Android项目刮刮奖详解(二)
前言
上一期我们已经实现了一个简易的刮刮卡功能,这一期我们来将其完善一下
目标
- 将刮刮奖的宽高改为合适高度
- 将刮刮奖位置居中
将信息层的图片换成文字(重点)
实现
将刮刮奖的宽高改为合适高度和将刮刮奖位置居中
这里其实很简单,我们直接到layout布局之中将大小修改一下即可,同时,在布局中利用
gravity修改位置将信息层的图片换成文字
之前我们信息层绘制的是中奖图片,如果没有图片怎么办?当然是直接拿文字来代替啦,canvas不仅可以画图片,还可以画文字,写文字
首先,我们来了解一下canvas的drawText方法参数
drawText(String text, float x, floaty, Paint paint);
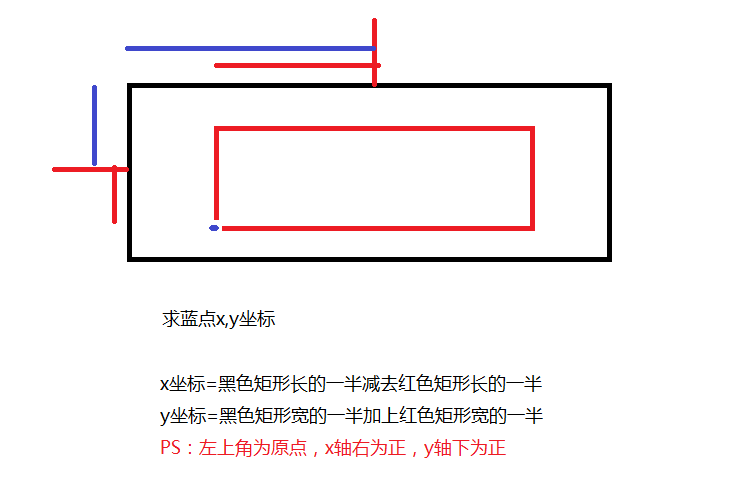
text即使要写的文字内容,x,y是写的位置,需要注意的是,这里的x,y坐标并不是文字的左上角,而是一个与左下角比较接近的位置。大概在这里:如图

最后一个参数就是画笔了,这个画笔设置与之前相似,待会再补充一下
我们想要把文字写在信息层的正中间,x,y的坐标该怎么写呢?由上图可以知道,canvas使用drawText方法,xy的坐标其实是位于文字的左下角的,下图便是图解
相信这张图还是很好理解的,我们继续,开始写代码
首先,我们需要个文字内容
String message = "恭喜中奖,3万元!";定义我们的画笔Paint,对其进行相关设置
这里得提一下,我们需要一个Rect矩形来得到文字内容的背景大小,也就是上图中的红色矩形,Paint画笔中提供了一个方法
getTextBounds,我们可以通过此方法来获得文字内容的背景大小
messagePaint.getTextBounds(String text,float start,float end,Rect rect);上述代码的意思是,截取text文字中的从start到end的长度,将截取的长度和文字的高度形成一个矩形,rect矩形接收这个矩形
Rect mBackground = new Rect();//用来接收getTextBounds返回的矩形 Paint messagePaint = new Paint(); messagePaint.setColor(Color.RED); messagePaint.setAntiAlias(true); messagePaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); messagePaint.getTextBounds(message,0,message.length(),mBackground); messagePaint.setTextSize(30);计算x,y坐标,canvas使用drawText写出文字
我们有两种方法来获得之前黑色矩形的长和宽,一种是使用getMeasured,另一种使用mBitmap.get方法来获得长和宽canvas.drawText(message,getMeasuredWidth()/2-mBackground.width()/2,getMeasuredHeight()/2+mBackground.height()/2,messagePaint);或者:
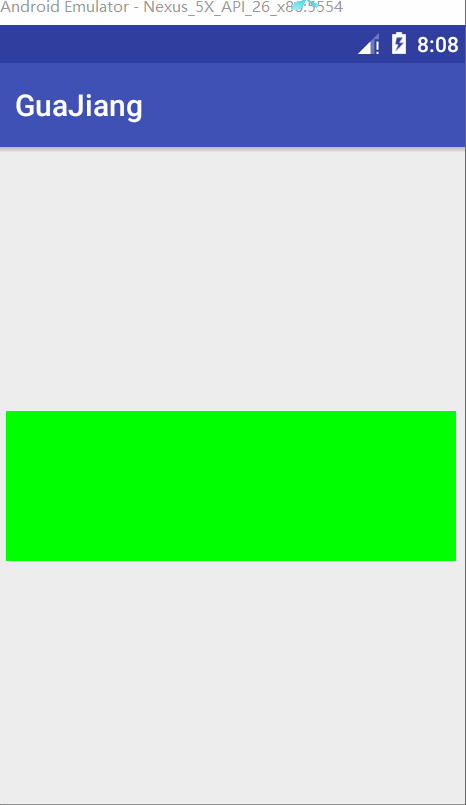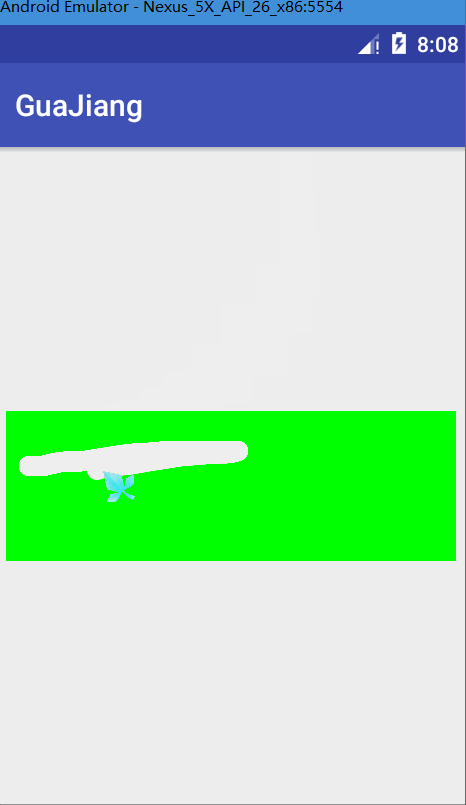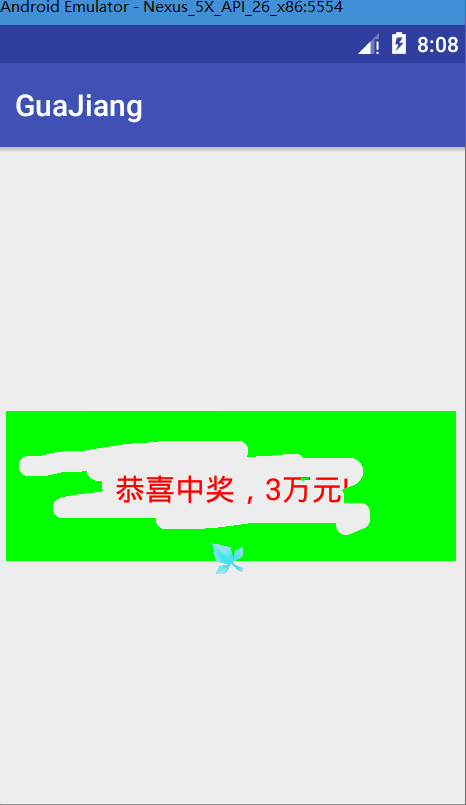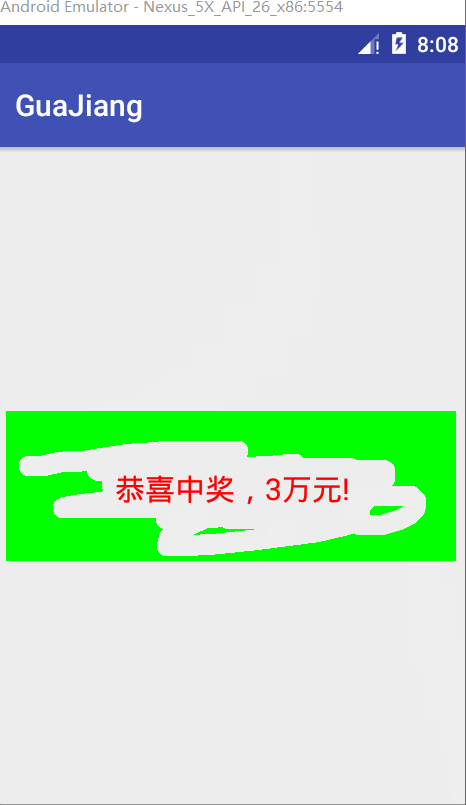
