DS18B20温度传感器 - arduino
DS18B20测量温度范围是-55℃至125℃,精度为0.5℃。采用单总线进行数据及命令传输,可在同一总线上连接多个DS18B20,并采用地址进行器件选择与数据传输
产品封装

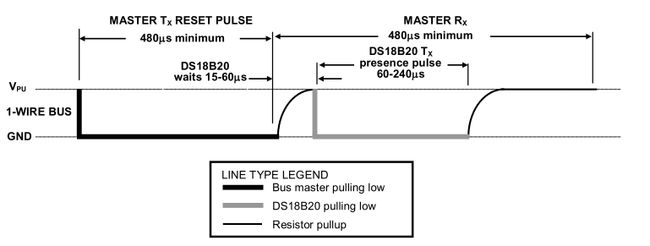
时序图

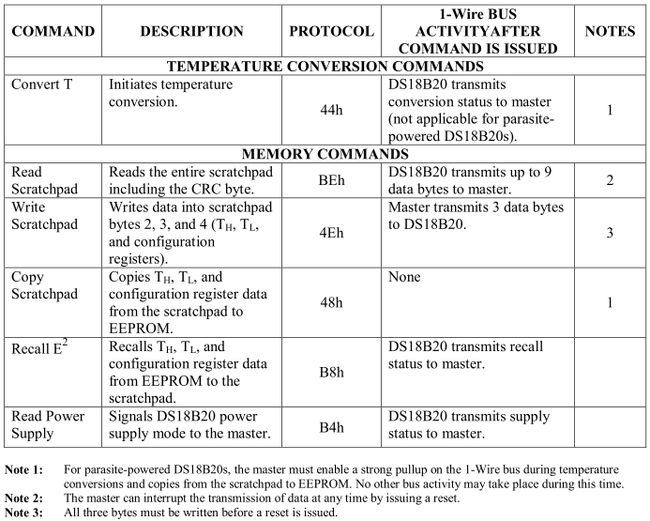
典型应用电路
arduino 程序
#ifndef DS18B20_h
#define DS18B20_h
#include 实现文件
/*
Base on OneWire v2.2
Edit by savage 2014-05-07
*/
#include "DS18B20.h"
DS18B20::DS18B20(uint8_t pin,byte sn)
{
PIN=pin;
pinMode(pin, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(PIN,1);
delayMicroseconds(1000);//初始化的时候,先要保证以高电平开始,顺便充电
senser_number=0;
byte li=10;
while(senser_number//查找传感器,直到数量超过设定值
search_again();
if(!li--)break;//最多10次
}
set(0x3F);//设定为10位模式(默认是12位模式)
}
void DS18B20::set(byte n){
reset();
write(0xCC);//skip
write(0x4E);//write
write(0);//Th
write(0);//Tl
write(n);//seting 10bit mode B00111111 10位模式
}
// Returns 1 if a device asserted a presence pulse, 0 otherwise.
//
uint8_t DS18B20::reset()
{
uint8_t r;
pinMode(PIN,OUTPUT);// 把总线设置成输出
digitalWrite(PIN,0); // 把总线拉低
delayMicroseconds(480);//拉低电位至少480um,reset
pinMode(PIN,INPUT); // 把总线设置成输入
noInterrupts();
delayMicroseconds(70);
r=!digitalRead(PIN);//传感器回应
interrupts();
delayMicroseconds(410);
return r;
}
//
// Write a bit. Port and bit is used to cut lookup time and provide
// more certain timing.
//
void DS18B20::write_bit(uint8_t v)
{
pinMode(PIN,OUTPUT); // 总线设置输出
if (v & 1) { //写1
noInterrupts();
digitalWrite(PIN,0); // 先把总线拉低
delayMicroseconds(5); // 延迟5us
digitalWrite(PIN,1); // 写入数据
interrupts();
delayMicroseconds(55);
} else { //写0
noInterrupts();
digitalWrite(PIN,0);
delayMicroseconds(60);
digitalWrite(PIN,1);
interrupts();
delayMicroseconds(5);
}
}
//
// Read a bit. Port and bit is used to cut lookup time and provide
// more certain timing.
