果你自己在linux内核中添加了一个文件夹,一定要在这个文件夹下创建一个Kconfig文件,然后在这个文件夹的上一层目录的Kconfig中source引入这个文件夹下的Kconfig文件。
(6)tristate和bool的含义:
tristate意思是三态(3种状态,对应Y、N、M三种选择方式),bool是要么真要么假(对应Y和N)。所以tristate的意思就是这个配置项可以被三种选择,bool的意思是这个配置项只能被2种选择。
(7)depends的含义:
本配置项依赖于另一个配置项。如果那个依赖的配置项为Y或者M,则本配置项才有意义;如果依赖的哪个配置项本身被设置为N,则本配置项根本没有意义。
depends项目会导致make menuconfig的时候找不到一些配置项。所以你在menuconfig中如果找不到一个选项,但是这个选项在Kconfig中却是有的,则可能的原因就是这个配置项依赖的一个配置项是不成立的。
depends并不要求依赖的配置项一定是一个,可以是多个,而且还可以有逻辑运算。这种时候只要依赖项目运算式子的裸机结果为真则依赖就成立。
(8)select:自动选择
(9)default:默认配置值,是n、y或者m