canvas.drawText(message,mBitmap.getWidth()/2-mBackground.width()/2,mBitmap.getHeight()/2+mBackground.height()/2,messagePaint);测试图
完整代码
public class GuajiangView extends View {
/**
* 绘制线条的Paint,即用户手指绘制Path
*/
private Paint mOutterPaint = new Paint();
/**
* 记录用户绘制的Path
*/
private Path mPath = new Path();
/**
* 内存中创建的Canvas
*/
private Canvas mCanvas;
/**
* mCanvas绘制内容在其上
*/
private Bitmap mBitmap;
private int mLastX;
private int mLastY;
private String message;//中奖信息
private Rect mBackground;//文字背景矩形大小
private Paint messagePaint = new Paint();//文字画笔
private boolean isClear = false;
public GuajiangView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public GuajiangView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public GuajiangView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
public GuajiangView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
Log.d(TAG, "onMeasure: 测量");
int width = getMeasuredWidth();
int height = getMeasuredHeight();
// 初始化bitmap
mBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(width, height, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);//以获得的宽高创建一个32位的bitmap
mCanvas = new Canvas(mBitmap);//以bitmap创建了一个画布
mCanvas.drawColor(Color.GREEN);//设置画布的颜色为绿色
mBackground = new Rect();
message = "恭喜中奖,3万元!";
messagePaint.setColor(Color.RED);
messagePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
messagePaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
messagePaint.getTextBounds(message,0,message.length(),mBackground);
messagePaint.setTextSize(30);
// 设置画笔
mOutterPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
mOutterPaint.setAntiAlias(true);//使用抗锯齿功能,会消耗较大资源,绘制图形速度会变慢