//
uint8_t DS18B20::read_bit()
{
uint8_t r;
pinMode(PIN,OUTPUT);
noInterrupts();
digitalWrite(PIN,0);//拉低电位1us以上
delayMicroseconds(2);
pinMode(PIN,INPUT);
delayMicroseconds(10);// let pin float, pull up will raise
r = digitalRead(PIN);//必须在15us内采样
interrupts();
delayMicroseconds(50);
return r;
}
//写
void DS18B20::write(uint8_t v) {
noInterrupts();
uint8_t bitMask;
for (bitMask = 0x01; bitMask; bitMask <<= 1) {
DS18B20::write_bit( (bitMask & v)?1:0);
}
interrupts();
}
void DS18B20::write_bytes(const uint8_t *buf, uint16_t count) {
for (uint16_t i = 0 ; i < count ; i++)
write(buf[i]);
}
// Read
uint8_t DS18B20::read() {
noInterrupts();
uint8_t bitMask;
uint8_t r = 0;
for (bitMask = 0x01; bitMask; bitMask <<= 1) {
if ( DS18B20::read_bit()) r |= bitMask;
}
interrupts();
return r;
}
void DS18B20::read_bytes(uint8_t *buf, uint16_t count) {
for (uint16_t i = 0 ; i < count ; i++)
buf[i] = read();
}
//
// Do a ROM select
//
void DS18B20::select(const uint8_t rom[8])
{
uint8_t i;
write(0x55); // Choose ROM
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) write(rom[i]);
}
// 开始温度转换
void DS18B20::start(byte n){
reset();
select(senser_addr[n]);
write(0x44);
}
void DS18B20::start(){
reset();
write(0xCC);//skip
write(0x44);
}
boolean DS18B20::ready(){
return read()&0x01;
}
float DS18B20::get(byte n){
if(n>=senser_number)return 210;//超过范围
reset();
select(senser_addr[n]);
write(0xBE); // 写入要求读取温度的命令到DS18B20
byte data[9];
byte i;
for ( i = 0; i < 9; i++) { // we need 9 bytes
data[i] = read(); // 每次读取1个字节..总共读取9个字节
}
if(crc8(data, 8)!=data[8])return 250;//crc 错误
int raw = (data[1] << 8) | data[0];
return raw*0.0625;
}
// You need to use this function to start a search again from the beginning.
// You do not need to do it for the first search, though you could.
//
void DS18B20::reset_search()
{
// reset the search state
LastDiscrepancy = 0;
LastDeviceFlag = FALSE;
for(int i = 7; ; i--) {
ROM_NO[i] = 0;
if ( i == 0) break;
}
}
//
// Perform a search. If this function returns a '1' then it has
// enumerated the next device and you may retrieve the ROM from the
// DS18B20::address variable. If there are no devices, no further
// devices, or something horrible happens in the middle of the
// enumeration then a 0 is returned. If a new device is found then
// its address is copied to newAddr. Use DS18B20::reset_search() to
// start over.
//
// --- Replaced by the one from the Dallas Semiconductor web site ---
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Perform the 1-Wire Search Algorithm on the 1-Wire bus using the existing
// search state.
// Return TRUE : device found, ROM number in ROM_NO buffer
// FALSE : device not found, end of search
//
byte DS18B20::getNumber(){
return senser_number;
}
void DS18B20::search_again(){
reset_search();
search();
}
void DS18B20::search(){
byte j=0;//最多8个地址
byte i;
senser_number=0;
byte search_err_count=10;//出错后最多重复10次
while(search_new()){
if(crc8(ROM_NO, 7) != ROM_NO[7]){//CRC验证错误
reset_search();
j=0;
search_err_count--;
if (!search_err_count)break;
}
for(i=0;i<8;i++){
senser_addr[j][i]=ROM_NO[i];
}
senser_number++;
j++;
if(j ==8)break;
}
}
byte DS18B20::search_new()
{
byte newAddr[8];
uint8_t id_bit_number;
uint8_t last_zero, rom_byte_number, search_result;
uint8_t id_bit, cmp_id_bit;
byte rom_byte_mask, search_direction;
// initialize for search
id_bit_number = 1;
last_zero = 0;
rom_byte_number = 0;
rom_byte_mask = 1;
search_result = 0;
// if the last call was not the last one
if (!LastDeviceFlag)
{
// 1-Wire reset
if (!reset())
{
// reset the search
LastDiscrepancy = 0;
LastDeviceFlag = FALSE;
return FALSE;
}
// issue the search command
write(0xF0);
// loop to do the search
do
{
// read a bit and its complement
id_bit = read_bit();
cmp_id_bit = read_bit();
// check for no devices on 1-wire
//10->all 1; 01->all 0; 00->have 0 and 1;11->no device
if ((id_bit == 1) && (cmp_id_bit == 1))
break;
else
{
// all devices coupled have 0 or 1
if (id_bit != cmp_id_bit)
search_direction = id_bit; // bit write value for search
else
{
// if this discrepancy if before the Last Discrepancy
// on a previous next then pick the same as last time
if (id_bit_number < LastDiscrepancy)
search_direction = ((ROM_NO[rom_byte_number] & rom_byte_mask) > 0);
else
// if equal to last pick 1, if not then pick 0
search_direction = (id_bit_number == LastDiscrepancy);
// if 0 was picked then record its position in LastZero
if (search_direction == 0)
{
last_zero = id_bit_number;
}
}
// set or clear the bit in the ROM byte rom_byte_number
// with mask rom_byte_mask
if (search_direction == 1)
ROM_NO[rom_byte_number] |= rom_byte_mask;
else
ROM_NO[rom_byte_number] &= ~rom_byte_mask;
// serial number search direction write bit
write_bit(search_direction);
// increment the byte counter id_bit_number
// and shift the mask rom_byte_mask
id_bit_number++;
rom_byte_mask <<= 1;
// if the mask is 0 then go to new SerialNum byte rom_byte_number and reset mask
//完成一个周期
if (rom_byte_mask == 0)
{
rom_byte_number++;
rom_byte_mask = 1;
}
}
}
while(rom_byte_number < 8); // loop until through all ROM bytes 0-7
// if the search was successful then
if (!(id_bit_number < 65))
{
// search successful so set LastDiscrepancy,LastDeviceFlag,search_result
LastDiscrepancy = last_zero;
// check for last device
if (LastDiscrepancy == 0)
LastDeviceFlag = TRUE;
search_result = TRUE;
}
}
// if no device found then reset counters so next 'search' will be like a first
if (!search_result || !ROM_NO[0])
{
LastDiscrepancy = 0;
LastDeviceFlag = FALSE;
search_result = FALSE;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) newAddr[i] = ROM_NO[i];
return search_result;
}
#if DS18B20_CRC
// The 1-Wire CRC scheme is described in Maxim Application Note 27:
// "Understanding and Using Cyclic Redundancy Checks with Maxim iButton Products"
// Compute a Dallas Semiconductor 8 bit CRC directly.
// this is much slower, but much smaller, than the lookup table.
//
uint8_t DS18B20::crc8(const uint8_t *addr, uint8_t len)
{
uint8_t crc = 0;
while (len--) {
uint8_t inbyte = *addr++;
for (uint8_t i = 8; i; i--) {
uint8_t mix = (crc ^ inbyte) & 0x01;
crc >>= 1;
if (mix) crc ^= 0x8C;
inbyte >>= 1;
}
}
return crc;
}
#endif 主程序代码
#include "DS18B20.h"
DS18B20 ds(9,1);//pin9,连接1个DS18B20
void setup() {
SERIAL_BEGIN();
byte i;
byte j;
for (j = 0; j < ds.getNumber(); j++) {
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
PRINT(ds.senser_addr[j][i]);
PRINT(",");
}
PRINT("CRC=");
PRINT(ds.crc8(ds.senser_addr[j], 7) );
PRINT("\n");
}
println(ds.getNumber(),10,serial_puts);
}
void loop() {
ds.start();//开始测量(所有传感器)
_delay_ms(200);
float a=ds.get(0);
PRINT("temp = ");
if (a>200)
PRINT("CRC error\n");
else
{
PRINT(a);
PRINT("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
setup();
while(1)
loop();
}