mOutterPaint.setDither(true);//图像抖动处理,会使绘制出来的图片颜色更加平滑和饱满,图像更加清晰
mOutterPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mOutterPaint.setStrokeJoin(Paint.Join.ROUND);//圆角,平滑
mOutterPaint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND); //圆角
mOutterPaint.setStrokeWidth(20); // 设置画笔宽度
messagePaint.setColor(Color.RED);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
Log.d(TAG, "onDraw: 画");
canvas.drawText(message,mBitmap.getWidth()/2-mBackground.width()/2,getMeasuredHeight()/2+mBackground.height()/2,messagePaint);
drawPath();
canvas.drawBitmap(mBitmap, 0,0, null);
}
private void drawPath() {
Log.d(TAG, "drawPath: ");
mOutterPaint.setXfermode(new PorterDuffXfermode(PorterDuff.Mode.DST_OUT));
mCanvas.drawPath(mPath, mOutterPaint);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
//当手指按到屏幕上的时候,Path路径之中就使用moveto方法,移动到手指当前位置,invalidate刷新View,回调onDraw方法,(还没有画出来)
//之后,手指移动,action是处于ACTION_MOVE的状态,Path路径使用lineto方法(画直线),
// 同时,将x,y坐标进行了更新,invalidate刷新View,回调onDraw方法,canvas通过drawpath使用画笔将path画了出来,之后如果用户没有抬起手指,则继续循环ACTION_MOVE中的步骤
int action = event.getAction();
int x = (int) event.getX();//获得x坐标
int y = (int) event.getY();//获得y坐标
switch (action){
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
mLastX = x;
mLastY = y;
mPath.moveTo(mLastX, mLastY);//之后回调onDraw方法canvas将path
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
mPath.lineTo(x, y);//之后回调onDraw方法时canvas画直线到(x,y)该点
mLastX = x;//更新x坐标
mLastY = y;//更新y坐标
break;
default:break;
}
invalidate();//刷新View,回调onDraw方法
Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent: invalidate");
return true;
}
}